French Polynesia is a group of islands located in the South Pacific Ocean, approximately 6,000 miles from the coast of California. The region is made up of five main archipelagos, including the Society Islands, the Tuamotu Archipelago, the Gambier Islands, the Marquesas Islands, and the Austral Islands.
The climate in French Polynesia is tropical, with warm temperatures and high humidity year-round. The islands are home to a diverse range of flora and fauna, including a variety of birds, fish, and marine mammals.
The coral reefs surrounding the islands are some of the most diverse and vibrant in the world, providing a habitat for countless species of fish and other marine life. Despite being home to a large human population, French Polynesia remains a largely untouched and pristine environment, making it a popular destination for eco-tourists and nature enthusiasts.
.
Types Of Ants In French Polynesia
The Types Of Ants In French Polynesia are listed here: Trap-Jaw Ants, Acrobat Ants, Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Crazy Ants, Trap-Jaw Ants, Crazy Ants, Parvaponera, Big Headed Ants, Emerys Sneaking Ants, Sneaking Ants, Sneaking Ants, Crypt Ants, Crypt Ants, Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Pharaoh Ants, Crazy Ants, Longhorn Crazy Ants, Big Headed Ants, Restless Ants, Fire Ants, Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Rogers Dacetine Ants, Pale-Footed Ants, Pavement Ants, Groove-Headed Fierce Ants, Singapore Ants.
If you’ve found some other ants in this region, contact us, and we will add them to the list!
1) Trap-Jaw Ants, Anochetus
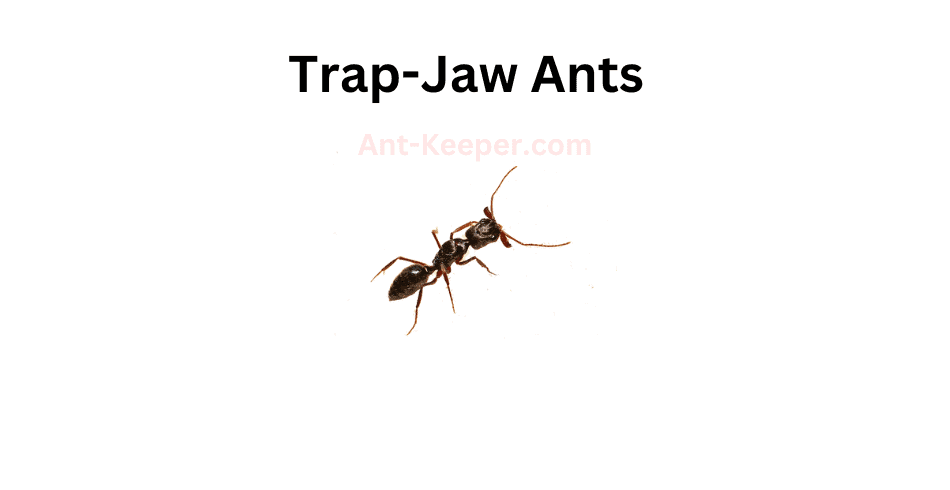
Trap-jaw ants are a species of ants that belong to the genus Odontomachus.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The mandibles of trap-jaw ants are capable of closing at incredible speeds, reaching up to 140 miles per hour.
This allows them to snap their jaws shut with incredible force, which can stun or kill their prey.
Trap-jaw ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically active during the day and are known to be highly territorial.
These ants are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to escape danger or to capture prey.
Trap-jaw ants are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on a variety of insects, including other ants, as well as nectar and other sweet substances.
These ants are also known to be scavengers, feeding on dead insects and other organic matter.
The colonies of trap-jaw ants are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
However, they are highly organized and have a strict social hierarchy.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, trap-jaw ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their environments.
Their powerful mandibles and jumping abilities make them formidable predators, while their social organization allows them to work together to protect their colonies and ensure their survival.
2) Acrobat Ants, Crematogaster

Acrobat ants, also known as Crematogaster spp., are a genus of ants that are found in various parts of the world.
These ants are known for their unique ability to contort their bodies and move in acrobatic ways, hence their name.
Acrobat ants are relatively small, with workers measuring between 2-5mm in length.
They are typically brown or black in color, with a slender body and long legs.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and will readily defend their nests against intruders.
One of the most interesting features of acrobat ants is their ability to use their mandibles to grip onto surfaces and contort their bodies in unusual ways.
This allows them to move along narrow branches, twigs, and other surfaces that would be difficult for other ants to navigate.
They are also able to use this ability to escape from predators, such as birds and other insects.
Acrobat ants are omnivorous, meaning that they will eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on insects, nectar, and honeydew, as well as fruits and seeds.
These ants are also known to tend to aphids, protecting them from predators in exchange for the sweet honeydew that the aphids produce.
In terms of their social structure, acrobat ants are typically organized into colonies that are led by a queen.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the nest.
Overall, acrobat ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted unique abilities to survive in their environments.
Their acrobatic abilities and aggressive behavior make them a formidable force in the insect world.
3) Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Monomorium

The Trailing Pharaoh ant, also known as the Monomorium pharaonis, is a small, reddish-brown ant species that is commonly found in urban areas.
These ants are known for their ability to form large colonies, which can consist of thousands of individuals.
One interesting behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant is their tendency to trail behind other ants.
This behavior is thought to be a form of communication, as the trailing ants are able to follow the scent trail left by the leading ants.
This behavior is also used to locate food sources, as the trailing ants are able to follow the trail to the source of the food.
In contrast to the bold behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant, the Timid ant, also known as the Temnothorax species, is a much more cautious species.
These ants are small and brown, and are often found in wooded areas.
They are known for their timid behavior, and will often retreat into their nests when threatened.
Despite their timid nature, the Timid ant is still able to form large colonies.
They are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, meadows, and even urban areas.
Overall, both the Trailing Pharaoh ant and the Timid ant are fascinating species that demonstrate unique behaviors and adaptations.
By studying these ants, scientists can gain a better understanding of the complex social behaviors and ecological roles of ants in their respective environments.
4) Crazy Ants, Nylanderia

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
5) Trap-Jaw Ants, Odontomachus

Trap-jaw ants are a species of ants that belong to the genus Odontomachus.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The mandibles of trap-jaw ants are capable of closing at incredible speeds, reaching up to 140 miles per hour.
This allows them to snap their jaws shut with incredible force, which can stun or kill their prey.
Trap-jaw ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically active during the day and are known to be highly territorial.
These ants are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to escape danger or to capture prey.
Trap-jaw ants are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on a variety of insects, including other ants, as well as nectar and other sweet substances.
These ants are also known to be scavengers, feeding on dead insects and other organic matter.
The colonies of trap-jaw ants are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
However, they are highly organized and have a strict social hierarchy.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, trap-jaw ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their environments.
Their powerful mandibles and jumping abilities make them formidable predators, while their social organization allows them to work together to protect their colonies and ensure their survival.
6) Crazy Ants, Paratrechina

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
7) Parvaponera
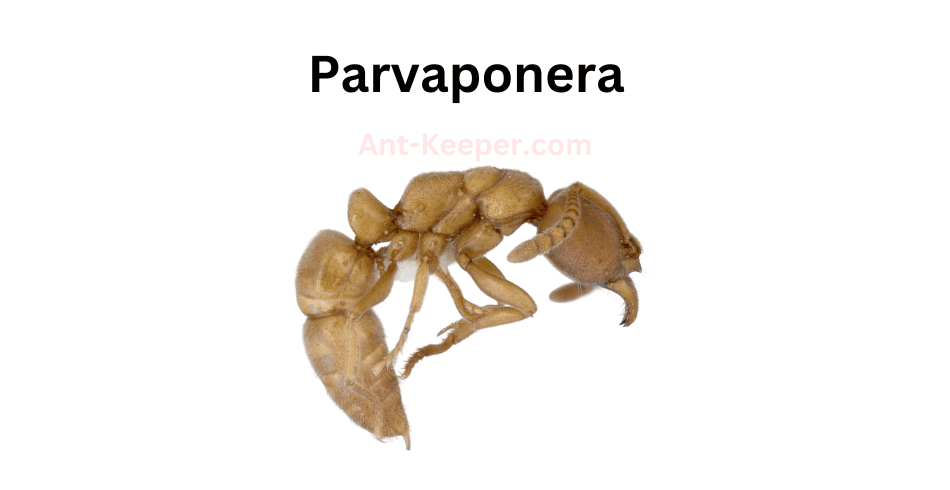

Parvaponerabe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
It is a relatively small ant, with workers measuring around 4-5 millimeters in length.
The ant has a dark brown or black coloration, with a shiny exoskeleton that is covered in fine hairs.
Parvaponerabe ants are known for their aggressive behavior and are often found in large colonies.
They are primarily ground-dwelling ants, but can also be found in trees and other vegetation.
The ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, fruits, and seeds.
One unique characteristic of Parvaponerabe ants is their ability to produce formic acid, which they use as a defense mechanism against predators.
When threatened, the ants will release the formic acid from their bodies, which can cause irritation and pain to potential predators.
Parvaponerabe ants are also known for their social behavior, with a clear division of labor among the different members of the colony.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, Parvaponerabe ants are an important part of many ecosystems, playing a key role in controlling insect populations and contributing to soil health.
8) Big Headed Ants, Pheidole

Big Headed Ants, also known as Pheidole megacephala, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive large heads, which are used for defense and communication within their colonies.
Big Headed Ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, seeds, and other small organisms.
One of the most interesting aspects of Big Headed Ants is their social behavior.
They live in large colonies, with a queen ant at the center of the hierarchy.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony perform various tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
Big Headed Ants are also known for their ability to displace other ant species in their habitats.
They are aggressive and have been known to attack and kill other ants, as well as compete with them for resources.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Big Headed Ants are not considered a major pest species.
However, their ability to displace other ant species and their potential impact on native ecosystems make them an important species to study and monitor.
9) Emerys Sneaking Ants, Cardiocondyla Emeryi

Emery's Sneaking Ants, also known as Pheidole emeryi, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their ability to sneak into other ant colonies and steal their resources without being detected.
Emery's Sneaking Ants are small in size, measuring only 2-3 mm in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a distinctively large head in proportion to their body.
Their mandibles are also relatively large, which allows them to carry larger food items back to their own colony.
These ants are primarily found in forested areas and are known to be opportunistic feeders.
They will consume a variety of food sources, including other insects, nectar, and honeydew.
However, they are also known to steal food from other ant colonies, which is where they get their name.
Emery's Sneaking Ants have a unique strategy for infiltrating other ant colonies.
They will send out scouts to locate a nearby colony and then send in a small group of worker ants to steal food.
These worker ants will use their small size and agility to sneak past the guards of the other colony and steal food without being detected.
Despite their sneaky behavior, Emery's Sneaking Ants are not considered harmful to other ant colonies.
They do not engage in aggressive behavior and are not known to cause any significant damage to other ant colonies.
However, they are still an interesting species to study and observe in their natural habitat.
10) Sneaking Ants, Cardiocondyla Minutior

Sneaking Ants, also known as Camponotus obscuripes, are a species of ant that are commonly found in forested areas.
These ants are known for their ability to move quietly and quickly, making them difficult to detect.
Sneaking Ants are typically black or dark brown in color and range in size from 5 to 12 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive, flattened head and a narrow waist, which helps them to navigate through tight spaces.
One of the most interesting aspects of Sneaking Ants is their behavior.
These ants are known for their ability to sneak up on other insects and steal their food.
They are also known to raid the nests of other ant species, taking their eggs and larvae back to their own colony to raise as their own.
Sneaking Ants are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
They have been observed feeding on nectar, honeydew, and small insects.
They are also known to scavenge for food, often taking advantage of the leftovers from other insects.
In terms of reproduction, Sneaking Ants have a unique system.
The colony is typically led by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs.
However, there are also a number of worker ants who are capable of laying eggs as well.
These eggs are typically unfertilized and produce male ants, which are used for mating purposes.
Overall, Sneaking Ants are a fascinating species with unique behaviors and adaptations.
Their ability to move quietly and quickly makes them a formidable predator, and their omnivorous diet allows them to thrive in a variety of environments.
11) Sneaking Ants, Cardiocondyla Wroughtonii

Sneaking Ants, also known as Camponotus obscuripes, are a species of ant that are commonly found in forested areas.
These ants are known for their ability to move quietly and quickly, making them difficult to detect.
Sneaking Ants are typically black or dark brown in color and range in size from 5 to 12 millimeters in length.
They have a distinctive, flattened head and a narrow waist, which helps them to navigate through tight spaces.
One of the most interesting aspects of Sneaking Ants is their behavior.
These ants are known for their ability to sneak up on other insects and steal their food.
They are also known to raid the nests of other ant species, taking their eggs and larvae back to their own colony to raise as their own.
Sneaking Ants are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
They have been observed feeding on nectar, honeydew, and small insects.
They are also known to scavenge for food, often taking advantage of the leftovers from other insects.
In terms of reproduction, Sneaking Ants have a unique system.
The colony is typically led by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs.
However, there are also a number of worker ants who are capable of laying eggs as well.
These eggs are typically unfertilized and produce male ants, which are used for mating purposes.
Overall, Sneaking Ants are a fascinating species with unique behaviors and adaptations.
Their ability to move quietly and quickly makes them a formidable predator, and their omnivorous diet allows them to thrive in a variety of environments.
12) Crypt Ants, Hypoponera Opaciceps

Crypt ants, also known as fungus-growing ants, are a group of ants that cultivate fungi for food.
They are found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
Crypt ants are known for their unique nesting behavior, as they construct underground chambers to house their fungal gardens.
These ants have a symbiotic relationship with the fungi they cultivate.
The ants provide the fungi with a suitable environment for growth, while the fungi provide the ants with a source of food.
The ants also protect their fungal gardens from other insects and parasites.
Crypt ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colonies are organized into castes, with the queen being the largest and most important member.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for tending to the fungal gardens and caring for the young.
One interesting aspect of crypt ants is their ability to create "satellite" nests.
These nests are smaller chambers located near the main nest, and they serve as storage areas for food and as a place for the queen to lay eggs.
The satellite nests are connected to the main nest by underground tunnels, allowing the ants to move between them.
Overall, crypt ants are fascinating insects that have developed a unique way of obtaining food.
Their symbiotic relationship with fungi and their complex nesting behavior make them an important species to study in the field of entomology.
13) Crypt Ants, Hypoponera Opacior

Crypt ants, also known as fungus-growing ants, are a group of ants that cultivate fungi for food.
They are found in various habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
Crypt ants are known for their unique nesting behavior, as they construct underground chambers to house their fungal gardens.
These ants have a symbiotic relationship with the fungi they cultivate.
The ants provide the fungi with a suitable environment for growth, while the fungi provide the ants with a source of food.
The ants also protect their fungal gardens from other insects and parasites.
Crypt ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colonies are organized into castes, with the queen being the largest and most important member.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for tending to the fungal gardens and caring for the young.
One interesting aspect of crypt ants is their ability to create "satellite" nests.
These nests are smaller chambers located near the main nest, and they serve as storage areas for food and as a place for the queen to lay eggs.
The satellite nests are connected to the main nest by underground tunnels, allowing the ants to move between them.
Overall, crypt ants are fascinating insects that have developed a unique way of obtaining food.
Their symbiotic relationship with fungi and their complex nesting behavior make them an important species to study in the field of entomology.
14) Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Monomorium Liliuokalanii

The Trailing Pharaoh ant, also known as the Monomorium pharaonis, is a small, reddish-brown ant species that is commonly found in urban areas.
These ants are known for their ability to form large colonies, which can consist of thousands of individuals.
One interesting behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant is their tendency to trail behind other ants.
This behavior is thought to be a form of communication, as the trailing ants are able to follow the scent trail left by the leading ants.
This behavior is also used to locate food sources, as the trailing ants are able to follow the trail to the source of the food.
In contrast to the bold behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant, the Timid ant, also known as the Temnothorax species, is a much more cautious species.
These ants are small and brown, and are often found in wooded areas.
They are known for their timid behavior, and will often retreat into their nests when threatened.
Despite their timid nature, the Timid ant is still able to form large colonies.
They are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, meadows, and even urban areas.
Overall, both the Trailing Pharaoh ant and the Timid ant are fascinating species that demonstrate unique behaviors and adaptations.
By studying these ants, scientists can gain a better understanding of the complex social behaviors and ecological roles of ants in their respective environments.
15) Pharaoh Ants, Monomorium Pharaonis

Pharaoh ants, scientifically known as Monomorium pharaonis, are small, yellowish-brown ants that measure about 2 mm in length.
They are commonly found in indoor environments such as homes, hospitals, and commercial buildings.
Pharaoh ants are known for their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
These colonies can contain thousands of workers and can quickly infest a building.
They are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments and can easily relocate their nests if disturbed.
Pharaoh ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of foods including sweets, meats, and other insects.
They are also known to feed on human fluids such as blood and wound exudates.
Due to their small size and ability to hide in small crevices, pharaoh ants can be difficult to control.
They are known to be resistant to many common insecticides and can quickly rebound after treatment.
Pharaoh ants are also a concern in healthcare settings as they can transmit diseases such as salmonella and staphylococcus.
They can also contaminate sterile equipment and supplies.
Overall, pharaoh ants are a common pest in indoor environments and can be difficult to control.
It is important to seek professional pest control services to effectively manage infestations.
16) Crazy Ants, Nylanderia Bourbonica

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
17) Longhorn Crazy Ants, Paratrechina Longicornis

The Longhorn Crazy Ant (Paratrechina longicornis) is a small, dark brown ant species that is known for its erratic and unpredictable behavior.
These ants are typically found in warm, humid environments and are often found in urban areas, where they can be a nuisance to homeowners and businesses.
One of the most distinctive features of the Longhorn Crazy Ant is its long, slender antennae, which can be up to twice the length of its body.
These antennae are used to detect chemical signals from other ants and to navigate through their environment.
Longhorn Crazy Ants are omnivorous and will feed on a wide variety of foods, including insects, fruits, and sweet liquids.
They are also known to be scavengers, and will often invade other ant colonies to steal food and resources.
One of the most interesting aspects of the Longhorn Crazy Ant is its behavior.
These ants are known for their erratic movements and unpredictable behavior, which can make them difficult to control.
They are also known for their ability to form large, sprawling colonies that can quickly take over an area.
Despite their small size, Longhorn Crazy Ants can be a significant pest problem, particularly in urban areas.
They can invade homes and businesses, contaminate food, and cause damage to electrical equipment.
As a result, it is important to take steps to control these ants and prevent infestations from occurring.
18) Big Headed Ants, Pheidole Fervens

Big Headed Ants, also known as Pheidole megacephala, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive large heads, which are used for defense and communication within their colonies.
Big Headed Ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they build their nests in soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter.
They are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of insects, seeds, and other small organisms.
One of the most interesting aspects of Big Headed Ants is their social behavior.
They live in large colonies, with a queen ant at the center of the hierarchy.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony perform various tasks such as foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony from predators.
Big Headed Ants are also known for their ability to displace other ant species in their habitats.
They are aggressive and have been known to attack and kill other ants, as well as compete with them for resources.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Big Headed Ants are not considered a major pest species.
However, their ability to displace other ant species and their potential impact on native ecosystems make them an important species to study and monitor.
19) Restless Ants, Plagiolepis Alluaudi

Restless Ants, also known as the Red Ants, are a species of ants that belong to the Formicidae family.
They are known for their highly active and restless behavior, constantly moving around in search of food and resources.
These ants are typically small in size, measuring around 2-3 mm in length.
They have a reddish-brown coloration and a slender body shape, with long legs and antennae.
Restless Ants are social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
Restless Ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of food sources including insects, fruits, and seeds.
They are also known to scavenge for food, often raiding the nests of other ant species to steal their resources.
One of the most interesting aspects of Restless Ants is their ability to adapt to changing environments.
They are able to quickly adjust their behavior and foraging patterns in response to changes in their surroundings, such as changes in temperature or the availability of food.
Restless Ants are also known for their aggressive behavior, particularly when defending their nests or resources.
They have powerful mandibles that they use to bite and defend themselves against predators or other ants.
Overall, Restless Ants are fascinating creatures that play an important role in their ecosystem.
Their highly active and adaptable behavior makes them a valuable species to study and understand.
20) Fire Ants, Solenopsis Globularia

Fire ants are a type of ant that belongs to the Solenopsis genus.
They are known for their reddish-brown color and their aggressive behavior.
Fire ants are social insects that live in colonies, which can range in size from a few hundred to several thousand individuals.
Fire ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of foods, including insects, seeds, and other small animals.
They are also known to scavenge for food and will often invade other ant colonies to steal their resources.
One of the most distinctive features of fire ants is their ability to sting.
They have a stinger located at the end of their abdomen, which they use to inject venom into their prey or enemies.
Fire ant stings can be painful and can cause an allergic reaction in some people.
Fire ants are also known for their ability to build large mounds, which can reach heights of up to 18 inches.
These mounds are made of soil and are used as a nesting site for the colony.
Fire ants are considered to be an invasive species in many parts of the world, as they can cause damage to crops and wildlife.
They are also a nuisance to humans, as their stings can be painful and their mounds can be unsightly.
Overall, fire ants are fascinating insects that have adapted to thrive in a variety of environments.
While they can be a nuisance, they are an important part of the ecosystem and play a vital role in controlling insect populations.
21) Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Strumigenys Godeffroyi

The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, scientifically known as Odontomachus sp., are a species of ants that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are relatively small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Their most distinctive feature is their mandibles, which are elongated and can snap shut with incredible force.
These mandibles are used to capture prey, crush seeds, and defend the colony against predators.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be active during the day and are often seen foraging for food.
These ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and seeds.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are social insects and live in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, the Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are fascinating insects that have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their environment.
Their powerful mandibles and social behavior make them an important part of many ecosystems.
22) Rogers Dacetine Ants, Strumigenys Rogeri
Roger's Dacetine Ants are a species of ant that belong to the Dacetini tribe.
They are known for their small size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
These ants are typically found in forested areas and are known to be arboreal, meaning they live in trees.
One of the unique characteristics of Roger's Dacetine Ants is their ability to form colonies with multiple queens.
This is a rare trait among ants, as most species have only one queen per colony.
The queens of this species are also known to be relatively small in size compared to other ant species.
Roger's Dacetine Ants are omnivorous, meaning they consume both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on small insects, nectar, and honeydew produced by aphids.
These ants are also known to have a mutualistic relationship with certain species of plants, where they protect the plant from herbivores in exchange for food.
Despite their small size, Roger's Dacetine Ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They help to control populations of small insects and contribute to the pollination of certain plant species.
However, like many other ant species, they are also susceptible to habitat loss and other threats to their survival.
23) Pale-Footed Ants, Technomyrmex Vitiensis

Pale-Footed Ants, also known as Pheidole pallidula, are a species of ant belonging to the family Formicidae.
These ants are typically small in size, measuring around 2-3mm in length, and are characterized by their pale yellowish-brown coloration and distinctive pale-colored feet.
Pale-Footed Ants are known for their highly organized social structure, which is divided into different castes including workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals.
Workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and maintaining the nest, while soldiers are tasked with defending the colony from predators and other threats.
One of the most interesting aspects of Pale-Footed Ant behavior is their ability to engage in "tandem running," a process in which two ants run together, with the follower using its antennae to track the movements of the leader.
This behavior is thought to help the ants navigate their environment more efficiently and locate food sources more quickly.
Pale-Footed Ants are also known for their unique feeding habits, which include a preference for sweet liquids such as nectar and honeydew.
They are also known to engage in trophallaxis, a process in which food is shared between members of the colony through mouth-to-mouth transfer.
Overall, Pale-Footed Ants are a fascinating species with a complex social structure and unique behaviors.
Their small size and inconspicuous appearance make them easy to overlook, but their importance in maintaining ecological balance and contributing to the overall health of their ecosystem should not be underestimated.
24) Pavement Ants, Tetramorium Pacificum
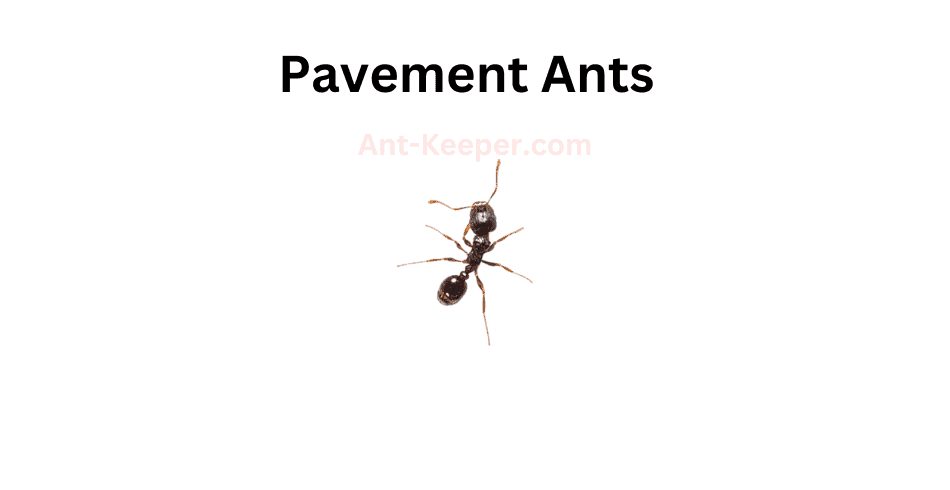
Pavement ants, also known as Tetramorium caespitum, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are commonly found in urban and suburban areas, where they build their nests in cracks and crevices in pavement, sidewalks, and buildings.
Pavement ants are small in size, measuring between 2.5 to 4 mm in length.
They are typically dark brown or black in color, with lighter colored legs and antennae.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and will defend their nests fiercely against intruders.
Pavement ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of foods including insects, seeds, and sweet substances such as honeydew and nectar.
They are also known to scavenge for food in garbage cans and other waste areas.
Pavement ants are social insects, living in colonies that can range in size from a few hundred to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony.
Pavement ants are considered a nuisance pest, as they can invade homes and buildings in search of food and shelter.
They are also known to cause damage to pavement and other structures by excavating soil and creating tunnels.
Overall, pavement ants are a common and adaptable species of ant that play an important role in urban ecosystems.
While they may be a nuisance to humans, they are an important food source for many other animals and help to maintain the balance of the ecosystem.
25) Groove-Headed Fierce Ants, Tetramorium Simillimum
Groove-Headed Fierce Ants, also known as GFA, are a species of ants that belong to the Formicidae family.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and their ability to defend their colonies fiercely.
The name "groove-headed" comes from the distinct groove on their head that separates their eyes from their antennae.
GFAs are relatively small, measuring only about 3-5 millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Their mandibles are long and sharp, which they use to capture prey and defend their colony.
These ants are social insects and live in large colonies that can contain up to several thousand individuals.
The colony is usually led by a queen ant, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
The workers, which are sterile females, are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
GFAs are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to scavenge for dead animals and consume plant material.
One of the most notable characteristics of GFAs is their aggressive behavior.
They are known to attack and kill other insects, including other ant species.
When threatened, they will swarm and bite their attacker, injecting formic acid into their wound.
This acid can cause pain and irritation to the attacker, and in some cases, can even be lethal.
Overall, GFAs are a fascinating species of ants that exhibit unique behaviors and characteristics.
Their fierce nature and ability to defend their colony make them an important part of their ecosystem.
26) Singapore Ants, Trichomyrmex Destructor
The Singapore ant, also known as the Asian needle ant, is a species of ant that belongs to the Formicidae family.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and are considered to be a nuisance pest in many areas.
They are typically found in urban and suburban environments, where they can be seen foraging for food and building their nests.
The Singapore ant is a small ant, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They are typically black or dark brown in color, with a slender body and long legs.
These ants are known for their sharp stingers, which they use to defend themselves and their colony.
The Singapore ant is a social insect, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
They are organized into a caste system, with workers, soldiers, and a queen.
The workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and maintaining the nest.
The soldiers are larger and more aggressive, and are responsible for defending the colony from predators.
These ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of foods including insects, fruits, and sweet substances.
They are known for their ability to adapt to different environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats including forests, grasslands, and urban areas.
Despite their small size, the Singapore ant can be a significant pest in urban areas.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and can sting humans and pets if provoked.
They can also damage crops and invade homes in search of food.
Overall, the Singapore ant is a fascinating species of ant that is well adapted to urban environments.
While they can be a nuisance pest, they play an important role in the ecosystem and are an important part of the food chain.
Check Out Some Of Our Other Ants By Location Posts
| Types Of Ants In Laos | Laos, a landlocked country in Southeast Asia, is known for its lush green forests, stunning waterfalls, and diverse wildlife. The country is situated in the ... |
| Types Of Ants In Moldova | Nestled in the heart of Eastern Europe lies the small country of Moldova, bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the east. Moldova ... |
| Types Of Ants In Greece | Greece, located in southeastern Europe, is a country known for its rich history and stunning landscapes. The country is situated on the Balkan Peninsula and ... |
| Types Of Ants In Guyana | Guyana, located in the northern region of South America, is a country known for its diverse and unique environment. With a tropical climate, Guyana experiences ... |
| Types Of Ants In Brunei Darussalam | Brunei Darussalam, a small country located on the northern coast of the island of Borneo in Southeast Asia, boasts a diverse and unique environment. With ... |