Nestled in the southernmost part of Japan, Okinawa is a region that boasts a unique blend of tropical and subtropical climates. With its crystal-clear waters, lush greenery, and diverse wildlife, Okinawa is a nature lover’s paradise.
The region is home to a variety of animals, including the Okinawan rail, the Ryukyu long-tailed giant rat, and the Okinawan habu snake. The warm and humid climate of Okinawa is perfect for the growth of a wide range of flora, including the hibiscus, bougainvillea, and plumeria.
The region’s natural beauty is further enhanced by its stunning coral reefs, which are home to a plethora of marine life. Despite being a part of Japan, Okinawa’s unique environment sets it apart from the rest of the country, making it a must-visit destination for nature enthusiasts.
.
Types Of Ants In Okinawa, Japan
The Types Of Ants In Okinawa, Japan are listed here: Acanthoponera, Acanthostichus, Coccid-Tending Ants, Army Ants, Allomerus, Trap-Jaw Ants, Anomalomyrma, Anoplolepis, Funnel Ants, Asphinctanilloides, Cercopia Ants, Brachyponera, Carpenter And Sugar Ants, Sneaking Ants, Marauder Ants, Carebarella, Army Ants, Cheliomyrmex, Acrobat Ants, Cryptic Ants, Cylindromyrmex, Daceton, Diacamma, Discothyrea, Dolly Ants, Army Ants, Ectatomma, Ectomomyrmex, Euponera, Wood Ants, Gigantiops, Hylomyrma, Crypt Ants, Moisture Ants, Lenomyrmex, Leptanilla, Leptanilloides, Razorjaw Ants, Leptothorax, Lordomyrma, Manica, Megalomyrmex, Harvester Ants, Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Mite-Eating Ants, Furrowed Ants, Myrmicocrypta, Crazy Ants, Ochetellus, Trap-Jaw Ants, Crazy Ants, Parvaponera, Big Headed Ants, Pheidologeton, Restless Ants, Amazon Ants, Spiny Ants, Porthole Ants, Winter Ants, Pristomyrmex, Probolomyrmex, Hairy Curltail Ants, Protalaridris, Protanilla, Recurvidris, Rhopalomastix, Sericomyrmex, Fire Ants, Leaf-Litter Ants, Vampire Ants, Strongylognathus, Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Tapinoma, Pale-Footed Ants, Slave-Making Ants, Pavement Ants, Old World Slender Ants, Vollenhovia, Wasmannia, Sneaking Ants, Black Garden Ants, Flower Ants, Pharaoh Ants, Longhorn Crazy Ants, Big Headed Ants.
If you’ve found some other ants in this region, contact us, and we will add them to the list!
1) Acanthoponera
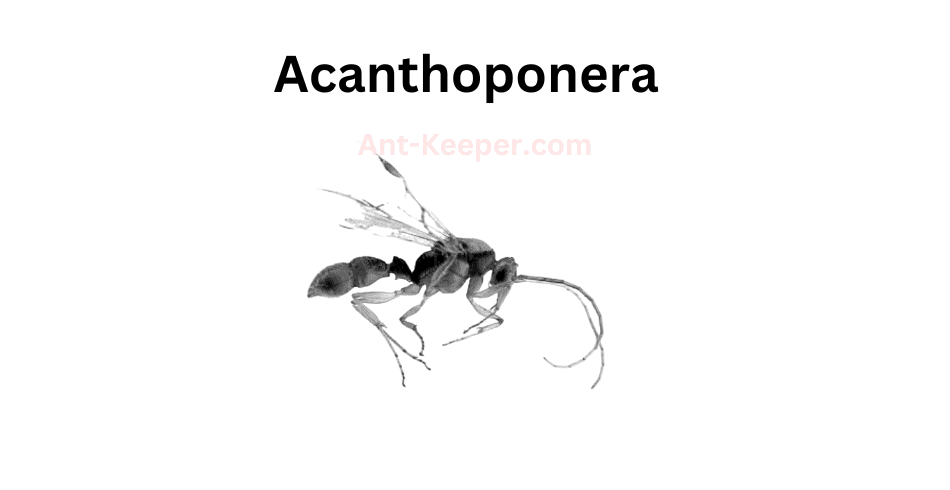
Acanthoponera be is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
It is commonly known as the "spiny ant" due to the presence of spines on its body.
The workers of this species are relatively large, measuring up to 15mm in length.
They are black in color and have a shiny exoskeleton.
Acanthoponera be is known for its aggressive behavior and powerful sting.
The venom of this ant is highly toxic and can cause severe pain, swelling, and even death in some cases.
Due to its aggressive nature, this ant is often considered a pest by humans.
This species of ant is found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and savannas.
They are known to build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and under rocks.
The colonies of Acanthoponera be are relatively small, with only a few hundred individuals.
The diet of this ant consists mainly of other insects, including termites, beetles, and caterpillars.
They are also known to scavenge on dead animals and feed on nectar from flowers.
Acanthoponera be is an important species in its ecosystem, as it helps to control the populations of other insects.
However, due to its aggressive behavior and powerful sting, it is important to exercise caution when encountering this ant in the wild.
2) Acanthostichus
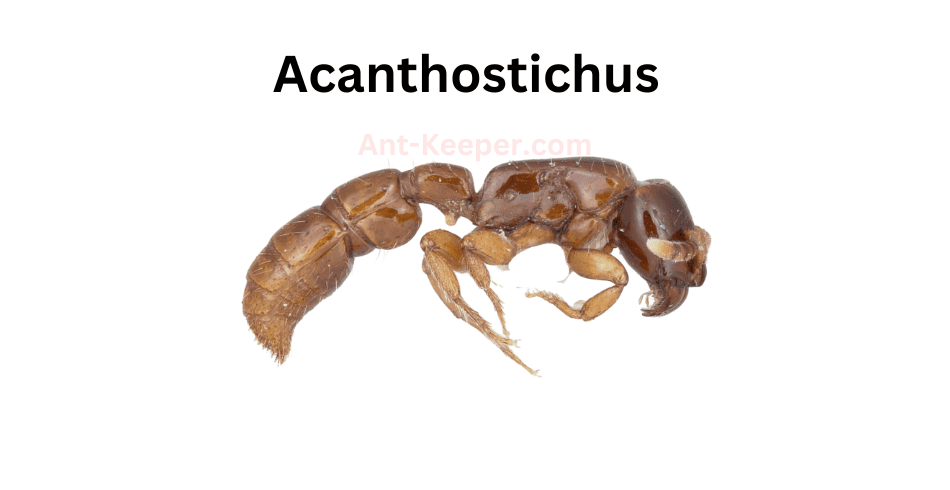

Acanthostichus is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dorylinae.
The ants in this genus are known for their aggressive behavior and are commonly referred to as "trap-jaw ants." Acanthostichus ants are typically small in size, ranging from 2 to 5 millimeters in length, and are characterized by their elongated mandibles that can snap shut with incredible speed and force, allowing them to capture prey or defend themselves from predators.
Acanthostichus ants are primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be highly social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colonies are typically headed by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's social structure.
One of the most interesting aspects of Acanthostichus ants is their hunting behavior.
These ants are known to be ambush predators, waiting in hidden locations for prey to pass by before striking with their powerful mandibles.
They are also known to be scavengers, feeding on a variety of dead insects and other small animals.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Acanthostichus ants are not considered to be a significant threat to humans.
However, their powerful mandibles can cause painful bites, and they should be handled with caution.
Overall, Acanthostichus ants are fascinating insects that play an important role in their ecosystems and provide valuable insights into the behavior and evolution of social insects.
3) Coccid-Tending Ants, Acropyga

Coccid-tending ants are a group of ants that have a mutualistic relationship with coccids, also known as scale insects.
These ants protect and care for the coccids, which in turn provide the ants with a sugary substance called honeydew.
Coccid-tending ants are typically small in size, ranging from 2 to 5 millimeters in length.
They have a reddish-brown coloration and a slender body shape.
These ants are commonly found in forests and grasslands, where they build nests in soil or under rocks.
The relationship between coccid-tending ants and coccids is a classic example of mutualism.
The ants protect the coccids from predators and parasites, and also move them to new feeding sites when necessary.
In return, the coccids secrete honeydew, which the ants consume as a source of energy.
Coccid-tending ants have been observed to actively farm and cultivate coccids, moving them to new locations and even pruning the plants on which they feed to encourage the growth of new coccids.
This behavior has been shown to increase the overall productivity of the ant-coccid mutualism.
Overall, coccid-tending ants are an important component of many ecosystems, playing a key role in the maintenance of plant and insect populations.
Their mutualistic relationship with coccids highlights the complex and interconnected nature of ecological systems.
4) Army Ants, Aenictus
Army ants are a type of ant that belong to the subfamily Dorylinae.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and their ability to form large colonies that can contain up to several million individuals.
Army ants are found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, and they play an important role in the ecosystems where they live.
One of the most distinctive features of army ants is their nomadic lifestyle.
Unlike other ants that build permanent nests, army ants are constantly on the move, searching for food and new nesting sites.
They are also known for their impressive hunting skills.
When they come across prey, they swarm over it in large numbers, overwhelming it with their sheer numbers and powerful jaws.
Army ants are also social insects, with a complex hierarchy that determines the roles of each individual in the colony.
The queen is the largest ant in the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
The soldiers are larger and have stronger jaws, which they use to protect the colony from predators.
Despite their aggressive behavior, army ants are an important part of many ecosystems.
They help to control the populations of other insects and small animals, and they provide food for larger predators such as birds and mammals.
In some cultures, army ants are even used as a source of food for humans.
Overall, army ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to life in some of the most challenging environments on Earth.
Their nomadic lifestyle, impressive hunting skills, and complex social structure make them one of the most interesting species of ants in the world.
5) Allomerus
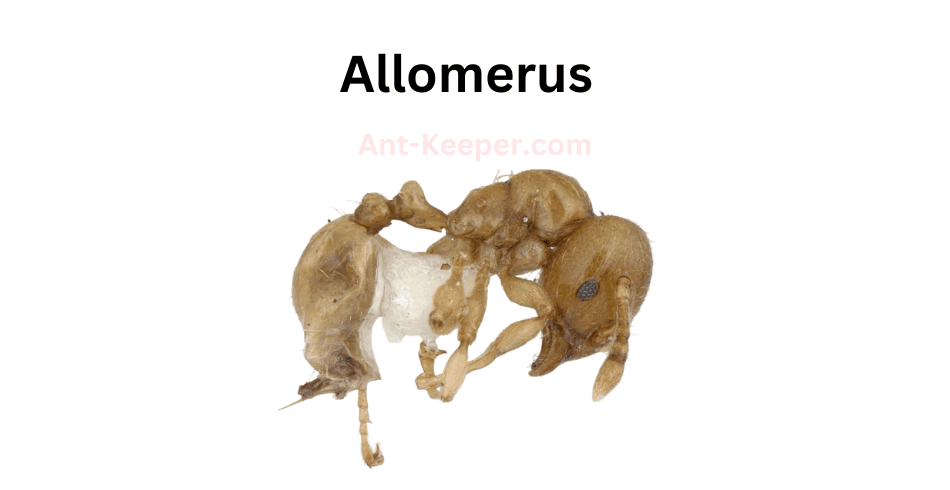
Allomerus is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique behavior of building traps to capture prey.
The species in this genus are arboreal, meaning they live in trees and other vegetation.
Allomerus ants build traps by manipulating the surrounding vegetation to create a structure that funnels prey towards a central chamber.
The ants then wait in the chamber for prey to fall in, at which point they swarm and subdue it.
This behavior is known as "agro-predation," as the ants use the plants around them to aid in their hunting.
Allomerus ants are also known for their symbiotic relationship with a species of plant called Hirtella physophora.
The ants live inside the hollow stems of these plants and protect them from herbivores.
In return, the plant provides the ants with nectar and a safe place to live.
There are several species of Allomerus ants, each with their own unique trap-building techniques.
Some species build traps on the undersides of leaves, while others build them on the stems of plants.
Despite their small size, Allomerus ants play an important role in their ecosystem as both predators and protectors of their host plants.
6) Trap-Jaw Ants, Anochetus
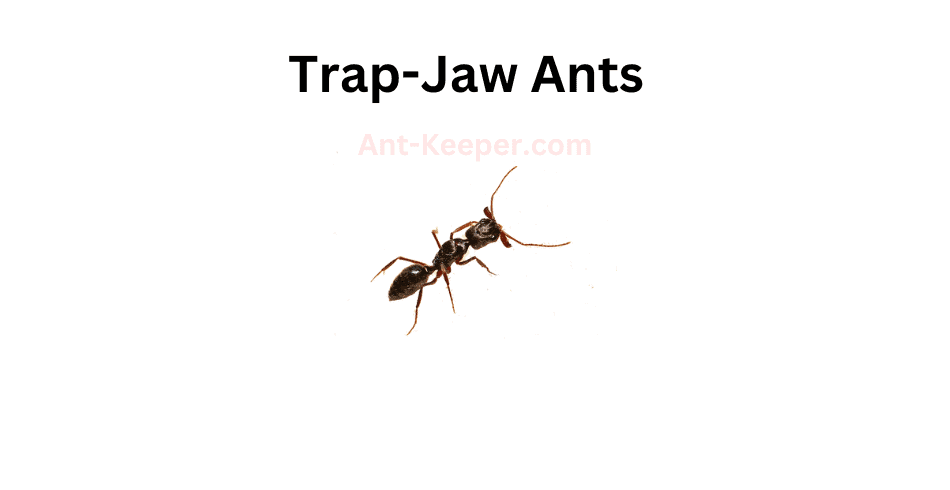
Trap-jaw ants are a species of ants that belong to the genus Odontomachus.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The mandibles of trap-jaw ants are capable of closing at incredible speeds, reaching up to 140 miles per hour.
This allows them to snap their jaws shut with incredible force, which can stun or kill their prey.
Trap-jaw ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically active during the day and are known to be highly territorial.
These ants are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to escape danger or to capture prey.
Trap-jaw ants are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on a variety of insects, including other ants, as well as nectar and other sweet substances.
These ants are also known to be scavengers, feeding on dead insects and other organic matter.
The colonies of trap-jaw ants are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
However, they are highly organized and have a strict social hierarchy.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, trap-jaw ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their environments.
Their powerful mandibles and jumping abilities make them formidable predators, while their social organization allows them to work together to protect their colonies and ensure their survival.
7) Anomalomyrma
Anomalomyrmabe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
This ant is known for its unique physical characteristics and behavior.
The workers of this species are small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
One of the most distinctive features of Anomalomyrmabe is its mandibles.
These ants have long, curved mandibles that are used for grasping and cutting.
The mandibles are also used for defense against predators and other ants.
Anomalomyrmabe is a social insect, living in colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colony is headed by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and producing new workers.
The workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
This ant is known for its aggressive behavior towards other ant species.
It will often attack and kill ants from other colonies, even those that are much larger in size.
Anomalomyrmabe is also known for its ability to adapt to different environments.
It can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
Overall, Anomalomyrmabe is a fascinating species of ant that has many unique characteristics.
Its physical features and behavior make it a valuable subject for scientific study and research.
8) Anoplolepis
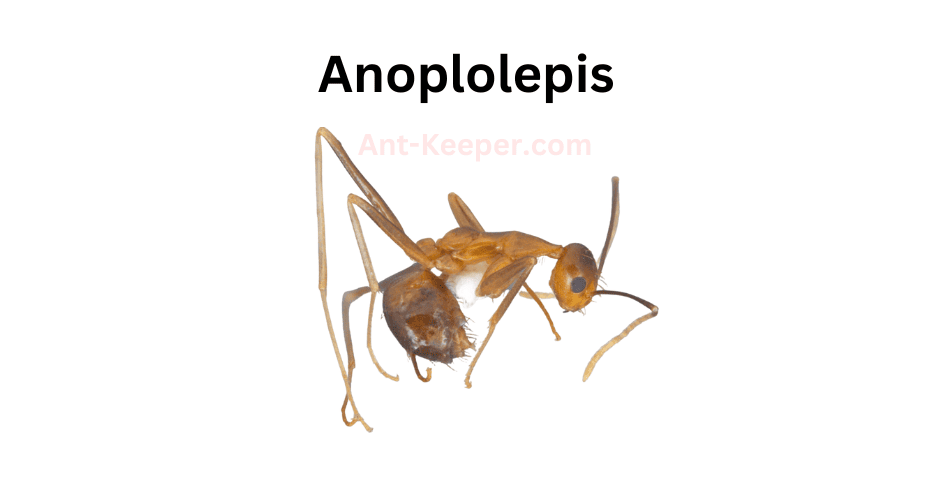
Anoplolepis is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Formicinae.
The most well-known species in this genus is Anoplolepis gracilipes, commonly known as the yellow crazy ant.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and ability to form large colonies.
Anoplolepis ants are small in size, measuring between 2-3 mm in length.
They have a yellowish-brown coloration and a slender body shape.
Their mandibles are long and curved, which they use to capture prey and defend their colony.
These ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to be attracted to sweet substances and can become a nuisance in households.
Anoplolepis ants are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
They are known to form supercolonies, which can consist of millions of individuals.
These supercolonies can have a significant impact on the ecosystem, as they can displace native ant species and disrupt the balance of the food chain.
Overall, Anoplolepis ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and adaptations.
While they can be a nuisance in households, they play an important role in the ecosystem and are an important subject of study for scientists.
9) Funnel Ants, Aphaenogaster
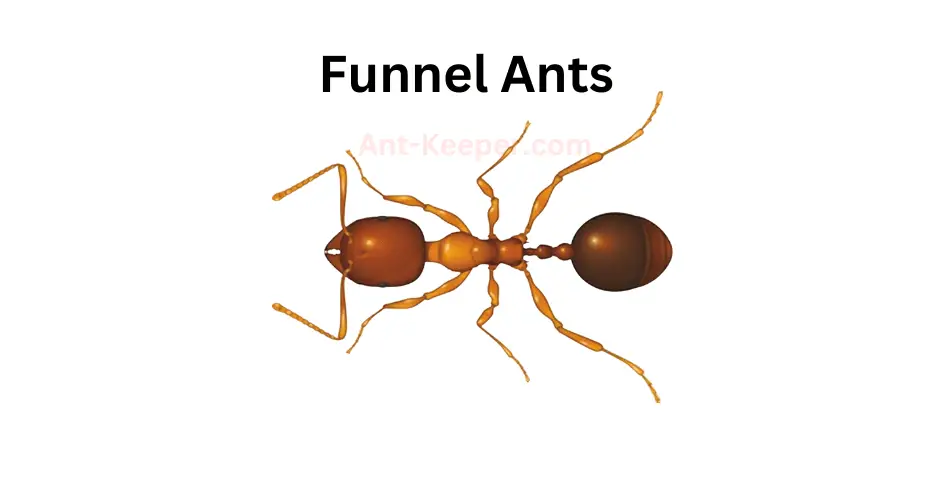

The Funnel Ants, also known as Aphaenogaster ants, are a species of ants that are commonly found in various habitats around the world.
These ants are known for their unique nesting behavior, where they construct funnel-shaped nests that are typically located in soil or leaf litter.
The Funnel Ants are relatively small in size, with workers measuring between 3-5mm in length.
They are typically reddish-brown in color and have a slender body shape.
These ants are known for their strong mandibles, which they use to collect and transport food back to their nests.
One of the most interesting aspects of the Funnel Ants is their nesting behavior.
These ants construct funnel-shaped nests that are typically located in soil or leaf litter.
The entrance to the nest is narrow and funnel-shaped, which helps to protect the colony from predators and other threats.
Inside the nest, the ants create a series of chambers and tunnels that are used for different purposes, such as storing food, caring for the brood, and housing the queen.
The Funnel Ants are omnivorous, meaning that they feed on both plant and animal matter.
They are known to collect a wide variety of food items, including seeds, insects, and other small invertebrates.
These ants are also known to tend to aphids, which they use for their honeydew secretion.
Overall, the Funnel Ants are a fascinating species of ants that are known for their unique nesting behavior and omnivorous diet.
They play an important role in their ecosystems, helping to control populations of other insects and contributing to nutrient cycling in the soil.
10) Asphinctanilloides

Asphinctanilloides is a genus of ants that belongs to the family Formicidae.
The ants in this genus are known for their small size and unique morphology.
Asphinctanilloides ants have a distinct waist that is constricted, giving them a segmented appearance.
They are also known for their elongated mandibles, which are used for capturing prey and defending their colony.
Asphinctanilloides ants are typically found in forested areas, where they live in small colonies.
They are known to be aggressive towards other ant species and will defend their territory fiercely.
Asphinctanilloides ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, fruits, and seeds.
One species of Asphinctanilloides, Asphinctanilloides be, is particularly interesting due to its unique behavior.
This species is known to be a specialist predator of springtails, a type of small arthropod that is found in soil and leaf litter.
Asphinctanilloides be will actively hunt for springtails, using its elongated mandibles to capture and subdue its prey.
Asphinctanilloides be is also known for its ability to camouflage itself.
The ants will cover themselves in soil and debris, making them difficult to spot by predators and prey alike.
This behavior is thought to be an adaptation to their forested habitat, where they need to blend in with their surroundings to avoid detection.
Overall, Asphinctanilloides ants are a fascinating group of insects that exhibit unique behaviors and adaptations.
Asphinctanilloides be, in particular, is an interesting species due to its specialized predatory behavior and camouflage abilities.
11) Cercopia Ants, Azteca

Cercopia ants are a species of ants that belong to the Formicidae family.
They are known for their large size, with workers measuring up to 1.5 centimeters in length.
These ants are typically reddish-brown in color and have a distinctive, elongated head.
Cercopia ants are primarily found in forested areas and are known to build their nests in soil or under rocks.
They are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, fruits, and nectar.
One unique characteristic of Cercopia ants is their ability to produce formic acid, which they use as a defense mechanism against predators.
When threatened, these ants will release formic acid from their bodies, which can cause irritation and pain to potential attackers.
Cercopia ants are also known for their complex social structure, with colonies consisting of multiple queens and thousands of workers.
These ants communicate with each other through a variety of chemical signals, including pheromones.
Overall, Cercopia ants are a fascinating species of ants that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their large size, unique defense mechanisms, and complex social structure make them a subject of interest for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
12) Brachyponera

Brachyponera is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Ponerinae.
One of the species in this genus is Brachyponera sennaarensis, commonly known as the Sennaar ant.
These ants are relatively large, measuring up to 12mm in length, and are known for their aggressive behavior.
The workers of Brachyponera sennaarensis are dark brown in color and have a shiny exoskeleton.
They have a powerful sting and are known to attack other insects and even small vertebrates.
These ants are also known to forage for food in large groups, and can quickly overwhelm their prey.
Brachyponera sennaarensis is found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to build their nests in soil, under rocks, and in tree trunks.
These ants are also known to be nocturnal, and are most active during the night.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Brachyponera sennaarensis is an important part of the ecosystem.
They help to control the population of other insects and play a vital role in the food chain.
However, their powerful sting and aggressive behavior make them a potential danger to humans and other animals.
13) Carpenter And Sugar Ants, Camponotus

Carpenter ants and sugar ants are two common species of ants found in many regions of the world.
Carpenter ants are known for their ability to excavate wood and create nests within it.
They are typically larger in size than sugar ants and have a black or dark brown coloration.
Carpenter ants are also known for their strong mandibles, which they use to chew through wood and other materials.
Sugar ants, on the other hand, are smaller in size and have a yellow or brown coloration.
They are named for their preference for sugary foods and are often found in kitchens and other areas where food is stored.
Sugar ants are also known for their ability to form large colonies, with thousands of individual ants working together to gather food and care for their young.
Both carpenter ants and sugar ants play important roles in their ecosystems.
Carpenter ants help to break down dead wood and other plant material, which helps to recycle nutrients back into the soil.
Sugar ants help to disperse seeds and pollinate plants, which helps to maintain healthy ecosystems.
However, both species can also be pests when they invade human homes and buildings.
Carpenter ants can cause damage to wooden structures, while sugar ants can contaminate food and be a nuisance to homeowners.
It is important to take steps to prevent ant infestations and to control them if they do occur, in order to protect both human health and the health of the environment.
14) Sneaking Ants, Cardiocondyla

Sneaking Ants, also known as Camponotus obscuripes, are a species of ant that are commonly found in forested areas.
These ants are known for their ability to move quietly and quickly, making them difficult to detect.
Sneaking Ants are typically black or dark brown in color and range in size from 5 to 12 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive, flattened head and a narrow waist, which helps them to navigate through tight spaces.
One of the most interesting aspects of Sneaking Ants is their behavior.
These ants are known for their ability to sneak up on other insects and steal their food.
They are also known to raid the nests of other ant species, taking their eggs and larvae back to their own colony to raise as their own.
Sneaking Ants are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
They have been observed feeding on nectar, honeydew, and small insects.
They are also known to scavenge for food, often taking advantage of the leftovers from other insects.
In terms of reproduction, Sneaking Ants have a unique system.
The colony is typically led by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs.
However, there are also a number of worker ants who are capable of laying eggs as well.
These eggs are typically unfertilized and produce male ants, which are used for mating purposes.
Overall, Sneaking Ants are a fascinating species with unique behaviors and adaptations.
Their ability to move quietly and quickly makes them a formidable predator, and their omnivorous diet allows them to thrive in a variety of environments.
15) Marauder Ants, Carebara

Marauder ants are a species of ants known for their aggressive behavior and large colony sizes.
They are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats including forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
These ants are known for their ability to raid other ant colonies and steal their resources, including food and brood.
They have powerful mandibles that allow them to overpower other ants and carry their prey back to their own colony.
Marauder ants are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments.
They can quickly adjust their foraging patterns and nesting sites in response to changes in their surroundings, allowing them to thrive in a variety of habitats.
Despite their aggressive behavior, marauder ants play an important role in their ecosystems.
They help to control populations of other insects and contribute to nutrient cycling in the soil.
Overall, marauder ants are a fascinating species of ants that have adapted to thrive in a variety of environments.
Their aggressive behavior and large colony sizes make them a formidable force in the ant world.
16) Carebarella
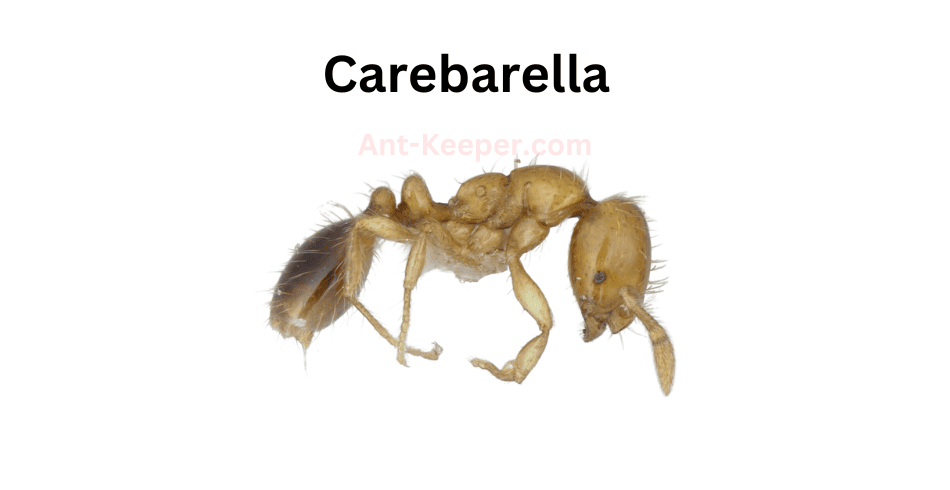
The Carebarellabe ant is a fascinating species known for its unique physical characteristics and social behavior.
These ants are relatively small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length, and are typically reddish-brown in color.
One of the most distinctive features of the Carebarellabe ant is its mandibles, which are elongated and curved, resembling the shape of a sickle.
These mandibles are used for a variety of tasks, including cutting and carrying food, defending the colony, and even grooming other ants.
Carebarellabe ants are highly social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
Within the colony, there is a strict hierarchy, with a queen ant at the top and various worker ants performing different tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Interestingly, Carebarellabe ants have also been observed engaging in a behavior known as "tandem running." This involves two ants running together, with the leading ant guiding the other to a food source or new nest location.
This behavior is thought to be a form of communication and cooperation within the colony.
Overall, the Carebarellabe ant is a fascinating species that continues to intrigue scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
Its unique physical characteristics and social behavior make it a valuable subject of study for those interested in the natural world.
17) Army Ants, Cerapachys
Army ants are a type of ant that belong to the subfamily Dorylinae.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and their ability to form large colonies that can contain up to several million individuals.
Army ants are found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, and they play an important role in the ecosystems where they live.
One of the most distinctive features of army ants is their nomadic lifestyle.
Unlike other ants that build permanent nests, army ants are constantly on the move, searching for food and new nesting sites.
They are also known for their impressive hunting skills.
When they come across prey, they swarm over it in large numbers, overwhelming it with their sheer numbers and powerful jaws.
Army ants are also social insects, with a complex hierarchy that determines the roles of each individual in the colony.
The queen is the largest ant in the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
The soldiers are larger and have stronger jaws, which they use to protect the colony from predators.
Despite their aggressive behavior, army ants are an important part of many ecosystems.
They help to control the populations of other insects and small animals, and they provide food for larger predators such as birds and mammals.
In some cultures, army ants are even used as a source of food for humans.
Overall, army ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to life in some of the most challenging environments on Earth.
Their nomadic lifestyle, impressive hunting skills, and complex social structure make them one of the most interesting species of ants in the world.
18) Cheliomyrmex

Cheliomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dolichoderinae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics, including a long and slender body, elongated mandibles, and a distinctively shaped head.
The genus is relatively small, with only a few known species.
Cheliomyrmex ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit forested areas and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and will defend their nests fiercely against intruders.
One of the most interesting aspects of Cheliomyrmex ants is their reproductive strategy.
Unlike many other ant species, Cheliomyrmex queens do not mate with multiple males.
Instead, they mate with a single male and store his sperm in a specialized organ called the spermatheca.
This allows the queen to fertilize her eggs over a long period of time, without the need for repeated mating.
Overall, Cheliomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that offer a unique glimpse into the diversity of life on our planet.
Their distinctive physical features, aggressive behavior, and unusual reproductive strategy make them a fascinating subject for scientific study.
19) Acrobat Ants, Crematogaster

Acrobat ants, also known as Crematogaster spp., are a genus of ants that are found in various parts of the world.
These ants are known for their unique ability to contort their bodies and move in acrobatic ways, hence their name.
Acrobat ants are relatively small, with workers measuring between 2-5mm in length.
They are typically brown or black in color, with a slender body and long legs.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and will readily defend their nests against intruders.
One of the most interesting features of acrobat ants is their ability to use their mandibles to grip onto surfaces and contort their bodies in unusual ways.
This allows them to move along narrow branches, twigs, and other surfaces that would be difficult for other ants to navigate.
They are also able to use this ability to escape from predators, such as birds and other insects.
Acrobat ants are omnivorous, meaning that they will eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on insects, nectar, and honeydew, as well as fruits and seeds.
These ants are also known to tend to aphids, protecting them from predators in exchange for the sweet honeydew that the aphids produce.
In terms of their social structure, acrobat ants are typically organized into colonies that are led by a queen.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the nest.
Overall, acrobat ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted unique abilities to survive in their environments.
Their acrobatic abilities and aggressive behavior make them a formidable force in the insect world.
20) Cryptic Ants, Cryptopone

Cryptic ants are a species of ants that are known for their ability to blend in with their surroundings.
They are typically small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length, and have a dark brown or black coloration that helps them to remain inconspicuous.
One of the most interesting features of cryptic ants is their ability to mimic the appearance of other insects.
For example, some species of cryptic ants have been observed mimicking the appearance of spiders, which helps them to avoid detection by predators that might otherwise prey on them.
Cryptic ants are also known for their highly social behavior.
They live in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals, and they work together to gather food, care for their young, and defend their territory from other ants and predators.
Despite their small size, cryptic ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They help to aerate the soil, control pest populations, and provide food for other animals.
In addition, they are an important food source for many birds and other predators.
Overall, cryptic ants are a fascinating species of ants that have evolved a number of unique adaptations to help them survive in their environment.
Their ability to blend in with their surroundings and mimic other insects is just one example of the many ways in which they have adapted to their surroundings over time.
21) Cylindromyrmex

Cylindromyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily of Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their cylindrical body shape and elongated mandibles.
The workers of Cylindromyrmex are typically small in size, measuring around 2-3 mm in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a shiny exoskeleton.
Cylindromyrmex ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be aggressive predators, feeding on other insects and small arthropods.
These ants are also known to have a unique hunting behavior, where they actively search for prey rather than waiting for it to come to them.
The reproductive caste of Cylindromyrmex ants consists of winged males and females.
The males are typically smaller than the females and have longer antennae.
The females have a larger body size and are responsible for laying eggs and starting new colonies.
Cylindromyrmex ants are known for their ability to adapt to different environments.
They have been observed living in both arboreal and ground-dwelling habitats.
These ants are also known to have a symbiotic relationship with certain plant species, where they protect the plants from herbivores in exchange for food and shelter.
Overall, Cylindromyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to a wide range of environments.
Their unique hunting behavior and symbiotic relationships make them an important part of many ecosystems.
22) Daceton
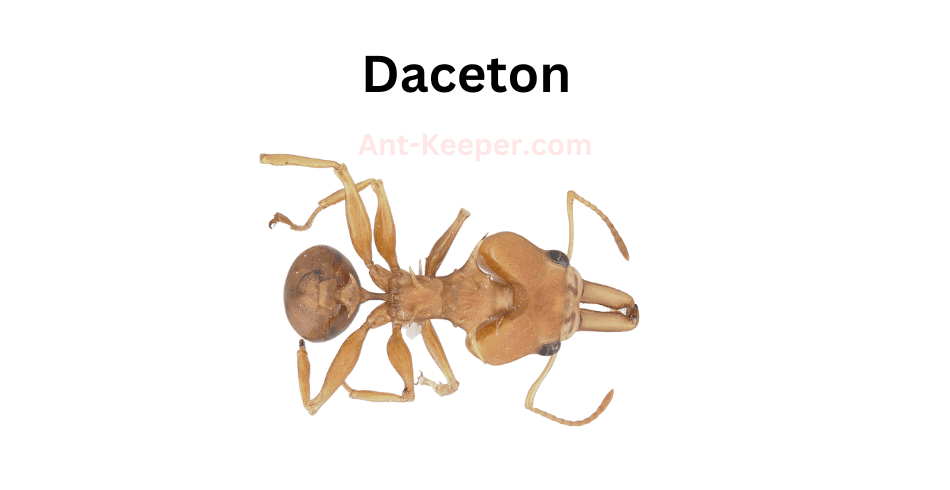
Daceton is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Ponerinae.
These ants are commonly known as "dracula ants" due to their unique feeding behavior.
They are found in tropical regions and are known for their aggressive behavior towards other ant species.
Daceton ants are relatively large, with workers measuring up to 10mm in length.
They have long, slender mandibles that are used to capture prey.
Unlike most ants, Daceton ants do not feed on sugary substances.
Instead, they feed on the hemolymph (blood) of other insects, which they obtain by piercing their prey with their mandibles.
Daceton ants are also known for their unique nesting behavior.
They build their nests in the soil, but instead of creating tunnels and chambers, they create a network of interconnected tubes.
These tubes are used to transport food and larvae between different parts of the nest.
Daceton ants are highly territorial and will aggressively defend their nests against other ant species.
They are also known to engage in battles with other Daceton colonies.
These battles can last for hours and involve hundreds of ants.
Overall, Daceton ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and adaptations.
Their aggressive nature and feeding habits make them a formidable force in the ant world.
23) Diacamma
Diacamma is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Ponerinae.
These ants are known for their unique behavior of forming long trails to forage for food.
They are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other ant species and their ability to defend their territory.
Diacamma ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, living in forests and other wooded areas.
They are known to build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and rotting wood.
The nests are typically small and consist of a few chambers, with the queen residing in the central chamber.
These ants are relatively large, with workers measuring up to 10mm in length.
They are dark brown or black in color, with a shiny exoskeleton.
The mandibles of Diacamma ants are long and curved, allowing them to capture and subdue their prey.
Diacamma ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, spiders, and other small invertebrates, as well as plant material.
They are also known to scavenge for food, and will often raid the nests of other ant species to steal their food.
One of the most interesting aspects of Diacamma ants is their social behavior.
They are known for their ability to form long trails to forage for food, with workers following a pheromone trail laid down by other members of the colony.
They are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other ant species, and will defend their territory fiercely.
Overall, Diacamma ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and adaptations that allow them to thrive in their environments.
24) Discothyrea

Discothyreabe is a species of ant that belongs to the Formicidae family.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics, including their elongated mandibles and slender bodies.
The workers of this species are typically around 3-4mm in length, while the queen can grow up to 7mm.
Discothyreabe ants are primarily found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be aggressive towards other ant species and will defend their territory fiercely.
These ants are also known to be nocturnal, which means they are most active during the night.
One of the most interesting aspects of Discothyreabe ants is their feeding habits.
They are known to be generalist feeders, which means they will eat a wide variety of foods.
They have been observed feeding on insects, nectar, and even carrion.
This adaptability allows them to thrive in a variety of environments.
Despite their small size, Discothyreabe ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They help to control insect populations and contribute to soil health through their nest-building activities.
They are also an important food source for many other animals, including birds and small mammals.
Overall, Discothyreabe ants are a fascinating species that have adapted to thrive in a variety of environments.
Their unique physical characteristics and feeding habits make them an important part of their ecosystem.
25) Dolly Ants, Dolichoderus

Dolly Ants, also known as Dolichoderus spp., are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive elongated heads and bodies, which give them a unique appearance compared to other ant species.
Dolly Ants are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or under rocks.
They are known to be highly social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
Within these colonies, there is a strict division of labor, with different ants taking on specific roles such as foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
One interesting aspect of Dolly Ant behavior is their use of chemical communication.
These ants use pheromones to communicate with each other, leaving trails of scent that other ants can follow to locate food sources or to find their way back to the nest.
They also use pheromones to signal danger, which can trigger a coordinated response from the colony to defend against predators.
Dolly Ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of foods including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
They are also known to have a mutualistic relationship with certain plant species, where they protect the plants from herbivores in exchange for a source of food.
Overall, Dolly Ants are a fascinating species of ant with unique physical and behavioral characteristics.
Their social structure and use of chemical communication make them an important subject of study for researchers interested in understanding the behavior of social insects.
26) Army Ants, Eciton
Army ants are a type of ant that belong to the subfamily Dorylinae.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and their ability to form large colonies that can contain up to several million individuals.
Army ants are found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world, and they play an important role in the ecosystems where they live.
One of the most distinctive features of army ants is their nomadic lifestyle.
Unlike other ants that build permanent nests, army ants are constantly on the move, searching for food and new nesting sites.
They are also known for their impressive hunting skills.
When they come across prey, they swarm over it in large numbers, overwhelming it with their sheer numbers and powerful jaws.
Army ants are also social insects, with a complex hierarchy that determines the roles of each individual in the colony.
The queen is the largest ant in the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
The soldiers are larger and have stronger jaws, which they use to protect the colony from predators.
Despite their aggressive behavior, army ants are an important part of many ecosystems.
They help to control the populations of other insects and small animals, and they provide food for larger predators such as birds and mammals.
In some cultures, army ants are even used as a source of food for humans.
Overall, army ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to life in some of the most challenging environments on Earth.
Their nomadic lifestyle, impressive hunting skills, and complex social structure make them one of the most interesting species of ants in the world.
27) Ectatomma
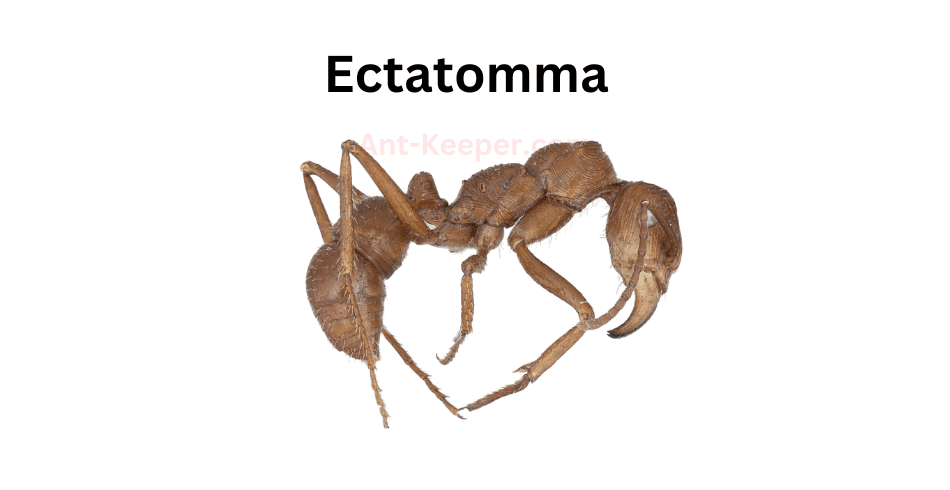

Ectatomma is a genus of ants that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are commonly known as "dracula ants" due to their unique feeding behavior.
Ectatomma ants are found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
The workers of Ectatomma ants are polymorphic, meaning they come in different sizes.
The larger workers are known as "majors," while the smaller ones are called "minors." The majors are responsible for defending the colony and foraging for food, while the minors take care of the brood and tend to the queen.
One of the most fascinating aspects of Ectatomma ants is their feeding behavior.
These ants are obligate predators, meaning they only feed on other insects.
However, they do not simply kill their prey and consume it.
Instead, they use their mandibles to puncture the exoskeleton of their prey and suck out its hemolymph, which is the insect equivalent of blood.
This feeding behavior is similar to that of a vampire, hence the nickname "dracula ants."
Ectatomma ants are also known for their unique nesting habits.
They build their nests in the soil, but instead of creating a traditional entrance, they create a small hole that leads to a tunnel system.
This tunnel system can extend for several meters and can have multiple chambers for the brood, food storage, and the queen.
Overall, Ectatomma ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and adaptations that make them stand out from other ant species.
28) Ectomomyrmex

Ectomomyrmex is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology and behavior.
They are small in size, measuring between 2-4 mm in length, and have a distinctive elongated head and mandibles.
The workers of this genus are polymorphic, meaning they come in different sizes and shapes.
Ectomomyrmex ants are primarily found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit forested areas.
They are known to be arboreal, meaning they live in trees and are often found on the branches and trunks of trees.
These ants are also known to be aggressive and territorial, often engaging in battles with other ant species.
One of the most interesting aspects of Ectomomyrmex ants is their symbiotic relationship with other organisms.
They are known to form mutualistic relationships with a variety of organisms, including plants, fungi, and insects.
For example, some species of Ectomomyrmex ants are known to cultivate fungi for food, while others are known to protect plants from herbivores in exchange for nectar.
Overall, Ectomomyrmex ants are a fascinating group of ants that exhibit unique morphology and behavior.
Their symbiotic relationships with other organisms make them an important part of many ecosystems, and their aggressive nature makes them a force to be reckoned with in the ant world.
29) Euponera

Euponerabe is a species of ant that belongs to the family of Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics and behavior.
They are relatively small in size, measuring around 5-6 millimeters in length.
Their bodies are dark brown or black in color, and they have long, slender legs that allow them to move quickly and efficiently.
One of the most distinctive features of Euponerabe ants is their mandibles.
These ants have large, powerful mandibles that they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
They are also known for their aggressive behavior, and will not hesitate to attack other ants or insects that they perceive as a threat.
Euponerabe ants are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in the soil or in decaying wood.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, fruits, and other plant materials.
They are also known to engage in trophallaxis, a behavior in which they exchange food and other nutrients with other members of their colony.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Euponerabe ants are not considered to be a major pest species.
They play an important role in their ecosystems, helping to control populations of other insects and contributing to the overall health of the forest.
They are also fascinating creatures to observe, with their unique physical characteristics and complex social behavior.
30) Wood Ants, Formica

Wood ants, also known as carpenter ants, are a species of ant that belong to the genus Camponotus.
They are widely distributed throughout the world and are commonly found in forests and woodlands.
These ants are known for their ability to excavate wood and create nests inside trees, logs, and other wooden structures.
Wood ants are typically large in size, with workers ranging from 6 to 13 millimeters in length.
They are usually black or brown in color and have a smooth, shiny exoskeleton.
These ants have strong mandibles that they use to chew through wood and defend their nests.
Wood ants are social insects that live in colonies consisting of a queen, workers, and soldiers.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers and soldiers are responsible for maintaining the nest and protecting it from predators.
These ants communicate with each other using chemical signals called pheromones.
Wood ants are omnivores and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, honeydew, and plant sap.
They are also known to scavenge for food and will sometimes raid the nests of other ant species.
Despite their ability to excavate wood, wood ants are not considered pests.
In fact, they play an important role in forest ecosystems by helping to decompose dead wood and recycle nutrients.
They also serve as a food source for many other animals, including birds, mammals, and other insects.
Overall, wood ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to live in a unique habitat.
Their ability to excavate wood and create nests inside trees is a testament to their ingenuity and resourcefulness.
31) Gigantiops
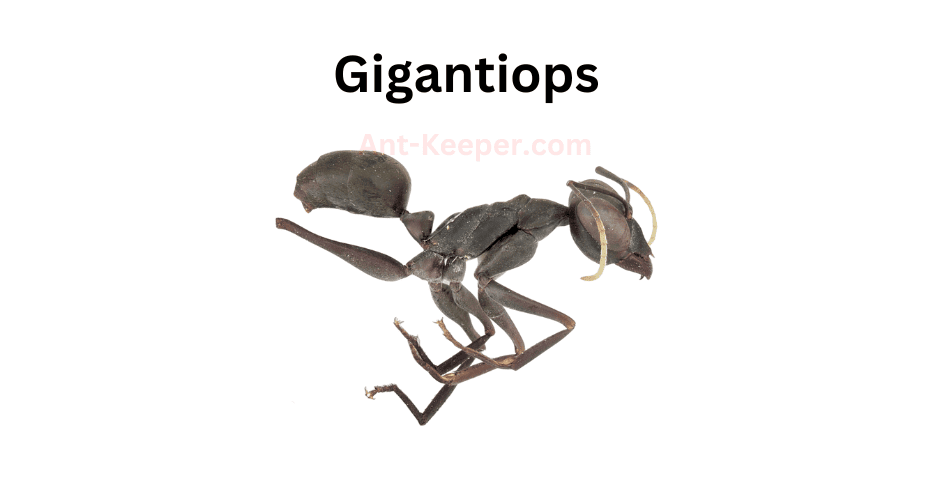
Gigantiops is a genus of ants belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their large size and unique physical characteristics.
The workers of Gigantiops are typically around 10-12 mm in length, making them some of the largest ants in the world.
They have elongated mandibles that are used for capturing prey and defending their colony.
Gigantiops ants are found in a variety of habitats, including rainforests and other tropical regions.
They are known to be arboreal, meaning they live in trees and other high places.
These ants are also known for their aggressive behavior, and will readily attack other insects and even small animals if they feel threatened.
One of the most interesting aspects of Gigantiops ants is their social structure.
Like many other ant species, they live in colonies that are organized around a queen.
However, unlike most ants, Gigantiops colonies are relatively small, with only a few hundred individuals.
This makes them easier to study and observe in the wild.
Overall, Gigantiops ants are fascinating creatures that offer a unique glimpse into the world of social insects.
Their large size, aggressive behavior, and unique social structure make them a popular subject of study for entomologists and other scientists.
32) Hylomyrma

Hylomyrmabe is a species of ant that belongs to the subfamily of Formicinae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics, including their elongated mandibles and slender bodies.
They are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or under logs.
Hylomyrmabe ants are known for their aggressive behavior and are often seen attacking other insects and even small animals.
They are also known to be territorial and will defend their nests fiercely against intruders.
These ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to cultivate and protect aphids, which produce honeydew that the ants feed on.
Hylomyrmabe ants are social insects and live in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
Overall, Hylomyrmabe ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their aggressive behavior and unique physical characteristics make them a fascinating species to study and observe.
33) Crypt Ants, Hypoponera

Crypt ants, also known as fungus-growing ants, are a group of ants that cultivate fungi for food.
They are found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
Crypt ants are known for their unique nesting behavior, as they construct underground chambers to house their fungal gardens.
These ants have a symbiotic relationship with the fungi they cultivate.
The ants provide the fungi with a suitable environment for growth, while the fungi provide the ants with a source of food.
The ants also protect their fungal gardens from other insects and parasites.
Crypt ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colonies are organized into castes, with the queen being the largest and most important member.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for tending to the fungal gardens and caring for the young.
One interesting aspect of crypt ants is their ability to create "satellite" nests.
These nests are smaller chambers located near the main nest, and they serve as storage areas for food and as a place for the queen to lay eggs.
The satellite nests are connected to the main nest by underground tunnels, allowing the ants to move between them.
Overall, crypt ants are fascinating insects that have developed a unique way of obtaining food.
Their symbiotic relationship with fungi and their complex nesting behavior make them an important species to study in the field of entomology.
34) Moisture Ants, Lasius

Moisture ants are a type of ant that is commonly found in damp environments.
They are known for their ability to thrive in areas with high levels of moisture, such as in rotting wood or in soil that is constantly moist.
These ants are typically small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length, and are usually yellow or brown in color.
Moisture ants are social insects that live in colonies, with each colony consisting of a queen, workers, and soldiers.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers and soldiers are responsible for maintaining the colony and protecting it from predators.
One of the unique characteristics of moisture ants is their ability to create satellite colonies.
These colonies are established in nearby locations and are connected to the main colony by a network of tunnels.
This allows the ants to expand their territory and increase their chances of survival.
Moisture ants are also known for their ability to control the moisture levels in their environment.
They do this by building intricate nests that are designed to regulate the humidity levels inside.
This is important for the survival of the colony, as too much moisture can lead to the growth of harmful fungi and bacteria.
Overall, moisture ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted to thrive in environments that would be inhospitable to many other species.
Their ability to control moisture levels and create satellite colonies makes them a formidable force in their ecosystem.
35) Lenomyrmex
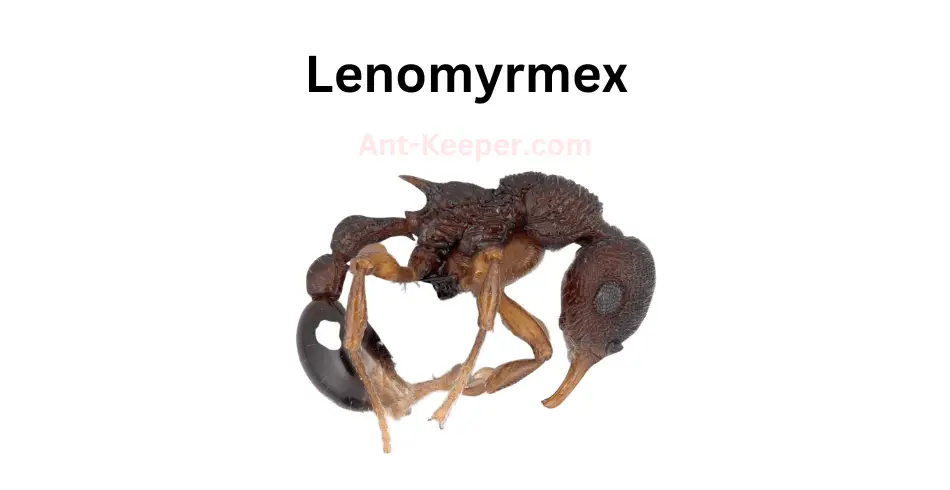

Lenomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a long and slender body, elongated mandibles, and a distinctive head shape.
The genus is relatively small, with only a few known species.
Lenomyrmex ants are typically found in forested areas, where they nest in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be aggressive predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other arthropods.
These ants are also known to exhibit a high degree of social organization, with colonies consisting of hundreds or even thousands of individuals.
One of the most interesting aspects of Lenomyrmex ants is their reproductive behavior.
Unlike many other ant species, Lenomyrmex queens do not mate with multiple males.
Instead, they mate with a single male and then store his sperm in a specialized organ called the spermatheca.
This allows the queen to fertilize eggs over a long period of time, without the need for repeated matings.
Overall, Lenomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that offer a unique glimpse into the complex world of social insects.
Their distinctive morphology, predatory behavior, and reproductive strategies make them a valuable subject of study for entomologists and other researchers.
36) Leptanilla

Leptanilla is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Leptanillinae.
These ants are known for their small size and subterranean lifestyle.
They are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they live in soil and leaf litter.
Leptanilla ants are unique in their morphology, with elongated bodies and long, slender legs.
They have small eyes and lack the ability to sting, relying instead on their powerful mandibles to defend themselves.
These ants are also known for their unusual behavior, with some species exhibiting a caste system where workers are divided into "major" and "minor" forms.
Despite their small size, Leptanilla ants play an important role in their ecosystems.
They are known to feed on small invertebrates and help to aerate soil through their burrowing activities.
Some species have also been observed engaging in mutualistic relationships with other insects, such as termites and beetles.
Due to their subterranean lifestyle, Leptanilla ants are not often encountered by humans.
However, they are of interest to researchers studying the evolution and behavior of social insects.
Their unique morphology and behavior make them a fascinating subject for scientific study.
37) Leptanilloides

Leptanilloides is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dorylinae.
These ants are known for their small size and cryptic behavior, making them difficult to study in the wild.
The genus is characterized by their elongated mandibles, which are used for capturing prey and defending the colony.
Leptanilloides ants are typically found in tropical regions, where they inhabit leaf litter and soil.
They are known to form small colonies, with only a few hundred individuals.
The colonies are typically headed by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony.
One interesting aspect of Leptanilloides ants is their behavior towards other ant species.
They are known to be highly aggressive towards other ants, and will attack and kill any intruders that enter their territory.
This behavior is thought to be a result of competition for resources, as Leptanilloides ants rely heavily on small arthropods for food.
Despite their small size and cryptic behavior, Leptanilloides ants play an important role in their ecosystems.
They help to control populations of small arthropods, and their aggressive behavior towards other ants may help to maintain balance in ant communities.
Further research is needed to fully understand the ecology and behavior of these fascinating ants.
38) Razorjaw Ants, Leptogenys

The Razorjaw Ant, also known as the Pachycondyla villosa, is a species of ant belonging to the subfamily Ponerinae.
These ants are known for their sharp mandibles, which are used for hunting and defense.
The workers of this species are typically around 8-10mm in length, while the queen can reach up to 15mm.
Razorjaw Ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be aggressive predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other arthropods.
These ants are also known to scavenge for food, and will even attack and kill other ant species to steal their food.
The nests of Razorjaw Ants are typically found in soil or leaf litter, and can be quite large.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, and the workers are responsible for caring for the brood and maintaining the nest.
These ants are also known for their ability to defend their nest, and will aggressively attack any intruders.
Overall, the Razorjaw Ant is a fascinating species of ant known for its sharp mandibles, aggressive behavior, and impressive hunting skills.
39) Leptothorax
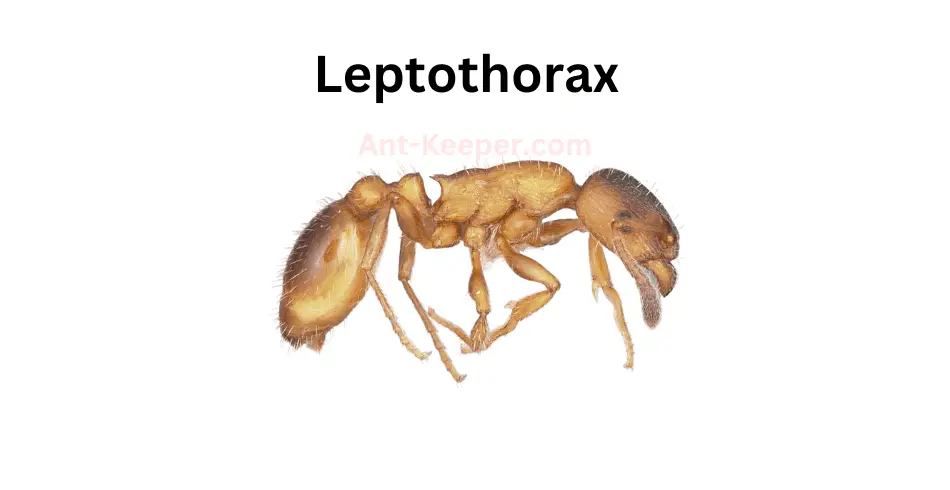

Leptothorax is a genus of ants that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are small in size, measuring between 2 to 4 millimeters in length.
They are commonly found in forests, grasslands, and other natural habitats.
Leptothorax ants are known for their social behavior, as they live in colonies that can range from a few dozen to several hundred individuals.
These ants have a hierarchical social structure, with a queen ant at the top and worker ants at the bottom.
The queen ant is responsible for laying eggs, while the worker ants take care of the young, gather food, and defend the colony from predators.
One interesting feature of Leptothorax ants is their ability to form temporary colonies with other ant species.
This behavior is known as "temporary social parasitism," and it allows Leptothorax ants to benefit from the resources of other ant colonies without having to invest in their own colony infrastructure.
Leptothorax ants are also known for their ability to navigate through complex environments.
They use a combination of visual cues and chemical signals to find their way back to the colony after foraging for food.
Overall, Leptothorax ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystems.
Their social behavior and navigational abilities make them a subject of interest for scientists studying animal behavior and ecology.
40) Lordomyrma
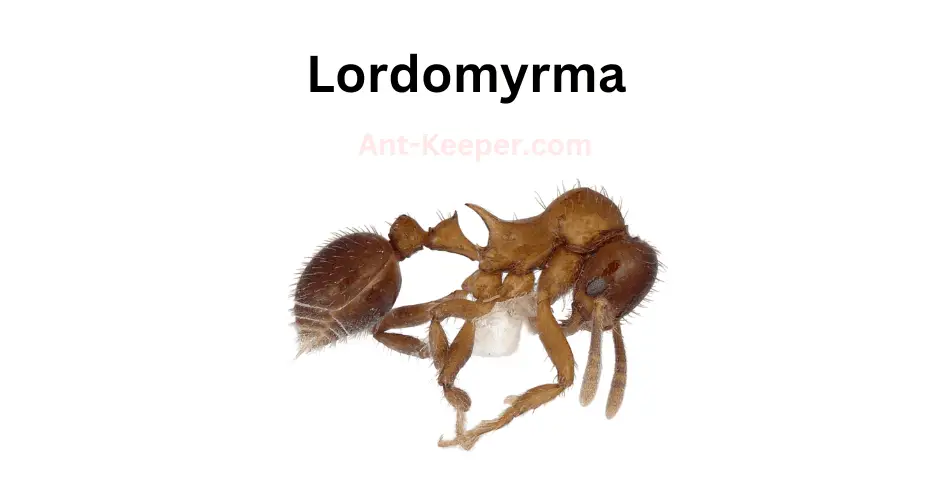
Lordomyrmabe is a genus of ants belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics and behavior.
They are small in size, measuring between 2-3 mm in length, and have a distinctively elongated head and mandibles.
The workers of this genus are polymorphic, meaning they come in different sizes and shapes.
Lordomyrmabe ants are known to be arboreal, meaning they live in trees and other elevated structures.
They are also known to be aggressive and territorial, often engaging in battles with other ant species for resources and territory.
These ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
One of the most interesting aspects of Lordomyrmabe ants is their reproductive behavior.
The queen ant is known to mate with multiple males, resulting in a genetically diverse colony.
The queen is also capable of reproducing asexually, producing clones of herself.
Overall, Lordomyrmabe ants are fascinating creatures with unique physical and behavioral characteristics.
Their arboreal lifestyle, aggressive behavior, and reproductive strategies make them a fascinating subject for scientific study.
41) Manica

The Manicabe ant, also known as the scientific name Manica rubida, is a species of ant that belongs to the Formicidae family.
These ants are known for their reddish-brown color and their aggressive behavior towards other ant species.
Manicabe ants are typically found in forested areas and are known to build their nests in soil or under rocks.
They are also known to be highly territorial and will defend their nests aggressively against any intruders.
One interesting behavior of the Manicabe ant is their ability to form large raiding parties.
These raids are typically carried out against other ant species and are known to be highly coordinated and efficient.
The ants will work together to overwhelm their opponents and steal their food and resources.
Manicabe ants are also known for their unique communication system.
They use a combination of chemical signals and physical cues to communicate with each other and coordinate their activities.
This communication system allows them to work together effectively and efficiently, even in large groups.
Overall, the Manicabe ant is a fascinating species that exhibits a wide range of interesting behaviors and adaptations.
Their aggressive nature and unique communication system make them a fascinating subject for scientific study.
42) Megalomyrmex

Megalomyrmex is a genus of ants belonging to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their large size and aggressive behavior.
The workers of Megalomyrmex are typically between 5-10 mm in length, with the queen being even larger.
They have a distinctive appearance, with a broad head and mandibles that are used for hunting and defense.
Megalomyrmex ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be opportunistic predators, feeding on a wide range of insects and other small animals.
They are also known to engage in symbiotic relationships with other insects, such as aphids and mealybugs, which they protect in exchange for a sugary secretion known as honeydew.
One of the most interesting aspects of Megalomyrmex ants is their social behavior.
They are highly organized, with a complex caste system that includes workers, soldiers, and a queen.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers and soldiers are responsible for maintaining the nest and defending it from predators.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Megalomyrmex ants are not considered to be a major pest species.
They are generally beneficial to the ecosystem, playing an important role in controlling insect populations and contributing to soil health.
However, they can become a nuisance if they invade homes or other structures in search of food or shelter.
Overall, Megalomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that have much to teach us about the complexities of social behavior and the importance of insects in the natural world.
43) Harvester Ants, Messor

Harvester ants are a type of ant that belongs to the genus Pogonomyrmex.
They are known for their impressive ability to collect and store seeds, which they use as their primary source of food.
These ants are typically found in arid and semi-arid regions, where they play an important role in the ecosystem by dispersing seeds and aerating the soil.
Harvester ants are social insects that live in large colonies, which can contain thousands of individuals.
The colony is typically headed by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the social structure of the colony.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, nest maintenance, and caring for the young.
One of the most impressive features of harvester ants is their ability to navigate long distances to find food.
They use a combination of visual cues and chemical signals to locate and retrieve seeds, which they then bring back to the nest.
Once inside the nest, the seeds are stored in underground chambers, where they are protected from predators and other environmental factors.
Harvester ants are also known for their aggressive behavior, particularly when it comes to defending their nest and food sources.
They have powerful mandibles that they use to bite and sting potential threats, including humans.
As a result, it is important to exercise caution when encountering these ants in the wild.
Overall, harvester ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their ability to collect and store seeds, navigate long distances, and defend their colony make them a formidable force in the world of insects.
44) Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Monomorium

The Trailing Pharaoh ant, also known as the Monomorium pharaonis, is a small, reddish-brown ant species that is commonly found in urban areas.
These ants are known for their ability to form large colonies, which can consist of thousands of individuals.
One interesting behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant is their tendency to trail behind other ants.
This behavior is thought to be a form of communication, as the trailing ants are able to follow the scent trail left by the leading ants.
This behavior is also used to locate food sources, as the trailing ants are able to follow the trail to the source of the food.
In contrast to the bold behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant, the Timid ant, also known as the Temnothorax species, is a much more cautious species.
These ants are small and brown, and are often found in wooded areas.
They are known for their timid behavior, and will often retreat into their nests when threatened.
Despite their timid nature, the Timid ant is still able to form large colonies.
They are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, meadows, and even urban areas.
Overall, both the Trailing Pharaoh ant and the Timid ant are fascinating species that demonstrate unique behaviors and adaptations.
By studying these ants, scientists can gain a better understanding of the complex social behaviors and ecological roles of ants in their respective environments.
45) Mite-Eating Ants, Myrmecina

The Mite-Eating Ant, also known as the Pheidole megacephala, is a species of ant that is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
These ants are known for their unique feeding habits, as they primarily feed on mites and other small arthropods.
The Mite-Eating Ant is a relatively small ant, with workers measuring between 2-3mm in length.
They have a distinctive head shape, with a large and elongated head that is almost as wide as their thorax.
Their bodies are typically a reddish-brown color, with darker legs and antennae.
These ants are highly social, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colonies are typically divided into two groups: workers and reproductive individuals.
The workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony, while the reproductive individuals are responsible for producing offspring.
One of the most interesting aspects of the Mite-Eating Ant is their feeding habits.
These ants are specialized predators, feeding almost exclusively on mites and other small arthropods.
They use their large mandibles to capture and kill their prey, and then carry it back to the colony to be consumed.
In addition to their unique feeding habits, the Mite-Eating Ant is also known for its ability to adapt to a wide range of environments.
They are able to thrive in both natural and urban environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and even in homes and buildings.
Overall, the Mite-Eating Ant is a fascinating species of ant that has adapted to a unique niche in the ecosystem.
Their specialized feeding habits and ability to thrive in a variety of environments make them an important species to study and understand.
46) Furrowed Ants, Myrmica

Furrowed ants, also known as Pheidole ruginoda, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are commonly found in various habitats such as forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known for their distinctive appearance, with a furrowed head and thorax, and a smooth and shiny abdomen.
Furrowed ants are social insects that live in colonies, which can range in size from a few hundred to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically headed by a queen ant, whose primary role is to lay eggs.
The workers, which are sterile females, are responsible for foraging, nest maintenance, and caring for the young.
These ants are omnivorous, meaning they feed on both plant and animal matter.
Their diet consists of seeds, insects, and other small invertebrates.
They are also known to tend to aphids, which produce a sugary substance that the ants feed on.
Furrowed ants are known for their aggressive behavior, and will defend their colony fiercely against intruders.
They have been observed engaging in territorial battles with other ant species, and will even attack larger insects such as grasshoppers and beetles.
Overall, furrowed ants are an important part of many ecosystems, playing a crucial role in seed dispersal and soil aeration.
Their unique appearance and behavior make them a fascinating subject for study and observation.
47) Myrmicocrypta
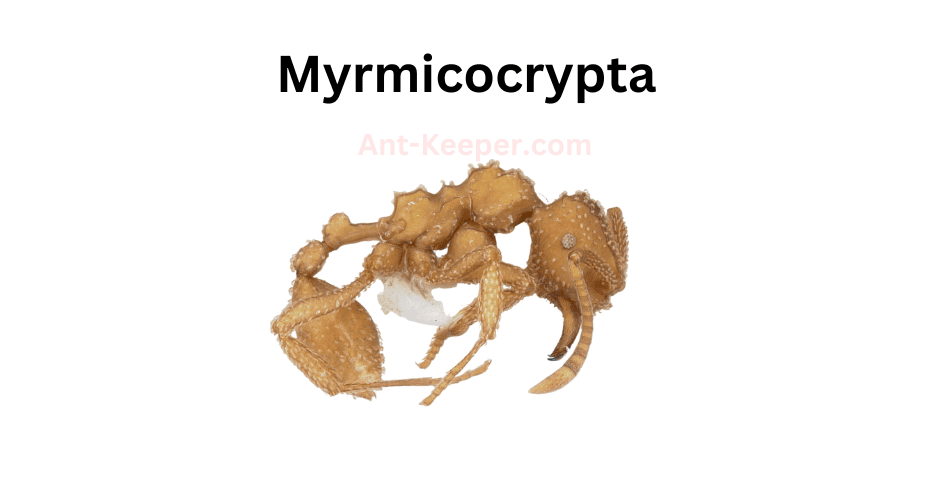
Myrmicocrypta is a genus of ants that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their cryptic behavior, which means they are very good at hiding and avoiding detection.
The name Myrmicocrypta is derived from the Greek words "myrmico" meaning ant and "crypta" meaning hidden or concealed.
The ants of the Myrmicocrypta genus are small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
These ants are known for their ability to live in small colonies, which typically consist of a queen and a few workers.
One of the most interesting aspects of Myrmicocrypta ants is their nesting behavior.
These ants are known for nesting in small crevices and cracks in rocks, trees, and other natural structures.
They are also known to nest in the soil, where they create small tunnels and chambers.
Myrmicocrypta ants are omnivorous, which means they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on small insects, nectar, and honeydew.
These ants are also known to tend to aphids, which produce honeydew that the ants feed on.
Overall, Myrmicocrypta ants are fascinating creatures that are well adapted to their environment.
Their cryptic behavior and nesting habits make them difficult to study, but researchers continue to learn more about these ants and their unique behaviors.
48) Crazy Ants, Nylanderia

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
49) Ochetellus

Ochetellus is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dolichoderinae.
These ants are small in size, measuring between 2-5 mm in length.
They are known for their distinctive appearance, with a slender and elongated body that is covered in fine hairs.
The head of Ochetellus ants is also elongated, with large mandibles that are used for hunting and defense.
Ochetellus ants are social insects that live in colonies.
The colonies are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Ochetellus ants are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to tend to aphids, which produce honeydew that the ants feed on.
Ochetellus ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be particularly abundant in areas with sandy soils.
These ants are important members of their ecosystems, playing a role in seed dispersal and soil health.
Overall, Ochetellus ants are fascinating insects that are well adapted to their environments.
Their unique appearance and behavior make them a popular subject of study for entomologists and nature enthusiasts alike.
50) Trap-Jaw Ants, Odontomachus

Trap-jaw ants are a species of ants that belong to the genus Odontomachus.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The mandibles of trap-jaw ants are capable of closing at incredible speeds, reaching up to 140 miles per hour.
This allows them to snap their jaws shut with incredible force, which can stun or kill their prey.
Trap-jaw ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically active during the day and are known to be highly territorial.
These ants are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to escape danger or to capture prey.
Trap-jaw ants are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on a variety of insects, including other ants, as well as nectar and other sweet substances.
These ants are also known to be scavengers, feeding on dead insects and other organic matter.
The colonies of trap-jaw ants are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
However, they are highly organized and have a strict social hierarchy.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, trap-jaw ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their environments.
Their powerful mandibles and jumping abilities make them formidable predators, while their social organization allows them to work together to protect their colonies and ensure their survival.
51) Crazy Ants, Paratrechina

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
52) Parvaponera
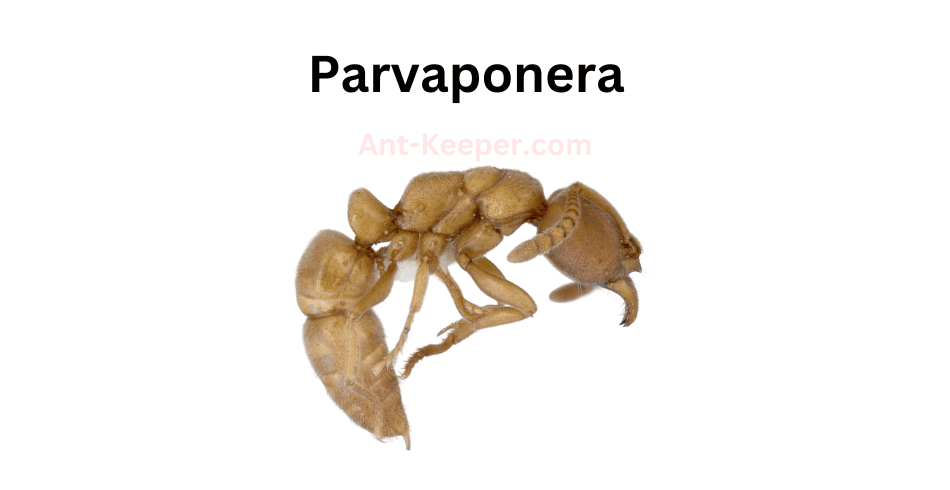

Parvaponerabe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
It is a relatively small ant, with workers measuring around 4-5 millimeters in length.
The ant has a dark brown or black coloration, with a shiny exoskeleton that is covered in fine hairs.
Parvaponerabe ants are known for their aggressive behavior and are often found in large colonies.
They are primarily ground-dwelling ants, but can also be found in trees and other vegetation.
The ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, fruits, and seeds.
One unique characteristic of Parvaponerabe ants is their ability to produce formic acid, which they use as a defense mechanism against predators.
When threatened, the ants will release the formic acid from their bodies, which can cause irritation and pain to potential predators.
Parvaponerabe ants are also known for their social behavior, with a clear division of labor among the different members of the colony.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, Parvaponerabe ants are an important part of many ecosystems, playing a key role in controlling insect populations and contributing to soil health.
53) Big Headed Ants, Pheidole

Big Headed Ants, also known as Pheidole megacephala, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive large heads, which are used for defense and communication within their colonies.
Big Headed Ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, seeds, and other small organisms.
One of the most interesting aspects of Big Headed Ants is their social behavior.
They live in large colonies, with a queen ant at the center of the hierarchy.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony perform various tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
Big Headed Ants are also known for their ability to displace other ant species in their habitats.
They are aggressive and have been known to attack and kill other ants, as well as compete with them for resources.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Big Headed Ants are not considered a major pest species.
However, their ability to displace other ant species and their potential impact on native ecosystems make them an important species to study and monitor.
54) Pheidologeton

Pheidologeton is a genus of ants belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are commonly known as weaver ants due to their unique ability to construct nests by weaving leaves together using silk produced by their larvae.
Pheidologeton ants are found in tropical regions and are known for their aggressive behavior and large colony sizes.
The workers of Pheidologeton ants are polymorphic, meaning they come in different sizes and perform different tasks within the colony.
The smaller workers are responsible for foraging and caring for the brood, while the larger workers defend the colony and construct the nests.
Pheidologeton ants are also known for their ability to form supercolonies, where multiple nests are connected and function as a single unit.
Pheidologeton ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, nectar, and other plant materials.
They are also known to engage in mutualistic relationships with other insects, such as scale insects and aphids, which provide them with honeydew in exchange for protection.
Overall, Pheidologeton ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and adaptations that allow them to thrive in their tropical habitats.
55) Restless Ants, Plagiolepis

Restless Ants, also known as the Red Ants, are a species of ants that belong to the Formicidae family.
They are known for their highly active and restless behavior, constantly moving around in search of food and resources.
These ants are typically small in size, measuring around 2-3 mm in length.
They have a reddish-brown coloration and a slender body shape, with long legs and antennae.
Restless Ants are social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
Restless Ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, fruits, and seeds.
They are also known to scavenge for food, often raiding the nests of other ant species to steal their resources.
One of the most interesting aspects of Restless Ants is their ability to adapt to changing environments.
They are able to quickly adjust their behavior and foraging patterns in response to changes in their surroundings, such as changes in temperature or the availability of food.
Restless Ants are also known for their aggressive behavior, particularly when defending their nests or resources.
They have powerful mandibles that they use to bite and defend themselves against predators or other ants.
Overall, Restless Ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their highly active and adaptable behavior makes them a valuable species to study and understand.
56) Amazon Ants, Polyergus
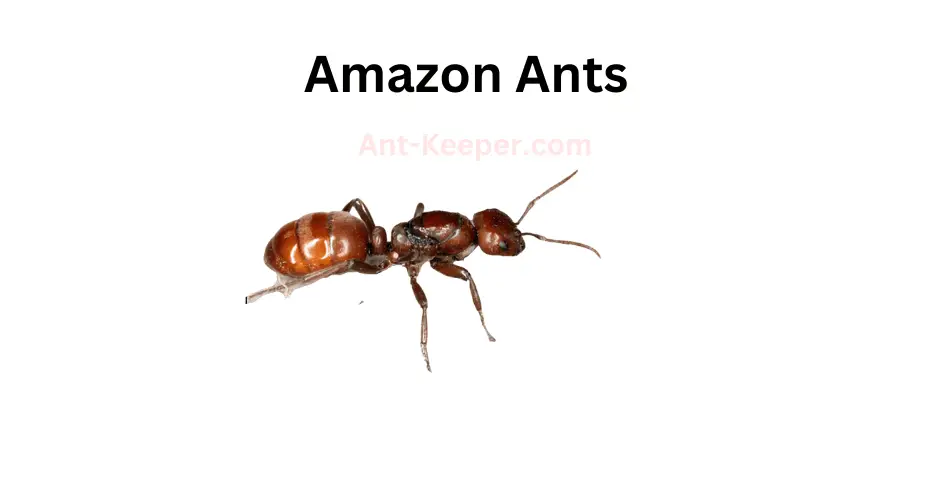

The Amazon Ant, also known as the Polyergus breviceps, is a species of ant that belongs to the Formicidae family.
These ants are known for their unique behavior of raiding other ant colonies and stealing their brood to raise as their own.
The Amazon Ants are typically black or dark brown in color and have a slender body with long legs.
They are relatively small in size, with workers measuring around 4-5 mm in length.
The queen ants are slightly larger, measuring around 7-8 mm in length.
These ants are social insects and live in large colonies that can consist of thousands of individuals.
The colonies are usually divided into different castes, including workers, soldiers, and reproductive ants.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the brood, and maintaining the nest, while the soldiers defend the colony from predators.
One of the most interesting aspects of the Amazon Ants is their unique behavior of raiding other ant colonies.
They do this by sending out a group of specialized workers, known as raiders, to infiltrate the target colony.
The raiders then steal the brood of the target colony and bring it back to their own nest.
Once the stolen brood hatches, the Amazon Ants use it to increase their own workforce.
The Amazon Ants are also known for their symbiotic relationship with a species of butterfly known as the Maculinea rebeli.
The butterfly larvae feed on the brood of the Amazon Ants, but in return, they secrete a substance that makes the ants more aggressive and better at raiding other colonies.
Overall, the Amazon Ants are fascinating creatures with unique behaviors and adaptations that allow them to thrive in their environment.
57) Spiny Ants, Polyrhachis

Spiny ants, also known as Polyrhachis sp., are a species of ants that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique appearance, with spines covering their bodies that serve as a form of protection against predators.
Spiny ants are typically black or dark brown in color and range in size from 4 to 10 millimeters in length.
They are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and will defend their nests fiercely.
Spiny ants are omnivores, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to tend to aphids, protecting them from predators in exchange for the sweet honeydew they produce.
These ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
Spiny ants play an important role in their ecosystems, serving as both predators and prey.
They help to control the populations of other insects and provide food for larger animals such as birds and reptiles.
Overall, spiny ants are a fascinating species of ants that are known for their unique appearance and aggressive behavior.
They play an important role in their ecosystems and are an important part of the natural world.
58) Porthole Ants, Ponera

Porthole ants, also known as Temnothorax spp., are a genus of small ants that are commonly found in forested areas.
These ants are known for their unique nesting behavior, as they create their nests in small cavities or "portholes" in trees, rocks, or other natural structures.
Porthole ants are typically less than 5mm in length and have a dark brown or black coloration.
They are social insects and live in colonies that can range from a few dozen to several hundred individuals.
The colonies are typically led by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's reproductive population.
One of the most interesting aspects of porthole ants is their nesting behavior.
Unlike many other ant species, porthole ants do not create large underground nests.
Instead, they seek out small cavities in natural structures and use them as their nesting sites.
These cavities can be as small as a few millimeters in diameter and are often located high up in trees or on rocky outcroppings.
Porthole ants are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
They are able to quickly relocate their nests if their current nesting site becomes unsuitable due to factors such as flooding or predation.
This adaptability allows them to thrive in a variety of habitats, from temperate forests to arid deserts.
Overall, porthole ants are a fascinating and unique species of ant that have adapted to their environment in a variety of ways.
Their nesting behavior and adaptability make them an important species to study for understanding the ecology of forested areas.
59) Winter Ants, Prenolepis

Winter ants, also known as Formica exsectoides, are a species of ant that are commonly found in temperate regions.
These ants are known for their ability to survive harsh winter conditions, which is where they get their name from.
Winter ants are typically black or dark brown in color and can range in size from 4 to 8 millimeters in length.
They are social insects and live in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
These colonies are typically located underground, where the ants construct elaborate tunnels and chambers.
One of the most interesting things about winter ants is their ability to survive the cold winter months.
Unlike many other ant species, winter ants do not hibernate during the winter.
Instead, they have developed a number of adaptations that allow them to survive in the cold.
One of these adaptations is the ability to regulate their body temperature.
Winter ants are able to generate heat by shivering their muscles, which allows them to maintain a temperature of around 25 degrees Celsius even when the outside temperature drops below freezing.
Winter ants also have a unique diet that helps them survive the winter.
They feed on the honeydew produced by aphids, which is a sugary substance that provides them with the energy they need to survive.
Overall, winter ants are a fascinating species of ant that have adapted to survive in some of the harshest conditions on earth.
Their ability to regulate their body temperature and feed on a unique diet make them a truly remarkable species.
60) Pristomyrmex
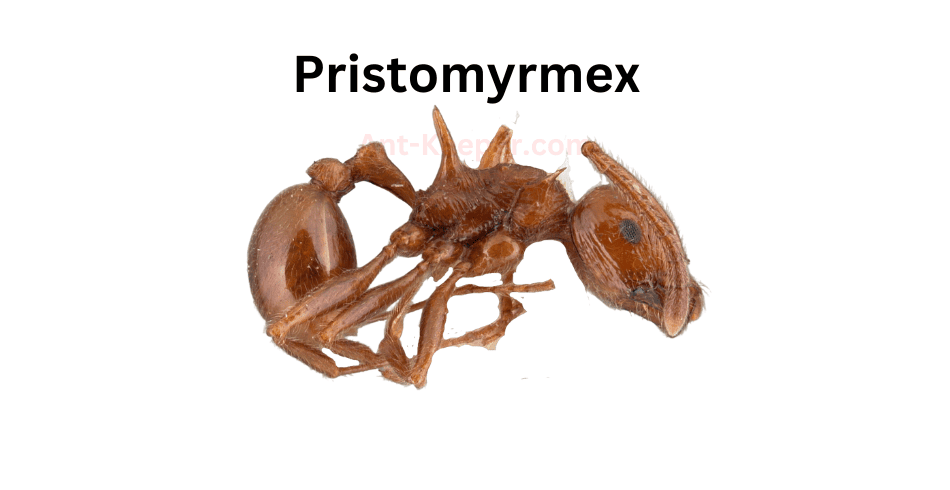

Pristomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
The ants in this genus are small in size, measuring between 2-4mm in length.
They are known for their distinctive appearance, with a slender and elongated body shape, and a narrow waist that separates the thorax and abdomen.
Pristomyrmex ants are typically found in forested areas, where they nest in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be aggressive predators, feeding on other insects and small invertebrates.
They are also known to have a mutualistic relationship with certain plant species, where they protect the plants from herbivores in exchange for food and shelter.
One species of Pristomyrmex, Pristomyrmex punctatus, is known for its unique behavior of "playing dead" when threatened.
When disturbed, these ants will curl up their legs and antennae and remain motionless, resembling a dead insect.
This behavior is thought to be a defense mechanism against predators.
Overall, Pristomyrmex ants are an important part of forest ecosystems, playing a role in both predation and mutualism.
Their unique appearance and behavior make them an interesting subject for study and observation.
61) Probolomyrmex

Probolomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Proceratiinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a long and slender body, a narrow head, and elongated mandibles.
The genus is characterized by the presence of a distinct petiole, which separates the thorax and the abdomen.
Probolomyrmex ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be highly aggressive and territorial, often engaging in fierce battles with other ant species.
One of the most interesting aspects of Probolomyrmex ants is their social behavior.
These ants are known to be highly organized, with a well-defined caste system that includes workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals.
The workers are responsible for foraging, nest maintenance, and caring for the young, while the soldiers defend the colony against predators and other threats.
Despite their small size, Probolomyrmex ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They are known to be efficient predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other small invertebrates.
They also help to aerate the soil and distribute nutrients, which can have a positive impact on plant growth.
Overall, Probolomyrmex ants are a fascinating and important group of insects that are worthy of further study and conservation efforts.
62) Hairy Curltail Ants, Proceratium

The Hairy Curltail Ant (Camponotus pilicornis) is a species of ant belonging to the genus Camponotus.
These ants are known for their distinctive hairy appearance, which covers their entire body.
The hairs on their body are long and curly, giving them a unique and striking appearance.
Hairy Curltail Ants are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in dead wood or under rocks.
They are known to be highly territorial and will aggressively defend their nests against intruders.
These ants are also known to be omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
The Hairy Curltail Ant is a relatively large ant species, with workers measuring between 6-12mm in length.
The queen ant is even larger, measuring up to 15mm in length.
These ants are also known for their strong mandibles, which they use to defend their nests and capture prey.
One interesting aspect of the Hairy Curltail Ant is their ability to communicate with each other through the use of pheromones.
These chemical signals are used to mark trails, identify nestmates, and coordinate foraging activities.
Overall, the Hairy Curltail Ant is a fascinating species of ant with a unique appearance and interesting behaviors.
Their presence in forested areas can have important ecological implications, as they play a role in the ecosystem as both predators and scavengers.
63) Protalaridris
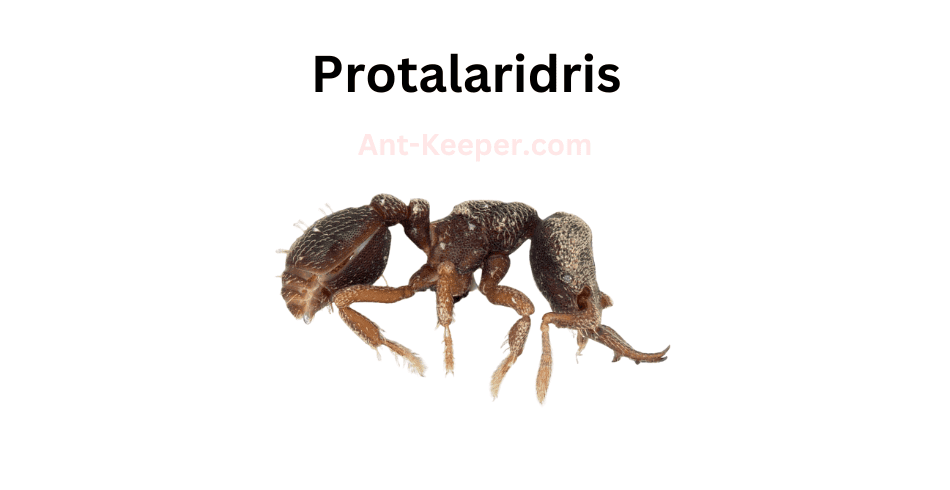
Protalaridrisbe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They are known for their unique physical characteristics, including their elongated mandibles and slender bodies.
Protalaridrisbe ants are typically found in forested areas, where they live in small colonies.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and will defend their territory fiercely against other ant species.
These ants are also known for their ability to climb trees and other vertical surfaces, which allows them to forage for food in a variety of different environments.
One of the most interesting aspects of Protalaridrisbe ants is their reproductive behavior.
Unlike many other ant species, these ants do not have a queen.
Instead, they rely on a system of multiple reproductive females, known as gamergates, to produce offspring.
These gamergates are able to mate with males and lay eggs, ensuring the survival of the colony.
Overall, Protalaridrisbe ants are a fascinating species that have adapted to thrive in a variety of different environments.
Their unique physical characteristics and reproductive behavior make them a subject of interest for researchers and ant enthusiasts alike.
64) Protanilla

Protanillabe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics and behavior.
They are small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length, and have a dark brown or black coloration.
The workers of this species are known to be highly aggressive and territorial, often engaging in fierce battles with other ant colonies.
Protanillabe ants are primarily found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
These ants are also known to have a symbiotic relationship with certain species of plants, where they protect the plants from herbivores in exchange for food and shelter.
One of the most interesting aspects of Protanillabe ants is their reproductive behavior.
The queen ant is responsible for laying eggs, which hatch into larvae that are cared for by worker ants.
Once the larvae mature, they develop into either workers or reproductive ants.
The reproductive ants are winged and leave the nest to mate with ants from other colonies.
After mating, the female ants shed their wings and return to the nest to start their own colony.
Overall, Protanillabe ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their aggressive behavior and symbiotic relationships with plants make them a unique and important species to study.
65) Recurvidris
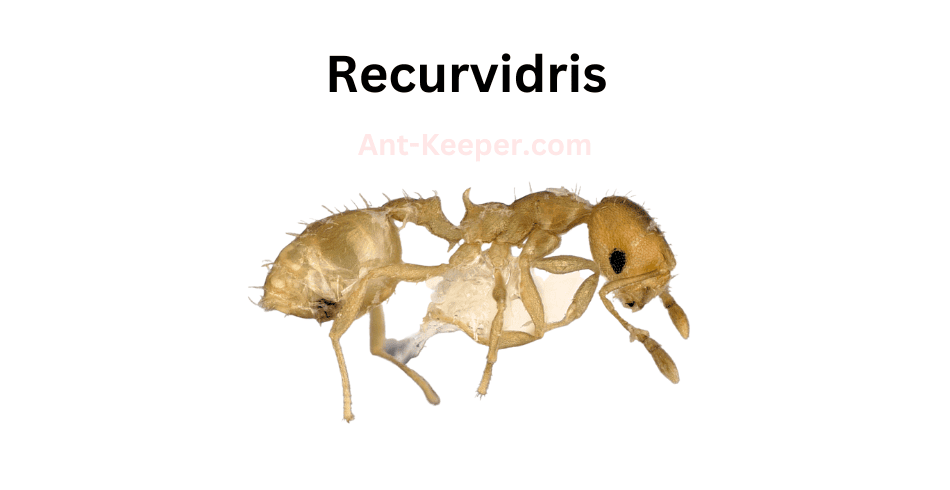
Recurvidrisbe is a species of ant that belongs to the Formicidae family.
These ants are known for their small size, typically measuring between 1.5 and 2.5 millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Recurvidrisbe ants are commonly found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be highly social insects, living in colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
Within these colonies, there is a clear division of labor, with different ants taking on specific roles such as foraging, caring for the young, and defending the nest.
One interesting aspect of Recurvidrisbe ants is their ability to communicate with each other through the use of pheromones.
These chemical signals are used to mark trails, identify nestmates, and coordinate group activities.
Recurvidrisbe ants are also known for their aggressive behavior, particularly when defending their nest from predators or other ant species.
Overall, Recurvidrisbe ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their social behavior and communication strategies make them a valuable subject of study for scientists interested in understanding the behavior of social insects.
66) Rhopalomastix
Rhopalomastix is a species of ant belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their small size, typically measuring between 2-3 millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape with long legs and antennae.
Rhopalomastix ants are commonly found in forested areas and are known to nest in soil or leaf litter.
They are also known to be arboreal, meaning they can climb trees and other vegetation.
These ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
One unique characteristic of Rhopalomastix ants is their ability to produce formic acid as a defense mechanism.
When threatened, these ants will release formic acid from their bodies, which can deter predators and other threats.
Rhopalomastix ants are also known for their social behavior, living in colonies with a queen and workers.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, Rhopalomastix ants are an important part of forest ecosystems, playing a role in nutrient cycling and serving as a food source for other organisms.
67) Sericomyrmex

Sericomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
These ants are known for their unique symbiotic relationship with fungi, which they cultivate in underground gardens.
The ants feed on the fungus, and in turn, the fungus benefits from the ants' care and protection.
Sericomyrmex ants are small in size, with workers measuring between 2 and 4 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive appearance, with elongated heads and mandibles that are adapted for cutting and carrying plant material.
The ants are typically reddish-brown in color, with some species having darker or lighter markings on their bodies.
One of the most interesting aspects of Sericomyrmex ants is their social structure.
These ants live in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colony is headed by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the population.
Workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and tending to the fungus gardens.
Sericomyrmex ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are most commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions, where the climate is warm and humid.
These ants play an important role in their ecosystems, as they help to break down plant material and recycle nutrients.
Overall, Sericomyrmex ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their environments.
Their symbiotic relationship with fungi is a testament to the complex interactions that occur in nature, and studying these ants can provide valuable insights into the workings of ecosystems.
68) Fire Ants, Solenopsis

Fire ants are a type of ant that belongs to the Solenopsis genus.
They are known for their reddish-brown color and their aggressive behavior.
Fire ants are social insects that live in colonies, which can range in size from a few hundred to several thousand individuals.
Fire ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of foods, including insects, seeds, and other small animals.
They are also known to scavenge for food and will often invade other ant colonies to steal their resources.
One of the most distinctive features of fire ants is their ability to sting.
They have a stinger located at the end of their abdomen, which they use to inject venom into their prey or enemies.
Fire ant stings can be painful and can cause an allergic reaction in some people.
Fire ants are also known for their ability to build large mounds, which can reach heights of up to 18 inches.
These mounds are made of soil and are used as a nesting site for the colony.
Fire ants are considered to be an invasive species in many parts of the world, as they can cause damage to crops and wildlife.
They are also a nuisance to humans, as their stings can be painful and their mounds can be unsightly.
Overall, fire ants are fascinating insects that have adapted to thrive in a variety of environments.
While they can be a nuisance, they are an important part of the ecosystem and play a vital role in controlling insect populations.
69) Leaf-Litter Ants, Stenamma

Leaf-litter ants are a group of ants that are commonly found in forested areas around the world.
They are known for their ability to live and forage in the leaf litter layer of the forest floor, where they play an important role in nutrient cycling and soil health.
Leaf-litter ants are typically small in size, ranging from 1-5mm in length.
They are often reddish-brown or black in color, and have a slender, elongated body shape.
These ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
One of the key characteristics of leaf-litter ants is their ability to forage for food in the leaf litter layer.
They are known to feed on a variety of organic matter, including dead insects, fungi, and plant material.
Leaf-litter ants are also important decomposers, breaking down organic matter and returning nutrients to the soil.
In addition to their role in nutrient cycling, leaf-litter ants also play an important role in the ecosystem as prey for other animals.
They are a food source for a variety of predators, including birds, reptiles, and other insects.
Overall, leaf-litter ants are an important and fascinating group of insects that play a critical role in maintaining the health and functioning of forest ecosystems around the world.
70) Vampire Ants, Stigmatomma

Vampire ants, also known as blood-sucking ants, are a species of ants that feed on the blood of other insects.
These ants are known for their unique feeding behavior, which involves biting into the exoskeleton of their prey and then sucking out their blood.
Vampire ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they live in colonies of up to several thousand individuals.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and will attack other insects, including larger prey such as grasshoppers and caterpillars.
One of the most interesting aspects of vampire ants is their ability to adapt to their environment.
In some cases, these ants have been known to feed on the blood of their own colony members when other sources of food are scarce.
Vampire ants are also known for their unique physical characteristics.
They have long, curved mandibles that are used to bite into the exoskeleton of their prey.
They also have specialized mouthparts that allow them to suck out the blood of their victims.
Despite their aggressive behavior and blood-sucking tendencies, vampire ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They help to control the populations of other insects and contribute to the overall balance of their environment.
Overall, vampire ants are a fascinating species of ants that have adapted to their environment in unique and interesting ways.
Their behavior and physical characteristics make them a subject of interest for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
71) Strongylognathus

Strongylognathus is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Myrmicinae.
The ants in this genus are small in size, measuring between 2 to 3 millimeters in length.
They are known for their distinctive mandibles that are long and slender, which they use to capture prey and defend their colony.
The Strongylognathus ants are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be highly territorial and aggressive towards other ant species that invade their territory.
The ants in this genus are also known to be omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
One of the most interesting features of the Strongylognathus ants is their ability to communicate with each other through the use of pheromones.
These chemical signals are used to mark trails, identify nestmates, and coordinate foraging activities.
The ants in this genus are also known to exhibit a high degree of social organization, with a clear division of labor among the different castes.
Overall, the Strongylognathus ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their unique physical and behavioral characteristics make them a subject of interest for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
72) Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Strumigenys

The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, scientifically known as Odontomachus sp., are a species of ants that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are relatively small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Their most distinctive feature is their mandibles, which are elongated and can snap shut with incredible force.
These mandibles are used to capture prey, crush seeds, and defend the colony against predators.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be active during the day and are often seen foraging for food.
These ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and seeds.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are social insects and live in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, the Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are fascinating insects that have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their environment.
Their powerful mandibles and social behavior make them an important part of many ecosystems.
73) Tapinoma

Tapinoma is a genus of ants that belongs to the family Formicidae.
The species Tapinoma is a small ant that measures about 2-3 mm in length.
They are commonly found in urban and suburban areas, and are known to invade homes and buildings in search of food and shelter.
Tapinoma ants are light brown in color and have a slender body with long legs.
They have a distinctively shaped head that is wider than their thorax, and they possess a pair of antennae that are bent at a right angle.
These ants are known for their ability to form large colonies, which can consist of thousands of individuals.
Tapinoma ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to scavenge for food in garbage cans and other waste areas.
These ants are attracted to sweet and sugary substances, and will often invade kitchens and pantries in search of food.
Tapinoma ants are not known to be aggressive towards humans, but they can become a nuisance when they invade homes and buildings.
They are known to build their nests in wall voids, under floors, and in other hidden areas.
If left unchecked, these ants can cause damage to structures and can contaminate food sources.
Overall, Tapinoma ants are a common pest in many parts of the world.
While they are not harmful to humans, they can be a nuisance when they invade homes and buildings.
Proper pest control measures can help to prevent infestations and keep these ants at bay.
74) Pale-Footed Ants, Technomyrmex

Pale-Footed Ants, also known as Pheidole pallidula, are a species of ant belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are typically small in size, measuring around 2-3mm in length, and are characterized by their pale yellowish-brown coloration and distinctive pale-colored feet.
Pale-Footed Ants are known for their highly organized social structure, which is divided into different castes including workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals.
Workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and maintaining the nest, while soldiers are tasked with defending the colony from predators and other threats.
One of the most interesting aspects of Pale-Footed Ant behavior is their ability to engage in "tandem running," a process in which two ants run together, with the follower using its antennae to track the movements of the leader.
This behavior is thought to help the ants navigate their environment more efficiently and locate food sources more quickly.
Pale-Footed Ants are also known for their unique feeding habits, which include a preference for sweet liquids such as nectar and honeydew.
They are also known to engage in trophallaxis, a process in which food is shared between members of the colony through mouth-to-mouth transfer.
Overall, Pale-Footed Ants are a fascinating species with a complex social structure and unique behaviors.
Their small size and inconspicuous appearance make them easy to overlook, but their importance in maintaining ecological balance and contributing to the overall health of their ecosystem should not be underestimated.
75) Slave-Making Ants, Temnothorax

The Slave-Making Ants, also known as Dulosis ants, are a group of social insects that engage in a unique behavior of raiding and enslaving other ant colonies.
These ants belong to the subfamily Formicinae and are found in various parts of the world.
The Slave-Making Ants have a complex social structure, with a queen, workers, and soldiers.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers and soldiers carry out various tasks such as foraging, nest building, and defense.
However, unlike other ant species, the Slave-Making Ants do not rely solely on their own colony for survival.
Instead, these ants raid nearby colonies of other ant species, using their superior strength and numbers to overpower the defenders.
The Slave-Making Ants then carry off the pupae of the conquered colony back to their own nest.
Once the pupae hatch, they are raised by the Slave-Making Ants and forced to work as slaves for the colony.
The Slave-Making Ants have evolved a number of adaptations to facilitate their slave-raiding behavior.
For example, they have a highly developed sense of smell, which allows them to locate and target specific ant colonies.
They also have strong mandibles and powerful stingers, which they use to subdue their prey.
Despite their aggressive behavior, the Slave-Making Ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
By raiding other ant colonies, they help to control the population of competing ant species.
Additionally, the enslaved ants provide a source of food and labor for the Slave-Making Ants, allowing them to thrive in environments where resources are scarce.
Overall, the Slave-Making Ants are a fascinating and unique species of ant, with a complex social structure and a highly specialized behavior.
While their slave-raiding behavior may seem cruel, it is an important part of their survival strategy and has helped them to thrive in a variety of environments.
76) Pavement Ants, Tetramorium
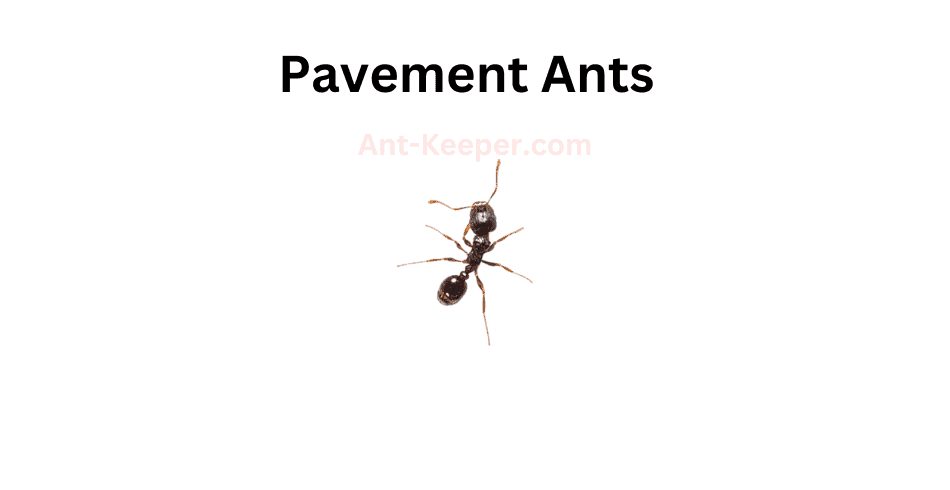
Pavement ants, also known as Tetramorium caespitum, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are commonly found in urban and suburban areas, where they build their nests in cracks and crevices in pavement, sidewalks, and buildings.
Pavement ants are small in size, measuring between 2.5 to 4 mm in length.
They are typically dark brown or black in color, with lighter colored legs and antennae.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and will defend their nests fiercely against intruders.
Pavement ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of foods including insects, seeds, and sweet substances such as honeydew and nectar.
They are also known to scavenge for food in garbage cans and other waste areas.
Pavement ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range in size from a few hundred to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony.
Pavement ants are considered a nuisance pest, as they can invade homes and buildings in search of food and shelter.
They are also known to cause damage to pavement and other structures by excavating soil and creating tunnels.
Overall, pavement ants are a common and adaptable species of ant that play an important role in urban ecosystems.
While they may be a nuisance to humans, they are an important food source for many other animals and help to maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
77) Old World Slender Ants, Tetraponera

The Old World Slender Ants are a group of ants belonging to the genus Leptomyrmex.
They are found in various regions of the world, including Asia, Africa, and Australia.
These ants are known for their slender and elongated bodies, which are typically brown or black in color.
Old World Slender Ants are social insects that live in colonies.
The colonies are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
The ants are highly organized and have a strict hierarchy, with a queen at the top and workers and soldiers below her.
The diet of Old World Slender Ants consists mainly of insects and other small invertebrates.
They are also known to feed on nectar and honeydew produced by aphids and other insects.
Old World Slender Ants are known for their aggressive behavior and are capable of inflicting painful stings.
They are also known to defend their colonies fiercely against intruders.
Overall, the Old World Slender Ants are an interesting and important group of ants that play an important role in their ecosystems.
Their unique physical characteristics and social behavior make them a fascinating subject for scientific study.
78) Vollenhovia

Vollenhoviabe is a species of ant that belongs to the Formicidae family.
It is a relatively small ant, with workers measuring around 2-3 millimeters in length.
The ant has a dark brown or black coloration, with a shiny exoskeleton that is covered in fine hairs.
Vollenhoviabe ants are known for their aggressive behavior, particularly when defending their nests.
They are also highly territorial and will fiercely defend their foraging areas from other ant species.
Despite their small size, Vollenhoviabe ants are capable of inflicting painful bites on humans and other animals.
The ant is primarily found in forested areas, where it nests in soil or under rocks.
It is an omnivorous species, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
Vollenhoviabe ants are also known to cultivate and protect aphids, which they use as a source of honeydew.
The reproductive cycle of Vollenhoviabe ants is similar to that of other ant species.
The queen ant is responsible for laying eggs, which hatch into larvae and eventually develop into workers.
The queen also produces male ants and new queen ants during the mating season.
Overall, Vollenhoviabe ants are an important part of the ecosystem, playing a vital role in soil health and nutrient cycling.
While they may be a nuisance to humans at times, they are a fascinating and complex species that deserves our respect and admiration.
79) Wasmannia
The Wasmanniabe ant is a fascinating species that belongs to the Formicidae family.
It is known for its unique physical characteristics and behavior, which make it stand out from other ant species.
One of the most distinctive features of the Wasmanniabe ant is its size.
It is relatively small, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
However, what it lacks in size, it makes up for in strength.
This ant is incredibly strong and can carry objects that are many times its own weight.
Another interesting aspect of the Wasmanniabe ant is its social behavior.
It lives in colonies that can consist of thousands of individuals.
The colony is led by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and ensuring the survival of the colony.
The other ants in the colony have specific roles, such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
The Wasmanniabe ant is also known for its intelligence.
It has been observed using tools to gather food and navigate its environment.
Additionally, it has a complex communication system that allows it to coordinate with other ants in the colony.
Overall, the Wasmanniabe ant is a remarkable species that has adapted to its environment in unique ways.
Its physical strength, social behavior, and intelligence make it a fascinating subject for scientific study.
80) Sneaking Ants, Cardiocondyla Minutior

Sneaking Ants, also known as Camponotus obscuripes, are a species of ant that are commonly found in forested areas.
These ants are known for their ability to move quietly and quickly, making them difficult to detect.
Sneaking Ants are typically black or dark brown in color and range in size from 5 to 12 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive, flattened head and a narrow waist, which helps them to navigate through tight spaces.
One of the most interesting aspects of Sneaking Ants is their behavior.
These ants are known for their ability to sneak up on other insects and steal their food.
They are also known to raid the nests of other ant species, taking their eggs and larvae back to their own colony to raise as their own.
Sneaking Ants are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
They have been observed feeding on nectar, honeydew, and small insects.
They are also known to scavenge for food, often taking advantage of the leftovers from other insects.
In terms of reproduction, Sneaking Ants have a unique system.
The colony is typically led by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs.
However, there are also a number of worker ants who are capable of laying eggs as well.
These eggs are typically unfertilized and produce male ants, which are used for mating purposes.
Overall, Sneaking Ants are a fascinating species with unique behaviors and adaptations.
Their ability to move quietly and quickly makes them a formidable predator, and their omnivorous diet allows them to thrive in a variety of environments.
81) Black Garden Ants, Lasius Niger
The Black Garden Ant, also known as Lasius niger, is a common species of ant found in many parts of the world.
These ants are typically black or dark brown in color and range in size from 2.5 to 4 mm in length.
Black Garden Ants are social insects that live in large colonies, which can contain thousands of individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and producing new workers.
The workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
These ants are omnivorous and will eat a variety of foods, including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to farm aphids, which they protect and feed in exchange for the sweet honeydew they produce.
Black Garden Ants are important members of their ecosystem, as they help to aerate soil and control populations of other insects.
However, they can also be considered pests when they invade homes and gardens in search of food and shelter.
Overall, the Black Garden Ant is a fascinating and important species of ant that plays a vital role in many ecosystems around the world.
82) Flower Ants, Monomorium Floricola
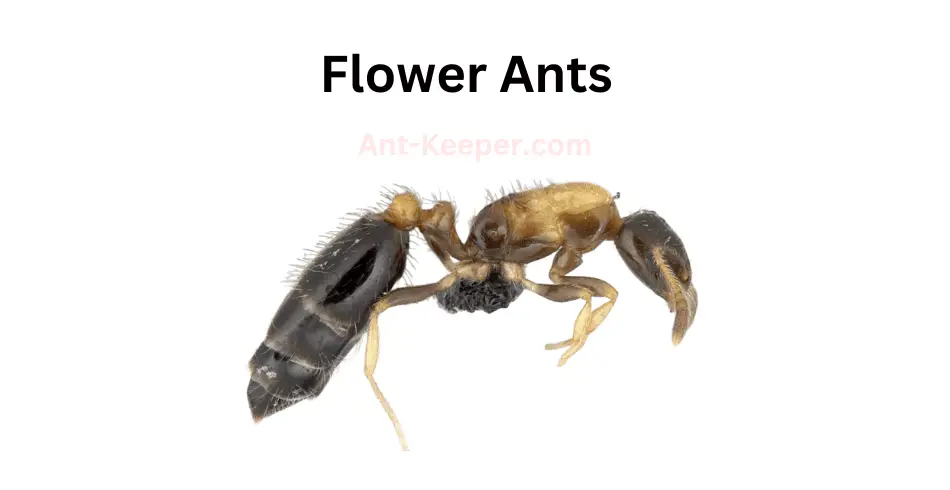

The Flower Ant, also known as the Camponotus consobrinus, is a species of ant that belongs to the Camponotus genus.
These ants are commonly found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and gardens.
They are known for their unique behavior of collecting nectar and pollen from flowers, hence their name.
The Flower Ants are relatively large, with workers measuring up to 12mm in length.
They have a black or dark brown body with reddish-brown legs and antennae.
The queen ants are even larger, measuring up to 18mm in length.
These ants are known for their strong mandibles, which they use to cut through plant material and defend their colony.
The Flower Ants are social insects that live in colonies consisting of a queen, workers, and males.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers take care of the young and forage for food.
The males are responsible for mating with the queen.
One of the unique characteristics of the Flower Ants is their relationship with plants.
They are known to collect nectar and pollen from flowers, which they use as a source of food.
In return, they help pollinate the flowers, which is essential for the plants' reproduction.
The Flower Ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other ant species.
They will defend their territory and resources fiercely, often engaging in battles with other ant colonies.
In conclusion, the Flower Ants are a fascinating species of ant that have a unique relationship with plants.
They play an important role in pollination and are essential for the ecosystem.
Their aggressive behavior towards other ant species also highlights their importance in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
83) Pharaoh Ants, Monomorium Pharaonis

Pharaoh ants, scientifically known as Monomorium pharaonis, are small, yellowish-brown ants that measure about 2 mm in length.
They are commonly found in indoor environments such as homes, hospitals, and commercial buildings.
Pharaoh ants are known for their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
These colonies can contain thousands of workers and can quickly infest a building.
They are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments and can easily relocate their nests if disturbed.
Pharaoh ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of foods including sweets, meats, and other insects.
They are also known to feed on human fluids such as blood and wound exudates.
Due to their small size and ability to hide in small crevices, pharaoh ants can be difficult to control.
They are known to be resistant to many common insecticides and can quickly rebound after treatment.
Pharaoh ants are also a concern in healthcare settings as they can transmit diseases such as salmonella and staphylococcus.
They can also contaminate sterile equipment and supplies.
Overall, pharaoh ants are a common pest in indoor environments and can be difficult to control.
It is important to seek professional pest control services to effectively manage infestations.
84) Longhorn Crazy Ants, Paratrechina Longicornis

The Longhorn Crazy Ant (Paratrechina longicornis) is a small, dark brown ant species that is known for its erratic and unpredictable behavior.
These ants are typically found in warm, humid environments and are often found in urban areas, where they can be a nuisance to homeowners and businesses.
One of the most distinctive features of the Longhorn Crazy Ant is its long, slender antennae, which can be up to twice the length of its body.
These antennae are used to detect chemical signals from other ants and to navigate through their environment.
Longhorn Crazy Ants are omnivorous and will feed on a wide variety of foods, including insects, fruits, and sweet liquids.
They are also known to be scavengers, and will often invade other ant colonies to steal food and resources.
One of the most interesting aspects of the Longhorn Crazy Ant is its behavior.
These ants are known for their erratic movements and unpredictable behavior, which can make them difficult to control.
They are also known for their ability to form large, sprawling colonies that can quickly take over an area.
Despite their small size, Longhorn Crazy Ants can be a significant pest problem, particularly in urban areas.
They can invade homes and businesses, contaminate food, and cause damage to electrical equipment.
As a result, it is important to take steps to control these ants and prevent infestations from occurring.
85) Big Headed Ants, Pheidole Fervens

Big Headed Ants, also known as Pheidole megacephala, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive large heads, which are used for defense and communication within their colonies.
Big Headed Ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, seeds, and other small organisms.
One of the most interesting aspects of Big Headed Ants is their social behavior.
They live in large colonies, with a queen ant at the center of the hierarchy.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony perform various tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
Big Headed Ants are also known for their ability to displace other ant species in their habitats.
They are aggressive and have been known to attack and kill other ants, as well as compete with them for resources.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Big Headed Ants are not considered a major pest species.
However, their ability to displace other ant species and their potential impact on native ecosystems make them an important species to study and monitor.
Check Out Some Of Our Other Ants By Location Posts
| Types Of Ants In India | India, located in South Asia, is a land of diverse landscapes and climates. From the snow-capped peaks of the Himalayas to the tropical beaches of ... |
| Types Of Ants In Venezuela | Venezuela, located in the northern region of South America, boasts a diverse and unique environment. The country’s tropical climate is characterized by high temperatures and ... |
| Types Of Ants In Texas, United States | Texas, located in the southern region of the United States, is a state known for its diverse and unique environment. From the arid deserts of ... |
| Types Of Ants In Ohio, United States | Ohio, located in the Midwestern region of the United States, boasts a diverse environment with a variety of weather patterns and wildlife. The state is ... |
| Types Of Ants In Colima, Mexico | Colima, a state located in western Mexico, is a region known for its diverse and unique environment. The state is situated on the Pacific coast ... |
