Guam, a small island territory located in the western Pacific Ocean, is a unique and diverse region with a rich natural environment. The island is situated in Micronesia, a subregion of Oceania, and is known for its tropical climate, stunning beaches, and lush forests.
The island is home to a variety of animal species, including several endemic birds and reptiles, as well as a diverse marine ecosystem. Despite its small size, Guam boasts a complex and fascinating natural environment that is worth exploring in detail.
In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of Guam’s environment, weather, and animal life, providing a scientific perspective on this fascinating region. .
Types Of Ants In Guam
The Types Of Ants In Guam are listed here: Trap-Jaw Ants, Carpenter And Sugar Ants, Acrobat Ants, Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Crazy Ants, Trap-Jaw Ants, Crazy Ants, Big Headed Ants, Platythyrea, Syllophopsis, Sneaking Ants, Flower Ants, Crazy Ants, Longhorn Crazy Ants, Big Headed Ants, Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Pale-Footed Ants.
If you’ve found some other ants in this region, contact us, and we will add them to the list!
1) Trap-Jaw Ants, Anochetus
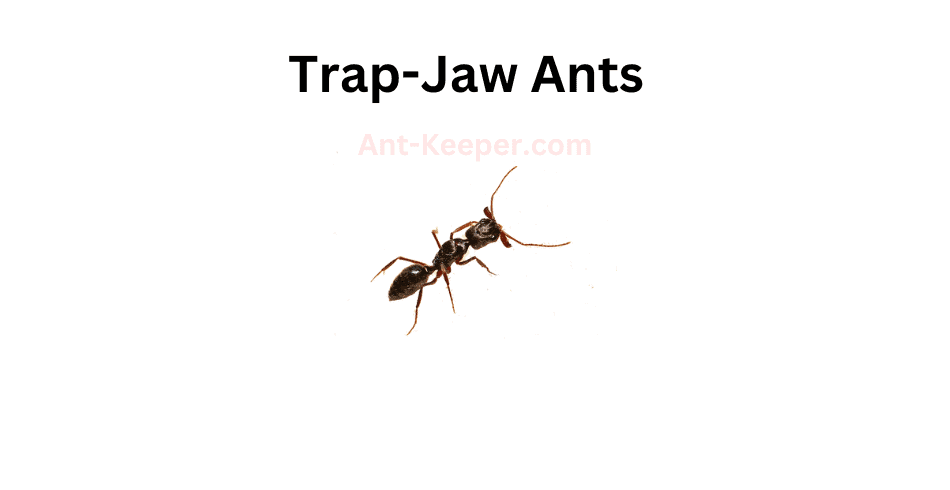
Trap-jaw ants are a species of ants that belong to the genus Odontomachus.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The mandibles of trap-jaw ants are capable of closing at incredible speeds, reaching up to 140 miles per hour.
This allows them to snap their jaws shut with incredible force, which can stun or kill their prey.
Trap-jaw ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically active during the day and are known to be highly territorial.
These ants are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to escape danger or to capture prey.
Trap-jaw ants are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on a variety of insects, including other ants, as well as nectar and other sweet substances.
These ants are also known to be scavengers, feeding on dead insects and other organic matter.
The colonies of trap-jaw ants are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
However, they are highly organized and have a strict social hierarchy.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, trap-jaw ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their environments.
Their powerful mandibles and jumping abilities make them formidable predators, while their social organization allows them to work together to protect their colonies and ensure their survival.
2) Carpenter And Sugar Ants, Camponotus

Carpenter ants and sugar ants are two common species of ants found in many regions of the world.
Carpenter ants are known for their ability to excavate wood and create nests within it.
They are typically larger in size than sugar ants and have a black or dark brown coloration.
Carpenter ants are also known for their strong mandibles, which they use to chew through wood and other materials.
Sugar ants, on the other hand, are smaller in size and have a yellow or brown coloration.
They are named for their preference for sugary foods and are often found in kitchens and other areas where food is stored.
Sugar ants are also known for their ability to form large colonies, with thousands of individual ants working together to gather food and care for their young.
Both carpenter ants and sugar ants play important roles in their ecosystems.
Carpenter ants help to break down dead wood and other plant material, which helps to recycle nutrients back into the soil.
Sugar ants help to disperse seeds and pollinate plants, which helps to maintain healthy ecosystems.
However, both species can also be pests when they invade human homes and buildings.
Carpenter ants can cause damage to wooden structures, while sugar ants can contaminate food and be a nuisance to homeowners.
It is important to take steps to prevent ant infestations and to control them if they do occur, in order to protect both human health and the health of the environment.
3) Acrobat Ants, Crematogaster

Acrobat ants, also known as Crematogaster spp., are a genus of ants that are found in various parts of the world.
These ants are known for their unique ability to contort their bodies and move in acrobatic ways, hence their name.
Acrobat ants are relatively small, with workers measuring between 2-5mm in length.
They are typically brown or black in color, with a slender body and long legs.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and will readily defend their nests against intruders.
One of the most interesting features of acrobat ants is their ability to use their mandibles to grip onto surfaces and contort their bodies in unusual ways.
This allows them to move along narrow branches, twigs, and other surfaces that would be difficult for other ants to navigate.
They are also able to use this ability to escape from predators, such as birds and other insects.
Acrobat ants are omnivorous, meaning that they will eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on insects, nectar, and honeydew, as well as fruits and seeds.
These ants are also known to tend to aphids, protecting them from predators in exchange for the sweet honeydew that the aphids produce.
In terms of their social structure, acrobat ants are typically organized into colonies that are led by a queen.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the nest.
Overall, acrobat ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted unique abilities to survive in their environments.
Their acrobatic abilities and aggressive behavior make them a formidable force in the insect world.
4) Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Monomorium

The Trailing Pharaoh ant, also known as the Monomorium pharaonis, is a small, reddish-brown ant species that is commonly found in urban areas.
These ants are known for their ability to form large colonies, which can consist of thousands of individuals.
One interesting behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant is their tendency to trail behind other ants.
This behavior is thought to be a form of communication, as the trailing ants are able to follow the scent trail left by the leading ants.
This behavior is also used to locate food sources, as the trailing ants are able to follow the trail to the source of the food.
In contrast to the bold behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant, the Timid ant, also known as the Temnothorax species, is a much more cautious species.
These ants are small and brown, and are often found in wooded areas.
They are known for their timid behavior, and will often retreat into their nests when threatened.
Despite their timid nature, the Timid ant is still able to form large colonies.
They are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, meadows, and even urban areas.
Overall, both the Trailing Pharaoh ant and the Timid ant are fascinating species that demonstrate unique behaviors and adaptations.
By studying these ants, scientists can gain a better understanding of the complex social behaviors and ecological roles of ants in their respective environments.
5) Crazy Ants, Nylanderia

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
6) Trap-Jaw Ants, Odontomachus

Trap-jaw ants are a species of ants that belong to the genus Odontomachus.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The mandibles of trap-jaw ants are capable of closing at incredible speeds, reaching up to 140 miles per hour.
This allows them to snap their jaws shut with incredible force, which can stun or kill their prey.
Trap-jaw ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically active during the day and are known to be highly territorial.
These ants are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to escape danger or to capture prey.
Trap-jaw ants are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on a variety of insects, including other ants, as well as nectar and other sweet substances.
These ants are also known to be scavengers, feeding on dead insects and other organic matter.
The colonies of trap-jaw ants are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
However, they are highly organized and have a strict social hierarchy.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, trap-jaw ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their environments.
Their powerful mandibles and jumping abilities make them formidable predators, while their social organization allows them to work together to protect their colonies and ensure their survival.
7) Crazy Ants, Paratrechina

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
8) Big Headed Ants, Pheidole

Big Headed Ants, also known as Pheidole megacephala, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive large heads, which are used for defense and communication within their colonies.
Big Headed Ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, seeds, and other small organisms.
One of the most interesting aspects of Big Headed Ants is their social behavior.
They live in large colonies, with a queen ant at the center of the hierarchy.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony perform various tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
Big Headed Ants are also known for their ability to displace other ant species in their habitats.
They are aggressive and have been known to attack and kill other ants, as well as compete with them for resources.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Big Headed Ants are not considered a major pest species.
However, their ability to displace other ant species and their potential impact on native ecosystems make them an important species to study and monitor.
9) Platythyrea

Platythyreabe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics, including their flattened bodies and elongated mandibles.
Platythyreabe ants are typically found in forested areas and are known to be active foragers, often hunting for small insects and other invertebrates.
One of the most interesting aspects of Platythyreabe ants is their social behavior.
These ants live in colonies that are typically composed of several hundred individuals.
Within these colonies, there is a strict hierarchy, with a single queen ant at the top.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony are responsible for caring for the young and maintaining the nest.
Platythyreabe ants are also known for their aggressive behavior.
When threatened, these ants will use their elongated mandibles to defend themselves and their colony.
They are also known to release a chemical signal that alerts other ants in the colony to the presence of a threat.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Platythyreabe ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They help to control populations of small insects and other invertebrates, and they also serve as a food source for larger predators.
Overall, Platythyreabe ants are fascinating creatures that offer a unique glimpse into the complex world of social insects.
10) Syllophopsis
Syllophopsisbe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their small size, measuring only about 2-3 millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Syllophopsisbe ants are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or leaf litter.
They are known to be arboreal, meaning they are capable of climbing trees and foraging for food in the canopy.
These ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
They are also known to engage in trophallaxis, a behavior where they exchange food and other substances with other members of their colony.
Syllophopsisbe ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several hundred individuals.
They have a hierarchical social structure, with a queen ant at the top and various worker ants performing different tasks such as foraging, nest building, and caring for the young.
Overall, Syllophopsisbe ants play an important role in forest ecosystems, contributing to nutrient cycling and serving as a food source for other animals.
11) Sneaking Ants, Cardiocondyla Minutior

Sneaking Ants, also known as Camponotus obscuripes, are a species of ant that are commonly found in forested areas.
These ants are known for their ability to move quietly and quickly, making them difficult to detect.
Sneaking Ants are typically black or dark brown in color and range in size from 5 to 12 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive, flattened head and a narrow waist, which helps them to navigate through tight spaces.
One of the most interesting aspects of Sneaking Ants is their behavior.
These ants are known for their ability to sneak up on other insects and steal their food.
They are also known to raid the nests of other ant species, taking their eggs and larvae back to their own colony to raise as their own.
Sneaking Ants are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
They have been observed feeding on nectar, honeydew, and small insects.
They are also known to scavenge for food, often taking advantage of the leftovers from other insects.
In terms of reproduction, Sneaking Ants have a unique system.
The colony is typically led by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs.
However, there are also a number of worker ants who are capable of laying eggs as well.
These eggs are typically unfertilized and produce male ants, which are used for mating purposes.
Overall, Sneaking Ants are a fascinating species with unique behaviors and adaptations.
Their ability to move quietly and quickly makes them a formidable predator, and their omnivorous diet allows them to thrive in a variety of environments.
12) Flower Ants, Monomorium Floricola
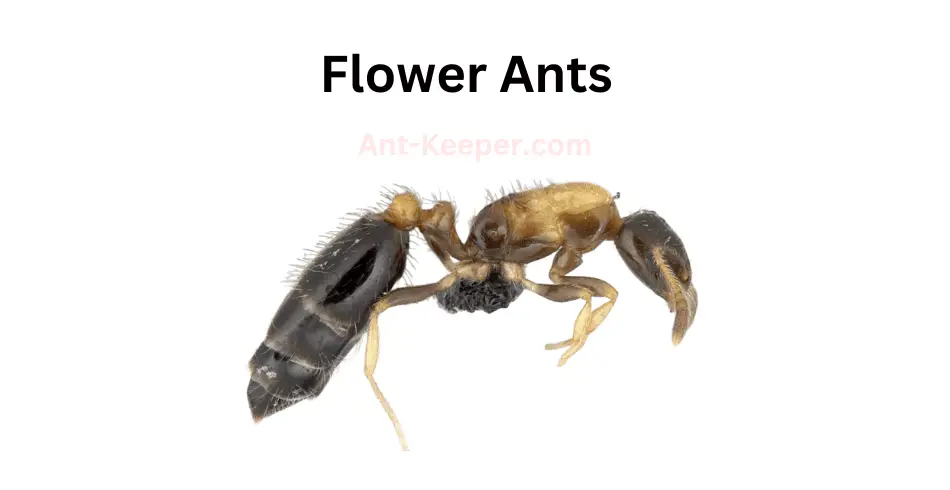

The Flower Ant, also known as the Camponotus consobrinus, is a species of ant that belongs to the Camponotus genus.
These ants are commonly found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and gardens.
They are known for their unique behavior of collecting nectar and pollen from flowers, hence their name.
The Flower Ants are relatively large, with workers measuring up to 12mm in length.
They have a black or dark brown body with reddish-brown legs and antennae.
The queen ants are even larger, measuring up to 18mm in length.
These ants are known for their strong mandibles, which they use to cut through plant material and defend their colony.
The Flower Ants are social insects that live in colonies consisting of a queen, workers, and males.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers take care of the young and forage for food.
The males are responsible for mating with the queen.
One of the unique characteristics of the Flower Ants is their relationship with plants.
They are known to collect nectar and pollen from flowers, which they use as a source of food.
In return, they help pollinate the flowers, which is essential for the plants' reproduction.
The Flower Ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other ant species.
They will defend their territory and resources fiercely, often engaging in battles with other ant colonies.
In conclusion, the Flower Ants are a fascinating species of ant that have a unique relationship with plants.
They play an important role in pollination and are essential for the ecosystem.
Their aggressive behavior towards other ant species also highlights their importance in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
13) Crazy Ants, Nylanderia Bourbonica

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
14) Longhorn Crazy Ants, Paratrechina Longicornis

The Longhorn Crazy Ant (Paratrechina longicornis) is a small, dark brown ant species that is known for its erratic and unpredictable behavior.
These ants are typically found in warm, humid environments and are often found in urban areas, where they can be a nuisance to homeowners and businesses.
One of the most distinctive features of the Longhorn Crazy Ant is its long, slender antennae, which can be up to twice the length of its body.
These antennae are used to detect chemical signals from other ants and to navigate through their environment.
Longhorn Crazy Ants are omnivorous and will feed on a wide variety of foods, including insects, fruits, and sweet liquids.
They are also known to be scavengers, and will often invade other ant colonies to steal food and resources.
One of the most interesting aspects of the Longhorn Crazy Ant is its behavior.
These ants are known for their erratic movements and unpredictable behavior, which can make them difficult to control.
They are also known for their ability to form large, sprawling colonies that can quickly take over an area.
Despite their small size, Longhorn Crazy Ants can be a significant pest problem, particularly in urban areas.
They can invade homes and businesses, contaminate food, and cause damage to electrical equipment.
As a result, it is important to take steps to control these ants and prevent infestations from occurring.
15) Big Headed Ants, Pheidole Megacephala

Big Headed Ants, also known as Pheidole megacephala, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive large heads, which are used for defense and communication within their colonies.
Big Headed Ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, seeds, and other small organisms.
One of the most interesting aspects of Big Headed Ants is their social behavior.
They live in large colonies, with a queen ant at the center of the hierarchy.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony perform various tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
Big Headed Ants are also known for their ability to displace other ant species in their habitats.
They are aggressive and have been known to attack and kill other ants, as well as compete with them for resources.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Big Headed Ants are not considered a major pest species.
However, their ability to displace other ant species and their potential impact on native ecosystems make them an important species to study and monitor.
16) Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Strumigenys Emmae

The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, scientifically known as Odontomachus sp., are a species of ants that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are relatively small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Their most distinctive feature is their mandibles, which are elongated and can snap shut with incredible force.
These mandibles are used to capture prey, crush seeds, and defend the colony against predators.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be active during the day and are often seen foraging for food.
These ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and seeds.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are social insects and live in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, the Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are fascinating insects that have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their environment.
Their powerful mandibles and social behavior make them an important part of many ecosystems.
17) Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Strumigenys Godeffroyi

The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, scientifically known as Odontomachus sp., are a species of ants that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are relatively small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Their most distinctive feature is their mandibles, which are elongated and can snap shut with incredible force.
These mandibles are used to capture prey, crush seeds, and defend the colony against predators.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be active during the day and are often seen foraging for food.
These ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and seeds.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are social insects and live in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, the Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are fascinating insects that have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their environment.
Their powerful mandibles and social behavior make them an important part of many ecosystems.
18) Pale-Footed Ants, Technomyrmex Difficilis

Pale-Footed Ants, also known as Pheidole pallidula, are a species of ant belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are typically small in size, measuring around 2-3mm in length, and are characterized by their pale yellowish-brown coloration and distinctive pale-colored feet.
Pale-Footed Ants are known for their highly organized social structure, which is divided into different castes including workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals.
Workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and maintaining the nest, while soldiers are tasked with defending the colony from predators and other threats.
One of the most interesting aspects of Pale-Footed Ant behavior is their ability to engage in "tandem running," a process in which two ants run together, with the follower using its antennae to track the movements of the leader.
This behavior is thought to help the ants navigate their environment more efficiently and locate food sources more quickly.
Pale-Footed Ants are also known for their unique feeding habits, which include a preference for sweet liquids such as nectar and honeydew.
They are also known to engage in trophallaxis, a process in which food is shared between members of the colony through mouth-to-mouth transfer.
Overall, Pale-Footed Ants are a fascinating species with a complex social structure and unique behaviors.
Their small size and inconspicuous appearance make them easy to overlook, but their importance in maintaining ecological balance and contributing to the overall health of their ecosystem should not be underestimated.
Check Out Some Of Our Other Ants By Location Posts
| Types Of Ants In Liberia | Liberia, located on the west coast of Africa, is a country known for its lush rainforests, diverse wildlife, and tropical climate. The country is bordered ... |
| Types Of Ants In Rio Grande Do Norte, Brazil | Rio Grande do Norte is a state located in the northeastern region of Brazil, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and east. The ... |
| Types Of Ants In Kalimantan, Indonesia | Kalimantan, the Indonesian part of the island of Borneo, is a region of unparalleled natural beauty. With its lush rainforests, diverse wildlife, and tropical climate, ... |
| Types Of Ants In Nigeria | Nigeria, located in West Africa, is a country known for its diverse landscapes and rich biodiversity. The country is home to a variety of ecosystems, ... |
| Types Of Ants In Cook Islands | Nestled in the heart of the South Pacific Ocean lies the Cook Islands, a stunning archipelago consisting of 15 islands and islets. The region is ... |
