Ants are fascinating insects with a wide variety of shapes and sizes.
Some species of ants have evolved to have disproportionately large heads, which serve various purposes such as defense, communication, and foraging.
This list post will explore 28 of the most exciting ants with big heads, providing you with tons of information and a picture about each to learn about their unique adaptations, features, and behaviors.
1) Shield Ants

Shield ants, also known as turtle ants, are a species of ant that belong to the genus Cephalotes.
They are found in tropical regions and are known for their unique physical characteristics.
One of the most distinctive features of shield ants is their flattened, disc-shaped head.
This head shape allows them to block the entrance to their nests, protecting them from predators and other threats.
In addition, shield ants have long, spindly legs that allow them to move quickly and easily through the forest canopy.
Shield ants are social insects and live in large colonies.
They are known for their complex communication systems, which involve chemical signals and physical gestures.
They also have a division of labor within their colonies, with different ants taking on different roles such as foraging, nest building, and caring for the young.
One interesting behavior of shield ants is their use of "backpacks." Some worker ants will carry small pieces of leaves or other materials on their backs as they move through the forest.
It is believed that these backpacks may serve as camouflage or protection from predators.
Overall, shield ants are a fascinating species of ant with unique physical and behavioral adaptations that allow them to thrive in their tropical habitats.
2) Turtle Ants

Turtle ants, also known as Cephalotes spp., are a genus of arboreal ants found in tropical regions around the world.
These ants are named for their unique ability to tuck their legs and antennae under their bodies, resembling a turtle when threatened.Turtle ants are known for their specialized morphology, including a flattened head and elongated, spiny legs that allow them to navigate through the dense vegetation of their forest habitats.
They also possess a unique, disc-shaped structure on their thorax that allows them to block the entrance to their nests, protecting them from predators.These ants are primarily herbivorous, feeding on the sugary exudates produced by plants and occasionally preying on small insects.
They are also known for their symbiotic relationship with a species of bacteria that lives in specialized structures on their bodies, providing them with essential nutrients.Turtle ants are social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
They have a complex social hierarchy, with specialized castes of workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals.
The queen ant is responsible for laying eggs, which hatch into larvae that are cared for by the workers.Overall, turtle ants are fascinating creatures with unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in their forest habitats.
Their specialized morphology, diet, and social behavior make them an important part of the ecosystem and a subject of interest for researchers studying ant biology.
3) Dolly Ants

Dolly Ants, also known as Dolichoderus spp., are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive elongated heads and bodies, which give them a unique appearance compared to other ant species.Dolly Ants are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or under rocks.
They are known to be highly social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
Within these colonies, there is a strict division of labor, with different ants taking on specific roles such as foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.One interesting aspect of Dolly Ant behavior is their use of chemical communication.
These ants use pheromones to communicate with each other, leaving trails of scent that other ants can follow to locate food sources or to find their way back to the nest.
They also use pheromones to signal danger, which can trigger a coordinated response from the colony to defend against predators.Dolly Ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of foods including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
They are also known to have a mutualistic relationship with certain plant species, where they protect the plants from herbivores in exchange for a source of food.Overall, Dolly Ants are a fascinating species of ant with unique physical and behavioral characteristics.
Their social structure and use of chemical communication make them an important subject of study for researchers interested in understanding the behavior of social insects.
4) Phalacromyrmex

Phalacromyrmex is a genus of ants belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a flattened head and elongated mandibles.
The genus is relatively small, with only a few known species.Phalacromyrmex ants are typically found in tropical regions, where they inhabit forested areas.
They are known to be arboreal, meaning they live in trees and other vegetation.
These ants are also known to be aggressive, and will defend their nests vigorously.One of the most interesting aspects of Phalacromyrmex ants is their diet.
These ants are known to be specialized predators of other ants.
They will raid the nests of other ant species, killing and consuming the workers and brood.
This behavior is known as "myrmecophagy," and is relatively rare among ants.Despite their aggressive behavior, Phalacromyrmex ants are not considered pests.
They do not typically invade human dwellings or cause damage to crops or other structures.
Instead, they play an important role in their ecosystems by controlling the populations of other ant species.Overall, Phalacromyrmex ants are fascinating creatures with unique adaptations and behaviors.
Further research is needed to fully understand their ecology and biology.
5) Octostruma
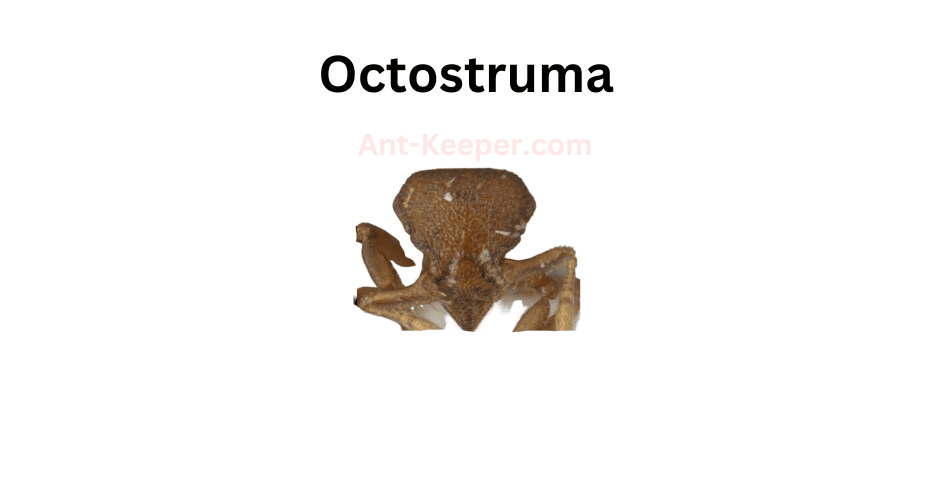
Octostrumabe is a fascinating species of ant that belongs to the scientific family of Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics and behavior, which make them stand out from other ant species.One of the most distinctive features of Octostrumabe ants is their octagonal-shaped head.
This head shape is believed to be an adaptation that allows them to navigate through narrow spaces and crevices with ease.
Additionally, their bodies are covered in fine hairs that help them to grip onto surfaces and climb up walls and trees.Octostrumabe ants are also known for their highly social behavior.
They live in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals, and each ant has a specific role to play within the colony.
Some ants are responsible for foraging for food, while others care for the young or defend the colony from predators.Interestingly, Octostrumabe ants have a unique way of communicating with each other.
They use a combination of chemical signals and physical touch to convey information about food sources, danger, and other important colony matters.Overall, Octostrumabe ants are a fascinating species that continue to intrigue scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Their unique physical characteristics and social behavior make them a valuable subject of study for those interested in the natural world.
6) Mite-Eating Ants

The Mite-Eating Ant, also known as the Pheidole megacephala, is a species of ant that is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
These ants are known for their unique feeding habits, as they primarily feed on mites and other small arthropods.The Mite-Eating Ant is a relatively small ant, with workers measuring between 2-3mm in length.
They have a distinctive head shape, with a large and elongated head that is almost as wide as their thorax.
Their bodies are typically a reddish-brown color, with darker legs and antennae.These ants are highly social, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colonies are typically divided into two groups: workers and reproductive individuals.
The workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony, while the reproductive individuals are responsible for producing offspring.One of the most interesting aspects of the Mite-Eating Ant is their feeding habits.
These ants are specialized predators, feeding almost exclusively on mites and other small arthropods.
They use their large mandibles to capture and kill their prey, and then carry it back to the colony to be consumed.In addition to their unique feeding habits, the Mite-Eating Ant is also known for its ability to adapt to a wide range of environments.
They are able to thrive in both natural and urban environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and even in homes and buildings.Overall, the Mite-Eating Ant is a fascinating species of ant that has adapted to a unique niche in the ecosystem.
Their specialized feeding habits and ability to thrive in a variety of environments make them an important species to study and understand.
7) Big Headed Ants

Big Headed Ants, also known as Pheidole megacephala, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive large heads, which are used for defense and communication within their colonies.Big Headed Ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, seeds, and other small organisms.One of the most interesting aspects of Big Headed Ants is their social behavior.
They live in large colonies, with a queen ant at the center of the hierarchy.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony perform various tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.Big Headed Ants are also known for their ability to displace other ant species in their habitats.
They are aggressive and have been known to attack and kill other ants, as well as compete with them for resources.Despite their aggressive behavior, Big Headed Ants are not considered a major pest species.
However, their ability to displace other ant species and their potential impact on native ecosystems make them an important species to study and monitor.
8) Calyptomyrmex

Calyptomyrmex is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a distinctively shaped head and a flattened, shield-like structure on the thorax.
The genus is relatively small, with only a few known species.Calyptomyrmex ants are typically found in forested areas, where they nest in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be predatory, feeding on other insects and small invertebrates.
These ants are also known to have a mutualistic relationship with certain species of plants, where they protect the plants from herbivores in exchange for food and shelter.One of the most interesting aspects of Calyptomyrmex ants is their social behavior.
These ants are highly organized, with a clear division of labor among the members of the colony.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.Overall, Calyptomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystems.
Their unique morphology, predatory behavior, and social organization make them a subject of interest for researchers and nature enthusiasts alike.
9) Mystrium
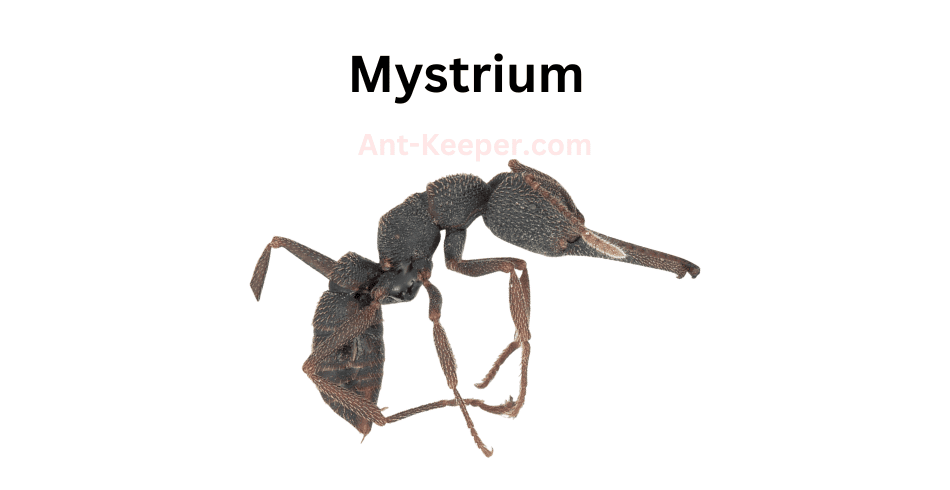
Mystrium is a genus of ants that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology and behavior.
They are medium-sized ants, with workers ranging from 3 to 6 mm in length.
The head of the ant is elongated and narrow, with large mandibles that are used for hunting and defense.
The antennae are long and slender, with 12 segments.Mystrium ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and are often seen attacking other ant species.
They are also known to be solitary hunters, with workers often hunting alone or in small groups.One of the most interesting aspects of Mystrium ants is their reproductive behavior.
Unlike most ants, Mystrium ants have a unique reproductive system where the queen produces both male and female offspring.
This is known as haplodiploidy, where males are haploid and females are diploid.
The males are produced from unfertilized eggs, while the females are produced from fertilized eggs.Mystrium ants are also known for their ability to communicate with each other through chemical signals.
They use pheromones to mark trails, identify nestmates, and signal danger.
They also use sound to communicate, with workers producing a high-pitched sound when they encounter a threat.Overall, Mystrium ants are fascinating creatures that have unique morphology, behavior, and reproductive systems.
They play an important role in their ecosystems and are a valuable subject of study for scientists.
10) Probolomyrmex

Probolomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Proceratiinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a long and slender body, a narrow head, and elongated mandibles.
The genus is characterized by the presence of a distinct petiole, which separates the thorax and the abdomen.Probolomyrmex ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be highly aggressive and territorial, often engaging in fierce battles with other ant species.One of the most interesting aspects of Probolomyrmex ants is their social behavior.
These ants are known to be highly organized, with a well-defined caste system that includes workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals.
The workers are responsible for foraging, nest maintenance, and caring for the young, while the soldiers defend the colony against predators and other threats.Despite their small size, Probolomyrmex ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They are known to be efficient predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other small invertebrates.
They also help to aerate the soil and distribute nutrients, which can have a positive impact on plant growth.Overall, Probolomyrmex ants are a fascinating and important group of insects that are worthy of further study and conservation efforts.
11) Fierce Pennet And Pavement Ants
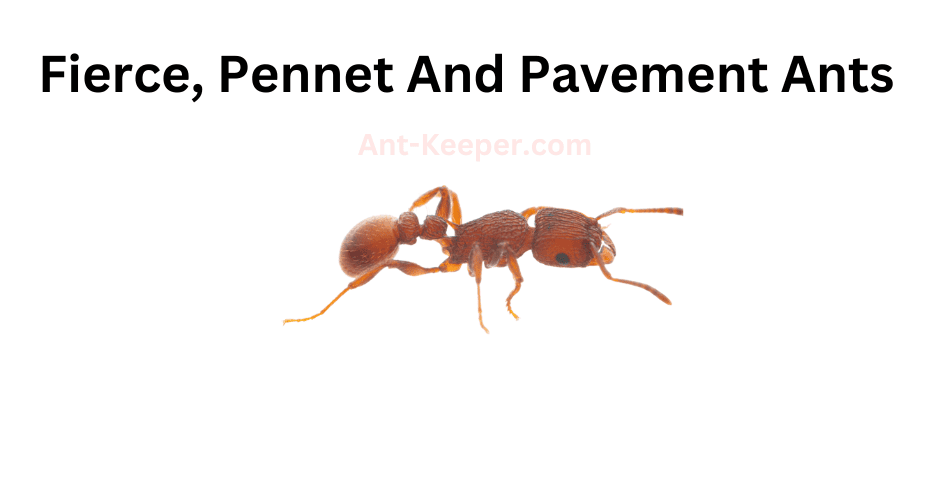
The Fierce Pennet Ant and Pavement Ant are two species of ants that are commonly found in urban and suburban environments.
Both species belong to the Formicidae family and are known for their aggressive behavior towards other ants and insects.The Fierce Pennet Ant, also known as Tetramorium caespitum, is a small ant species that typically measures between 2.5 and 3.5 mm in length.
They are reddish-brown in color and have a distinctive heart-shaped head.
Fierce Pennet Ants are known for their aggressive behavior towards other ant species and will often engage in territorial battles to defend their colonies.Pavement Ants, also known as Tetramorium immigrans, are slightly larger than Fierce Pennet Ants, measuring between 2.5 and 4 mm in length.
They are dark brown to black in color and have a distinct thorax with parallel lines.
Pavement Ants are commonly found in urban environments and are known for their ability to nest in cracks and crevices in pavement and concrete.Both Fierce Pennet and Pavement Ants are omnivorous and will feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, seeds, and sugary substances.
They are also known for their ability to form large colonies, with some colonies containing thousands of individual ants.Despite their small size, both Fierce Pennet and Pavement Ants can be a nuisance to humans, particularly when they invade homes and buildings in search of food and shelter.
However, they also play an important role in the ecosystem, helping to control populations of other insects and serving as a food source for larger animals.
12) Thaumatomyrmex

Thaumatomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Ponerinae.
The ants in this genus are known for their unique morphology and behavior.
Thaumatomyrmex ants are small in size, measuring between 2-5 mm in length.
They have a distinctive head shape, with a narrow and elongated mandible that is used for capturing prey.Thaumatomyrmex ants are also known for their aggressive behavior.
They are solitary hunters and do not form large colonies like other ant species.
Instead, they hunt individually or in small groups.
Thaumatomyrmex ants are known to attack and kill other ant species, including those that are much larger than themselves.The diet of Thaumatomyrmex ants consists mainly of other insects, such as termites and other ants.
They are also known to feed on nectar and honeydew produced by aphids and other plant-sucking insects.Thaumatomyrmex ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions.Overall, Thaumatomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures with unique morphology and behavior.
Their aggressive hunting behavior and solitary lifestyle make them stand out among other ant species.
13) Acanthostichus
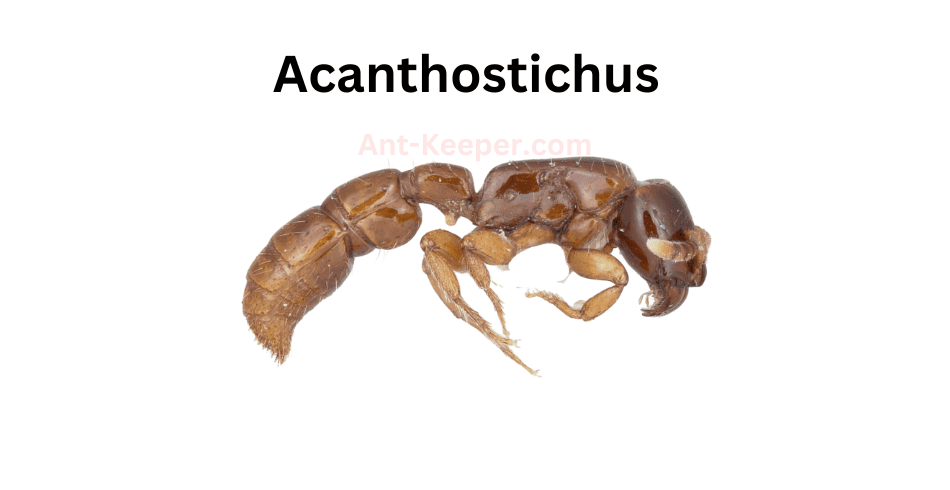

Acanthostichus is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dorylinae.
The ants in this genus are known for their aggressive behavior and are commonly referred to as "trap-jaw ants." Acanthostichus ants are typically small in size, ranging from 2 to 5 millimeters in length, and are characterized by their elongated mandibles that can snap shut with incredible speed and force, allowing them to capture prey or defend themselves from predators.Acanthostichus ants are primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be highly social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colonies are typically headed by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's social structure.One of the most interesting aspects of Acanthostichus ants is their hunting behavior.
These ants are known to be ambush predators, waiting in hidden locations for prey to pass by before striking with their powerful mandibles.
They are also known to be scavengers, feeding on a variety of dead insects and other small animals.Despite their aggressive behavior, Acanthostichus ants are not considered to be a significant threat to humans.
However, their powerful mandibles can cause painful bites, and they should be handled with caution.
Overall, Acanthostichus ants are fascinating insects that play an important role in their ecosystems and provide valuable insights into the behavior and evolution of social insects.
14) Adelomyrmex

Adelomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology and behavior.
Adelomyrmex ants are small in size, measuring between 2 to 4 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive appearance, with a slender body and long legs.
The head of Adelomyrmex ants is elongated and narrow, with large compound eyes and long antennae.Adelomyrmex ants are social insects that live in colonies.
The colonies are usually small, consisting of a few hundred individuals.
The colonies are typically found in the soil, under rocks, or in dead wood.
Adelomyrmex ants are known for their aggressive behavior towards other ant species.
They will attack and kill other ants that invade their territory.Adelomyrmex ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources.
They will consume insects, nectar, and honeydew produced by aphids.
Adelomyrmex ants are also known to tend to mealybugs, protecting them from predators in exchange for their sweet secretions.The reproductive system of Adelomyrmex ants is unique.
The colonies are headed by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs.
However, the queen does not mate with males.
Instead, she reproduces asexually, producing genetically identical offspring.In conclusion, Adelomyrmex ants are fascinating insects with unique morphology and behavior.
They are aggressive towards other ant species and have a unique reproductive system.
These ants play an important role in their ecosystem, consuming insects and tending to mealybugs.
15) Kalathomyrmex

Kalathomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are relatively small in size, with workers measuring between 2.5 to 3.5 millimeters in length.
The genus is characterized by its unique morphology, including a distinctive head shape and a narrow waist.Kalathomyrmex ants are known to inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically found nesting in soil or leaf litter, and are known to be active foragers, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, seeds, and nectar.The reproductive biology of Kalathomyrmex ants is not well understood, but it is believed that they have a typical ant reproductive system, with queens and males mating during a nuptial flight.
The colony size of Kalathomyrmex ants is relatively small, with only a few hundred individuals per colony.Overall, Kalathomyrmex ants are an interesting and unique genus of ants that are still being studied by scientists to better understand their behavior, ecology, and evolutionary history.
16) Lachnomyrmex

Lachnomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Formicinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology and behavior.
They are small in size, measuring between 2-5 mm in length, and have a distinctive appearance with a slender body and long legs.
The head of Lachnomyrmex ants is elongated and narrow, with large compound eyes and long antennae.Lachnomyrmex ants are primarily arboreal, meaning they live in trees and other vegetation.
They are known to form small colonies, with a queen and a few dozen workers.
These ants are highly territorial and will defend their nests aggressively against intruders.One of the most interesting aspects of Lachnomyrmex ants is their relationship with other insects.
They are known to form mutualistic relationships with aphids, which provide them with a source of honeydew in exchange for protection.
Lachnomyrmex ants will actively tend to the aphids, protecting them from predators and moving them to new feeding sites when necessary.Overall, Lachnomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and relationships with other insects.
Their small size and arboreal lifestyle make them difficult to study, but researchers continue to learn more about these ants and their role in the ecosystem.
17) Leptanilloides

Leptanilloides is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dorylinae.
These ants are known for their small size and cryptic behavior, making them difficult to study in the wild.
The genus is characterized by their elongated mandibles, which are used for capturing prey and defending the colony.Leptanilloides ants are typically found in tropical regions, where they inhabit leaf litter and soil.
They are known to form small colonies, with only a few hundred individuals.
The colonies are typically headed by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony.One interesting aspect of Leptanilloides ants is their behavior towards other ant species.
They are known to be highly aggressive towards other ants, and will attack and kill any intruders that enter their territory.
This behavior is thought to be a result of competition for resources, as Leptanilloides ants rely heavily on small arthropods for food.Despite their small size and cryptic behavior, Leptanilloides ants play an important role in their ecosystems.
They help to control populations of small arthropods, and their aggressive behavior towards other ants may help to maintain balance in ant communities.
Further research is needed to fully understand the ecology and behavior of these fascinating ants.
18) Mycetarotes
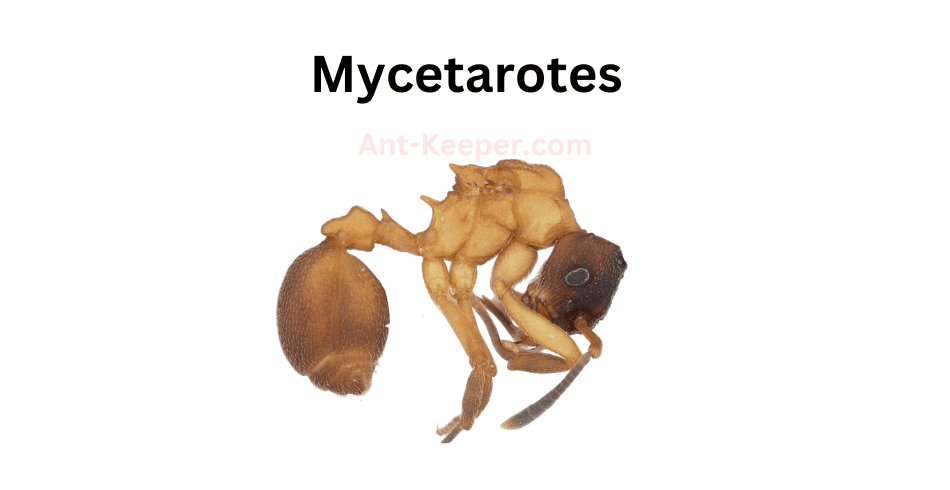
Mycetarotesbe is a species of ant that belongs to the Formicidae family.
These ants are known for their unique behavior of cultivating fungi as their primary food source.
They are commonly found in forested areas and have a symbiotic relationship with the fungi they cultivate.Mycetarotesbe ants are small in size, measuring around 2-3 mm in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a distinctively shaped head that is wider than their thorax.
These ants are known for their strong mandibles, which they use to cut and transport plant material to their underground nests.One of the most interesting aspects of Mycetarotesbe ants is their farming behavior.
They cultivate a specific type of fungus called Leucocoprinus gongylophorus, which they feed on exclusively.
The ants collect plant material, such as leaves and twigs, and bring it back to their nests where they use it to grow the fungus.
The ants then feed on the fungus, which provides them with all the nutrients they need to survive.Mycetarotesbe ants live in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
They have a complex social structure, with different castes of ants performing different tasks.
The queen ant is responsible for laying eggs, while the worker ants are responsible for foraging, farming, and caring for the young.Overall, Mycetarotesbe ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved a unique way of life.
Their farming behavior and symbiotic relationship with fungi make them an important species in forest ecosystems.
19) Ochetomyrmex

Ochetomyrmex is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are small in size, measuring between 2-4 mm in length.
They are known for their distinctive appearance, with a slender and elongated body shape and a narrow waist.
The head of Ochetomyrmex ants is also elongated, with large compound eyes and long antennae.Ochetomyrmex ants are typically found in arid and semi-arid regions, where they inhabit sandy soils and rocky areas.
They are known to be opportunistic feeders, consuming a variety of food sources including insects, seeds, and nectar.
These ants are also known to be aggressive defenders of their nests, using their powerful mandibles to ward off potential threats.One unique characteristic of Ochetomyrmex ants is their ability to tolerate high temperatures.
They are able to survive in environments with temperatures exceeding 40°C, making them well-suited to life in hot and dry regions.
Ochetomyrmex ants are also known for their ability to form large colonies, with some species having populations of up to several thousand individuals.Overall, Ochetomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to thrive in some of the harshest environments on Earth.
Their unique physical characteristics and behaviors make them a subject of interest for researchers and enthusiasts alike.
20) Paramycetophylax
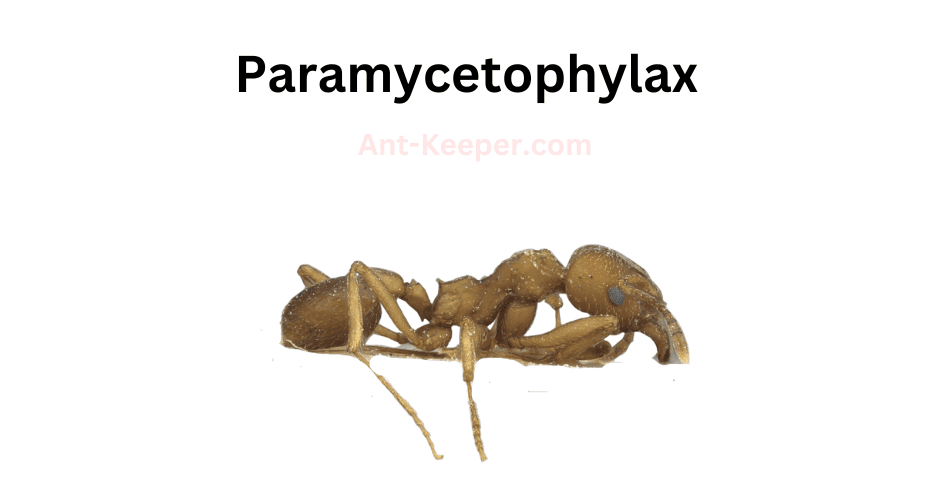
Paramycetophylax is a genus of ants belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their small size and unique physical characteristics.
The workers of this genus are typically between 1.5 and 2.5 millimeters in length, with a dark brown or black coloration.
They have a distinctively elongated head and mandibles that are curved downwards.Paramycetophylax ants are primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be highly adaptable and can thrive in both natural and disturbed environments.These ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colonies are typically polygynous, meaning they have multiple queens.
The queens are responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.Paramycetophylax ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
They are also known to engage in mutualistic relationships with other insects, such as aphids, which provide them with a source of honeydew in exchange for protection.Overall, Paramycetophylax ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystems.
Their unique physical characteristics and adaptable nature make them a valuable subject of study for scientists and researchers.
21) Rhopalothrix

Rhopalothrix is a genus of ants belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology and behavior.
The workers of Rhopalothrix are small in size, measuring between 2-4 mm in length.
They have a distinct head shape, with a narrow and elongated head that is wider at the base.
The antennae of Rhopalothrix are also elongated and have a distinct club-like shape at the end.Rhopalothrix ants are known for their cryptic behavior.
They are often found living in small colonies in the leaf litter or soil.
These ants are also known for their specialized diet, which consists of small arthropods such as mites and springtails.
Rhopalothrix ants have been observed using their elongated heads to probe into small crevices and cracks in the soil to capture their prey.One of the most interesting aspects of Rhopalothrix ants is their reproductive behavior.
Unlike most ants, Rhopalothrix colonies are often headed by a single queen.
However, in some species, multiple queens may be present in a colony.
These queens are known to engage in a behavior called "pleometrosis," where they work together to establish a new colony.
This behavior is rare in ants and is thought to be an adaptation to living in harsh environments.Overall, Rhopalothrix ants are a fascinating group of insects with unique morphology and behavior.
Their specialized diet and reproductive behavior make them an important subject of study for entomologists and ecologists alike.
22) Sericomyrmex

Sericomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique symbiotic relationship with fungi, which they cultivate in underground gardens.
The ants feed on the fungus, and in turn, the fungus benefits from the ants' care and protection.Sericomyrmex ants are small in size, with workers measuring between 2 and 4 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive appearance, with elongated heads and mandibles that are adapted for cutting and carrying plant material.
The ants are typically reddish-brown in color, with some species having darker or lighter markings on their bodies.One of the most interesting aspects of Sericomyrmex ants is their social structure.
These ants live in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colony is headed by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the population.
Workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and tending to the fungus gardens.Sericomyrmex ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions, where the climate is warm and humid.
These ants play an important role in their ecosystems, as they help to break down plant material and recycle nutrients.Overall, Sericomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their environments.
Their symbiotic relationship with fungi is a testament to the complex interactions that occur in nature, and studying these ants can provide valuable insights into the workings of ecosystems.
23) Tropidomyrmex
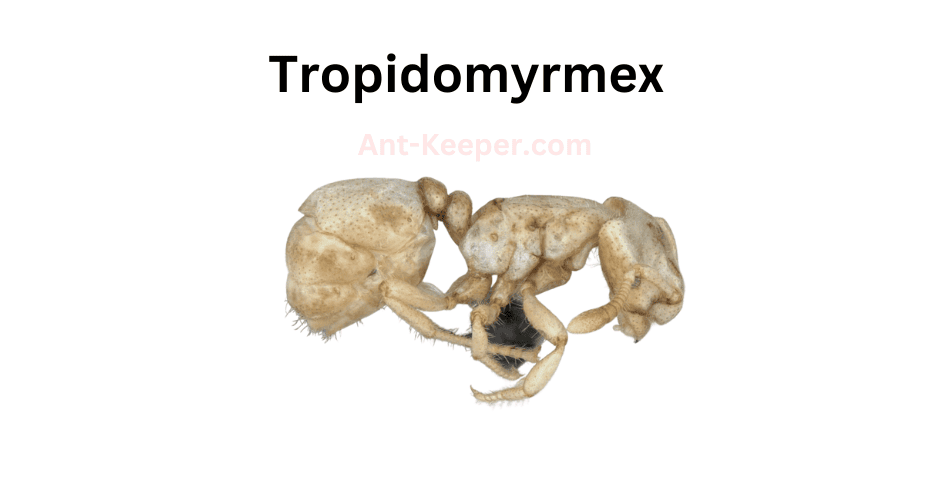
Tropidomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a distinctively shaped head and elongated mandibles.
The genus is relatively small, with only a few known species.Tropidomyrmex ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and savannas.
They are known to be aggressive predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other small invertebrates.One of the most distinctive features of Tropidomyrmex ants is their elongated mandibles, which are used for capturing and subduing prey.
These mandibles are also used in intraspecific competition, where individuals will engage in aggressive behavior to establish dominance over others.Tropidomyrmex ants are also known for their unique head shape, which is characterized by a distinctively concave profile.
This shape is thought to be an adaptation for capturing and manipulating prey, as it allows the ants to more easily grasp and hold onto their prey.Overall, Tropidomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that exhibit a number of unique adaptations for survival in their respective habitats.
While they may not be as well-known as some other ant genera, they are certainly worth studying and appreciating for their unique characteristics and behaviors.
24) Typhlomyrmex

Typhlomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their subterranean lifestyle and are commonly referred to as "blind ants" due to their lack of functional eyes.
The genus is characterized by their elongated mandibles and the presence of a unique gland on the underside of their head, which produces a sticky substance used for nest building.Typhlomyrmex ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit soil and leaf litter.
They are known to form small colonies, with only a few hundred individuals.
These ants are also known for their unique feeding habits, as they primarily feed on the exudates of plant roots and fungi.The reproductive behavior of Typhlomyrmex ants is also unique, as they are known to have a reproductive caste that is intermediate between workers and queens.
These "intercastes" are capable of laying eggs and can even mate with males, but they do not have the full reproductive capabilities of a queen.Overall, Typhlomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to life underground in a variety of ways.
Their unique morphology, feeding habits, and reproductive behavior make them a fascinating subject for study in the field of entomology.
25) Lenomyrmex
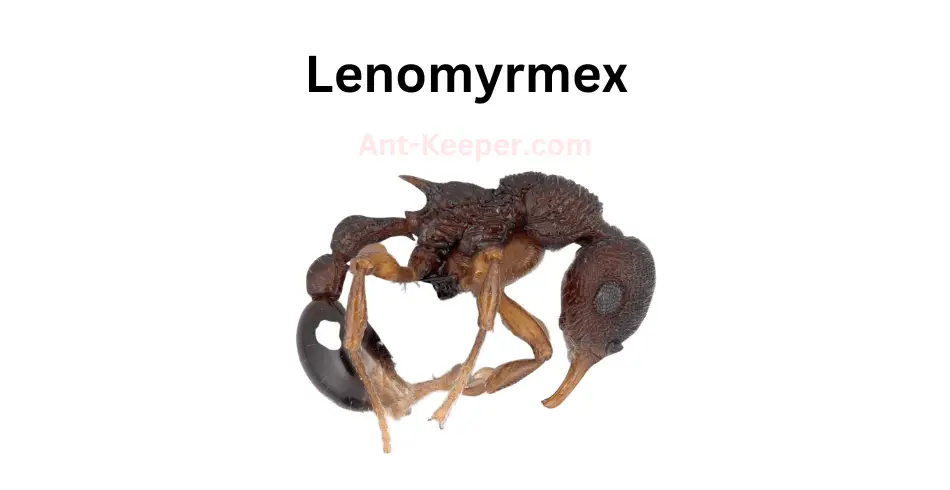

Lenomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a long and slender body, elongated mandibles, and a distinctive head shape.
The genus is relatively small, with only a few known species.Lenomyrmex ants are typically found in forested areas, where they nest in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be aggressive predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other arthropods.
These ants are also known to exhibit a high degree of social organization, with colonies consisting of hundreds or even thousands of individuals.One of the most interesting aspects of Lenomyrmex ants is their reproductive behavior.
Unlike many other ant species, Lenomyrmex queens do not mate with multiple males.
Instead, they mate with a single male and then store his sperm in a specialized organ called the spermatheca.
This allows the queen to fertilize eggs over a long period of time, without the need for repeated matings.Overall, Lenomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that offer a unique glimpse into the complex world of social insects.
Their distinctive morphology, predatory behavior, and reproductive strategies make them a valuable subject of study for entomologists and other researchers.
26) Megalomyrmex

Megalomyrmex is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their large size and aggressive behavior.
The workers of Megalomyrmex are typically between 5-10 mm in length, with the queen being even larger.
They have a distinctive appearance, with a broad head and mandibles that are used for hunting and defense.Megalomyrmex ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be opportunistic predators, feeding on a wide range of insects and other small animals.
They are also known to engage in symbiotic relationships with other insects, such as aphids and mealybugs, which they protect in exchange for a sugary secretion known as honeydew.One of the most interesting aspects of Megalomyrmex ants is their social behavior.
They are highly organized, with a complex caste system that includes workers, soldiers, and a queen.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers and soldiers are responsible for maintaining the nest and defending it from predators.Despite their aggressive behavior, Megalomyrmex ants are not considered to be a major pest species.
They are generally beneficial to the ecosystem, playing an important role in controlling insect populations and contributing to soil health.
However, they can become a nuisance if they invade homes or other structures in search of food or shelter.Overall, Megalomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that have much to teach us about the complexities of social behavior and the importance of insects in the natural world.
27) Ochetellus

Ochetellus is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dolichoderinae.
These ants are small in size, measuring between 2-5 mm in length.
They are known for their distinctive appearance, with a slender and elongated body that is covered in fine hairs.
The head of Ochetellus ants is also elongated, with large mandibles that are used for hunting and defense.Ochetellus ants are social insects that live in colonies.
The colonies are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.Ochetellus ants are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to tend to aphids, which produce honeydew that the ants feed on.Ochetellus ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be particularly abundant in areas with sandy soils.
These ants are important members of their ecosystems, playing a role in seed dispersal and soil health.Overall, Ochetellus ants are fascinating insects that are well adapted to their environments.
Their unique appearance and behavior make them a popular subject of study for entomologists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Check Out Some Of Our Other Ant By Location Posts
| 308 Different Types Of Ants With Red Heads [Full List With Partial Images] | Ants are our favorite insects here at Ant-keeper.com (I bet you couldn’t have guessed that!). One of the most exciting aspects of ants is their ... |
| 28 Different Types Of Ants With Big Heads [Full List With Images] | Ants are fascinating insects with a wide variety of shapes and sizes. Some species of ants have evolved to have disproportionately large heads, which serve ... |
| 23 Different Types Of Ants With Multiple Queens [Full Breakdown With Some Images] | Ants are our favorite insects here at Ant-keeper.com (I bet you couldn’t have guessed that!). One of the most exciting aspects of ants is their ... |