Bermuda, a British Overseas Territory located in the North Atlantic Ocean, is a small archipelago consisting of 181 islands. The region is known for its crystal-clear waters, pink sand beaches, and lush greenery.
The subtropical climate of Bermuda is characterized by warm temperatures and high humidity throughout the year, with occasional hurricanes during the summer and fall months. The unique environment of Bermuda is home to a variety of endemic species, including the Bermuda skink, Bermuda petrel, and Bermuda cedar.
The waters surrounding the islands are also home to a diverse range of marine life, such as sea turtles, dolphins, and colorful fish. Despite its small size, Bermuda’s natural beauty and biodiversity make it a popular destination for tourists and nature enthusiasts alike.
.
Types Of Ants In Bermuda
The Types Of Ants In Bermuda are listed here: Trap-Jaw Ants, Carpenter And Sugar Ants, Acrobat Ants, Dolly Ants, Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Mite-Eating Ants, Crazy Ants, Crazy Ants, Platythyrea, Porthole Ants, Probolomyrmex, Vampire Ants, Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Tapinoma, Argentine Ants.
If you’ve found some other ants in this region, contact us, and we will add them to the list!
1) Trap-Jaw Ants, Anochetus
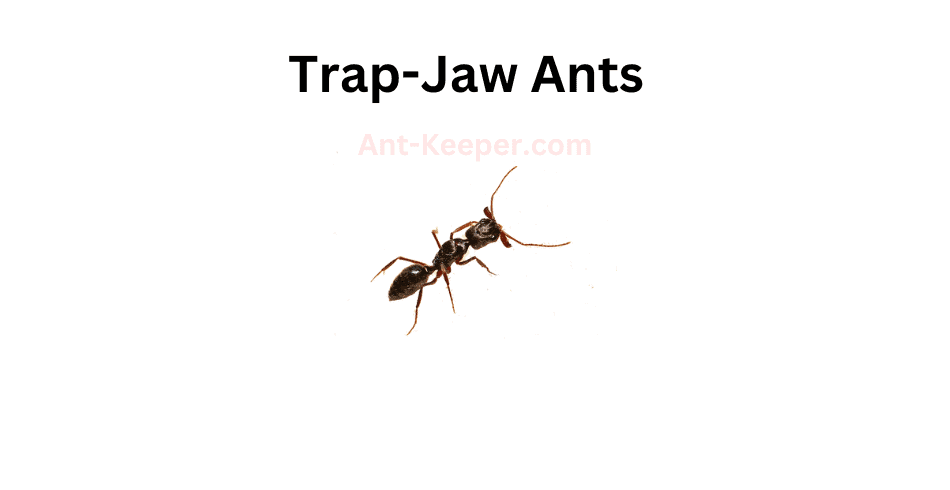
Trap-jaw ants are a species of ants that belong to the genus Odontomachus.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The mandibles of trap-jaw ants are capable of closing at incredible speeds, reaching up to 140 miles per hour.
This allows them to snap their jaws shut with incredible force, which can stun or kill their prey.
Trap-jaw ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are typically active during the day and are known to be highly territorial.
These ants are also known for their ability to jump, which they use to escape danger or to capture prey.
Trap-jaw ants are omnivorous, meaning that they eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on a variety of insects, including other ants, as well as nectar and other sweet substances.
These ants are also known to be scavengers, feeding on dead insects and other organic matter.
The colonies of trap-jaw ants are typically small, with only a few hundred individuals.
However, they are highly organized and have a strict social hierarchy.
The queen is the largest member of the colony and is responsible for laying eggs.
The workers, which are all female, are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, trap-jaw ants are fascinating creatures that have evolved unique adaptations to help them survive in their environments.
Their powerful mandibles and jumping abilities make them formidable predators, while their social organization allows them to work together to protect their colonies and ensure their survival.
2) Carpenter And Sugar Ants, Camponotus

Carpenter ants and sugar ants are two common species of ants found in many regions of the world.
Carpenter ants are known for their ability to excavate wood and create nests within it.
They are typically larger in size than sugar ants and have a black or dark brown coloration.
Carpenter ants are also known for their strong mandibles, which they use to chew through wood and other materials.
Sugar ants, on the other hand, are smaller in size and have a yellow or brown coloration.
They are named for their preference for sugary foods and are often found in kitchens and other areas where food is stored.
Sugar ants are also known for their ability to form large colonies, with thousands of individual ants working together to gather food and care for their young.
Both carpenter ants and sugar ants play important roles in their ecosystems.
Carpenter ants help to break down dead wood and other plant material, which helps to recycle nutrients back into the soil.
Sugar ants help to disperse seeds and pollinate plants, which helps to maintain healthy ecosystems.
However, both species can also be pests when they invade human homes and buildings.
Carpenter ants can cause damage to wooden structures, while sugar ants can contaminate food and be a nuisance to homeowners.
It is important to take steps to prevent ant infestations and to control them if they do occur, in order to protect both human health and the health of the environment.
3) Acrobat Ants, Crematogaster

Acrobat ants, also known as Crematogaster spp., are a genus of ants that are found in various parts of the world.
These ants are known for their unique ability to contort their bodies and move in acrobatic ways, hence their name.
Acrobat ants are relatively small, with workers measuring between 2-5mm in length.
They are typically brown or black in color, with a slender body and long legs.
These ants are known for their aggressive behavior and will readily defend their nests against intruders.
One of the most interesting features of acrobat ants is their ability to use their mandibles to grip onto surfaces and contort their bodies in unusual ways.
This allows them to move along narrow branches, twigs, and other surfaces that would be difficult for other ants to navigate.
They are also able to use this ability to escape from predators, such as birds and other insects.
Acrobat ants are omnivorous, meaning that they will eat both plant and animal matter.
They are known to feed on insects, nectar, and honeydew, as well as fruits and seeds.
These ants are also known to tend to aphids, protecting them from predators in exchange for the sweet honeydew that the aphids produce.
In terms of their social structure, acrobat ants are typically organized into colonies that are led by a queen.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the nest.
Overall, acrobat ants are fascinating creatures that have adapted unique abilities to survive in their environments.
Their acrobatic abilities and aggressive behavior make them a formidable force in the insect world.
4) Dolly Ants, Dolichoderus

Dolly Ants, also known as Dolichoderus spp., are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their distinctive elongated heads and bodies, which give them a unique appearance compared to other ant species.
Dolly Ants are typically found in forested areas, where they build their nests in soil or under rocks.
They are known to be highly social insects, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
Within these colonies, there is a strict division of labor, with different ants taking on specific roles such as foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
One interesting aspect of Dolly Ant behavior is their use of chemical communication.
These ants use pheromones to communicate with each other, leaving trails of scent that other ants can follow to locate food sources or to find their way back to the nest.
They also use pheromones to signal danger, which can trigger a coordinated response from the colony to defend against predators.
Dolly Ants are omnivorous, feeding on a variety of foods including insects, nectar, and plant sap.
They are also known to have a mutualistic relationship with certain plant species, where they protect the plants from herbivores in exchange for a source of food.
Overall, Dolly Ants are a fascinating species of ant with unique physical and behavioral characteristics.
Their social structure and use of chemical communication make them an important subject of study for researchers interested in understanding the behavior of social insects.
5) Trailing Pharaoh And Timid Ants, Monomorium

The Trailing Pharaoh ant, also known as the Monomorium pharaonis, is a small, reddish-brown ant species that is commonly found in urban areas.
These ants are known for their ability to form large colonies, which can consist of thousands of individuals.
One interesting behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant is their tendency to trail behind other ants.
This behavior is thought to be a form of communication, as the trailing ants are able to follow the scent trail left by the leading ants.
This behavior is also used to locate food sources, as the trailing ants are able to follow the trail to the source of the food.
In contrast to the bold behavior of the Trailing Pharaoh ant, the Timid ant, also known as the Temnothorax species, is a much more cautious species.
These ants are small and brown, and are often found in wooded areas.
They are known for their timid behavior, and will often retreat into their nests when threatened.
Despite their timid nature, the Timid ant is still able to form large colonies.
They are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, meadows, and even urban areas.
Overall, both the Trailing Pharaoh ant and the Timid ant are fascinating species that demonstrate unique behaviors and adaptations.
By studying these ants, scientists can gain a better understanding of the complex social behaviors and ecological roles of ants in their respective environments.
6) Mite-Eating Ants, Myrmecina

The Mite-Eating Ant, also known as the Pheidole megacephala, is a species of ant that is commonly found in tropical and subtropical regions around the world.
These ants are known for their unique feeding habits, as they primarily feed on mites and other small arthropods.
The Mite-Eating Ant is a relatively small ant, with workers measuring between 2-3mm in length.
They have a distinctive head shape, with a large and elongated head that is almost as wide as their thorax.
Their bodies are typically a reddish-brown color, with darker legs and antennae.
These ants are highly social, living in large colonies that can contain thousands of individuals.
The colonies are typically divided into two groups: workers and reproductive individuals.
The workers are responsible for foraging for food, caring for the young, and defending the colony, while the reproductive individuals are responsible for producing offspring.
One of the most interesting aspects of the Mite-Eating Ant is their feeding habits.
These ants are specialized predators, feeding almost exclusively on mites and other small arthropods.
They use their large mandibles to capture and kill their prey, and then carry it back to the colony to be consumed.
In addition to their unique feeding habits, the Mite-Eating Ant is also known for its ability to adapt to a wide range of environments.
They are able to thrive in both natural and urban environments, and can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and even in homes and buildings.
Overall, the Mite-Eating Ant is a fascinating species of ant that has adapted to a unique niche in the ecosystem.
Their specialized feeding habits and ability to thrive in a variety of environments make them an important species to study and understand.
7) Crazy Ants, Nylanderia

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
8) Crazy Ants, Paratrechina

Crazy ants, also known as Nylanderia fulva, are a species of ant that belong to the family Formicidae.
They are small in size, measuring only about 2.2 to 3 mm in length, and are reddish-brown in color.
These ants are known for their erratic and unpredictable behavior, hence the name "crazy ants."
Crazy ants are native to South America, but have since spread to other parts of the world, including North America, Asia, and Australia.
They are highly adaptable and can thrive in a variety of environments, including urban areas, forests, and grasslands.
One of the most notable characteristics of crazy ants is their ability to form large colonies with multiple queens.
This allows them to quickly establish themselves in new areas and outcompete other ant species.
Crazy ants are also known for their aggressive behavior towards other insects and animals, including humans.
In addition to their aggressive behavior, crazy ants are also known for their ability to cause damage to electrical equipment.
They are attracted to electrical currents and can easily short-circuit electronics, causing damage and potentially starting fires.
Despite their small size, crazy ants are a formidable species that can have a significant impact on their environment.
As they continue to spread to new areas, it is important to monitor their behavior and take steps to control their populations in order to minimize their impact on ecosystems and human infrastructure.
9) Platythyrea

Platythyreabe is a species of ant that belongs to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique physical characteristics, including their flattened bodies and elongated mandibles.
Platythyreabe ants are typically found in forested areas and are known to be active foragers, often hunting for small insects and other invertebrates.
One of the most interesting aspects of Platythyreabe ants is their social behavior.
These ants live in colonies that are typically composed of several hundred individuals.
Within these colonies, there is a strict hierarchy, with a single queen ant at the top.
The queen is responsible for laying eggs, while the other ants in the colony are responsible for caring for the young and maintaining the nest.
Platythyreabe ants are also known for their aggressive behavior.
When threatened, these ants will use their elongated mandibles to defend themselves and their colony.
They are also known to release a chemical signal that alerts other ants in the colony to the presence of a threat.
Despite their aggressive behavior, Platythyreabe ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They help to control populations of small insects and other invertebrates, and they also serve as a food source for larger predators.
Overall, Platythyreabe ants are fascinating creatures that offer a unique glimpse into the complex world of social insects.
10) Porthole Ants, Ponera

Porthole ants, also known as Temnothorax spp., are a genus of small ants that are commonly found in forested areas.
These ants are known for their unique nesting behavior, as they create their nests in small cavities or "portholes" in trees, rocks, or other natural structures.
Porthole ants are typically less than 5mm in length and have a dark brown or black coloration.
They are social insects and live in colonies that can range from a few dozen to several hundred individuals.
The colonies are typically led by a single queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's reproductive population.
One of the most interesting aspects of porthole ants is their nesting behavior.
Unlike many other ant species, porthole ants do not create large underground nests.
Instead, they seek out small cavities in natural structures and use them as their nesting sites.
These cavities can be as small as a few millimeters in diameter and are often located high up in trees or on rocky outcroppings.
Porthole ants are also known for their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions.
They are able to quickly relocate their nests if their current nesting site becomes unsuitable due to factors such as flooding or predation.
This adaptability allows them to thrive in a variety of habitats, from temperate forests to arid deserts.
Overall, porthole ants are a fascinating and unique species of ant that have adapted to their environment in a variety of ways.
Their nesting behavior and adaptability make them an important species to study for understanding the ecology of forested areas.
11) Probolomyrmex

Probolomyrmex is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Proceratiinae.
These ants are known for their unique morphology, which includes a long and slender body, a narrow head, and elongated mandibles.
The genus is characterized by the presence of a distinct petiole, which separates the thorax and the abdomen.
Probolomyrmex ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they inhabit a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be highly aggressive and territorial, often engaging in fierce battles with other ant species.
One of the most interesting aspects of Probolomyrmex ants is their social behavior.
These ants are known to be highly organized, with a well-defined caste system that includes workers, soldiers, and reproductive individuals.
The workers are responsible for foraging, nest maintenance, and caring for the young, while the soldiers defend the colony against predators and other threats.
Despite their small size, Probolomyrmex ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They are known to be efficient predators, feeding on a variety of insects and other small invertebrates.
They also help to aerate the soil and distribute nutrients, which can have a positive impact on plant growth.
Overall, Probolomyrmex ants are a fascinating and important group of insects that are worthy of further study and conservation efforts.
12) Vampire Ants, Stigmatomma

Vampire ants, also known as blood-sucking ants, are a species of ants that feed on the blood of other insects.
These ants are known for their unique feeding behavior, which involves biting into the exoskeleton of their prey and then sucking out their blood.
Vampire ants are typically found in tropical and subtropical regions, where they live in colonies of up to several thousand individuals.
They are known for their aggressive behavior and will attack other insects, including larger prey such as grasshoppers and caterpillars.
One of the most interesting aspects of vampire ants is their ability to adapt to their environment.
In some cases, these ants have been known to feed on the blood of their own colony members when other sources of food are scarce.
Vampire ants are also known for their unique physical characteristics.
They have long, curved mandibles that are used to bite into the exoskeleton of their prey.
They also have specialized mouthparts that allow them to suck out the blood of their victims.
Despite their aggressive behavior and blood-sucking tendencies, vampire ants play an important role in their ecosystem.
They help to control the populations of other insects and contribute to the overall balance of their environment.
Overall, vampire ants are a fascinating species of ants that have adapted to their environment in unique and interesting ways.
Their behavior and physical characteristics make them a subject of interest for scientists and nature enthusiasts alike.
13) Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, Strumigenys

The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants, scientifically known as Odontomachus sp., are a species of ants that belong to the family Formicidae.
These ants are known for their unique and powerful mandibles, which they use to capture prey and defend their colonies.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are relatively small in size, measuring only a few millimeters in length.
They have a dark brown or black coloration and a slender body shape.
Their most distinctive feature is their mandibles, which are elongated and can snap shut with incredible force.
These mandibles are used to capture prey, crush seeds, and defend the colony against predators.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, grasslands, and deserts.
They are known to be active during the day and are often seen foraging for food.
These ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and seeds.
The Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are social insects and live in colonies that can range in size from a few dozen to several thousand individuals.
The colony is typically led by a queen, who is responsible for laying eggs and maintaining the colony's population.
The workers are responsible for foraging, caring for the young, and defending the colony.
Overall, the Miniature Trap-Jaw Ants are fascinating insects that have evolved unique adaptations to survive in their environment.
Their powerful mandibles and social behavior make them an important part of many ecosystems.
14) Tapinoma

Tapinoma is a genus of ants that belongs to the family Formicidae.
The species Tapinoma is a small ant that measures about 2-3 mm in length.
They are commonly found in urban and suburban areas, and are known to invade homes and buildings in search of food and shelter.
Tapinoma ants are light brown in color and have a slender body with long legs.
They have a distinctively shaped head that is wider than their thorax, and they possess a pair of antennae that are bent at a right angle.
These ants are known for their ability to form large colonies, which can consist of thousands of individuals.
Tapinoma ants are omnivorous and feed on a variety of food sources, including insects, nectar, and honeydew.
They are also known to scavenge for food in garbage cans and other waste areas.
These ants are attracted to sweet and sugary substances, and will often invade kitchens and pantries in search of food.
Tapinoma ants are not known to be aggressive towards humans, but they can become a nuisance when they invade homes and buildings.
They are known to build their nests in wall voids, under floors, and in other hidden areas.
If left unchecked, these ants can cause damage to structures and can contaminate food sources.
Overall, Tapinoma ants are a common pest in many parts of the world.
While they are not harmful to humans, they can be a nuisance when they invade homes and buildings.
Proper pest control measures can help to prevent infestations and keep these ants at bay.
15) Argentine Ants, Linepithema Humile

Argentine ants (Linepithema humile) are a species of small, brownish-black ants that are known for their highly invasive behavior.
They are native to South America but have spread to many parts of the world, including North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Argentine ants are social insects that live in large colonies, with thousands of individuals working together to gather food, care for the young, and defend the nest.
They are known for their ability to form supercolonies, which can span vast areas and contain millions of ants.
One of the key factors that has contributed to the success of Argentine ants as an invasive species is their ability to outcompete native ant species for resources.
They are highly aggressive and will attack and kill other ant species, as well as other insects and spiders.
Argentine ants are also known for their ability to form symbiotic relationships with other insects, such as aphids and mealybugs.
These insects produce a sugary substance called honeydew, which the ants feed on in exchange for protection from predators.
Despite their invasive behavior, Argentine ants are not considered to be a significant threat to human health or property.
However, they can be a nuisance when they invade homes and buildings in search of food and water.
Overall, Argentine ants are a fascinating and complex species that have adapted well to a wide range of environments.
Their ability to form large, cooperative colonies and outcompete other ant species has made them a formidable force in the world of insects.
Check Out Some Of Our Other Ants By Location Posts
| Types Of Ants In Northern Territory, Australia | The Northern Territory of Australia is a vast and diverse region located in the northern part of the country. It is bordered by Western Australia ... |
| Types Of Ants In Hainan, China | Hainan, a tropical island province located in the southernmost part of China, is known for its lush greenery, pristine beaches, and diverse wildlife. The region ... |
| Types Of Ants In Baja California Sur, Mexico | Baja California Sur is a region located in the southern part of the Baja California Peninsula in Mexico. This region is known for its unique ... |
| Types Of Ants In Solomon Islands | The Solomon Islands, located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, is a tropical paradise that boasts a diverse range of flora and fauna. The archipelago is ... |
| Types Of Ants In Yemen | Yemen, located in the southwestern region of the Arabian Peninsula, is a country with a diverse and unique environment. The country is characterized by its ... |

