The next time you see an ant, take a closer look. Notice how tiny these tiny creatures don’t seem to be breathing (or ever standing still). Leads us to question how they are ever able to breathe. It Turns out that ants have a unique way of getting the oxygen they need to survive.
Ants take in oxygen through spiracles and not lungs. An ant’s respiratory system comprises a set of holes, spiracles, on its exoskeleton. Through these openings, oxygen enters, and carbon dioxide leaves the ant’s body. The number of spiracles an ant has depends on the ant species.
We dug deep into the research to find this out, and we promise you’ll learn something new after this article.

Why do ants not have lungs?
Ants are small creatures. Biologically, their body size is tiny, allowing efficient gaseous exchange through diffusion. Ants do not have lungs because their air needs are adequately met through diffusion. Further, ants close air passage valves in phases, especially when resting, significantly reducing the oxygen inhaled.
In other words, ants’ breathing is discontinuous. The erratic breathing can last for long periods per cycle depending on body needs and environmental conditions.
This breathing adaptation eliminates the need for lungs.

In contrast, the air needs of terrestrial animals whose body surface area is large cannot be sustained through diffusion. (Source)
In these animals, respiration is a continuous process, and this constant air need led to the biological evolution of specialized organs and mechanisms to aid steady breathing.
These animals have gills, noses, and lungs to help respiration because diffusion by itself, as is the case with ants, is inadequate. (Source)
How do ants live without lungs?
Ants have developed an alternative breathing system to accommodate a complex respiratory system in their tiny bodies. Instead of lungs and gills, ants have a network of tubes spread throughout their body that assist in circulating the air. The tracheae tubes carry sufficient oxygen around the ant’s body parts.
It’s because of this adaptation that ants don’t have lungs.
Also, because ants do not have lungs and blood to pump air, they leverage the body’s motion, and the movement helps the oxygen circulate.
Tiny insects like ants don’t need a constant air supply like larger animals.

Oxygen needs depend on metabolic requirements or movement activities.
In times of low activity, they don’t inhale more oxygen.
They hold their breath for hours until the subsequent need for oxygen when they gasp for air, as happens during hibernation. (Source)
Where do ants breathe from?
Ants breathe using the trachea system. The spiracles positioned on the ant’s exoskeleton are the openings at the end of the trachea. The spiracles have valves that open and close depending on the ant’s air needs. The opening and closing of these valves enable ants to hold their breath.
The breathing openings are positioned laterally along the body. A body segment has a pair of spiracles, but some segments don’t.
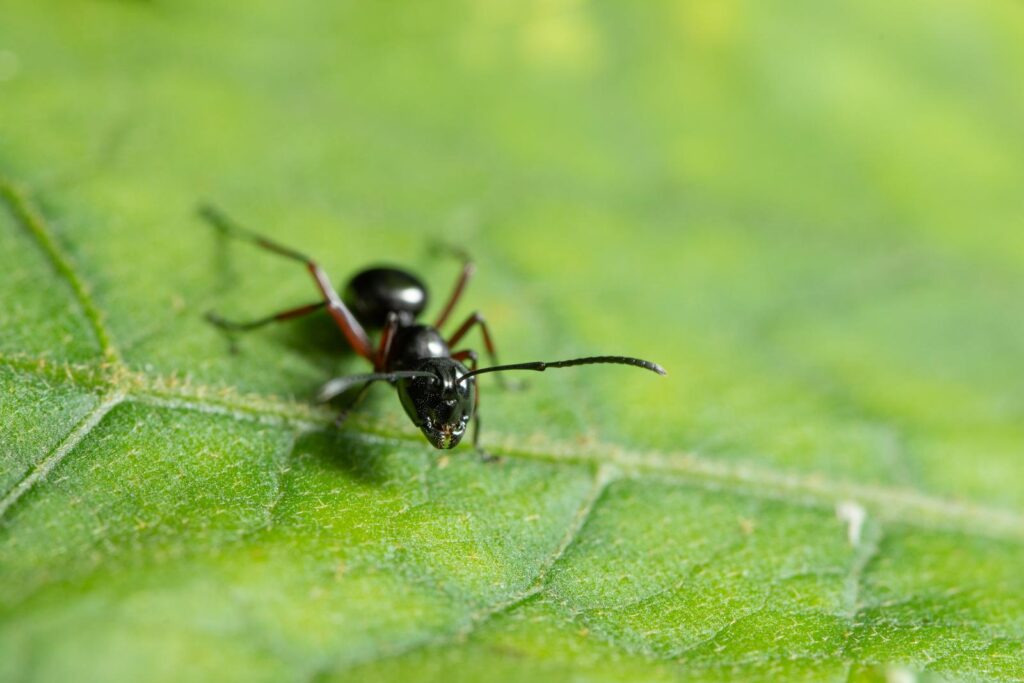

Adults have a maximum of 10 pairs, but the number varies by species of ants and maturity—the trachea transport oxygen to all body parts.
The spiracular system is not just for air regulation. Ants open and close their spiracles to prevent dust, parasites, or pests such as fungi from entering. (Source)
Do Ants Need Oxygen?
Like all living organisms, ants require oxygen for optimal body functioning. Unlike humans, who need to breathe oxygen throughout, ants can survive with small amounts of oxygen. A continuous oxygen intake by ants causes oxygen poisoning; to avoid this, they practice a discontinuous exchange of gas.
Another purpose of discontinuous ventilation is to safeguard against the loss of water.
Additionally, ants survive in harsh conditions through the intermittent exchange of gas.
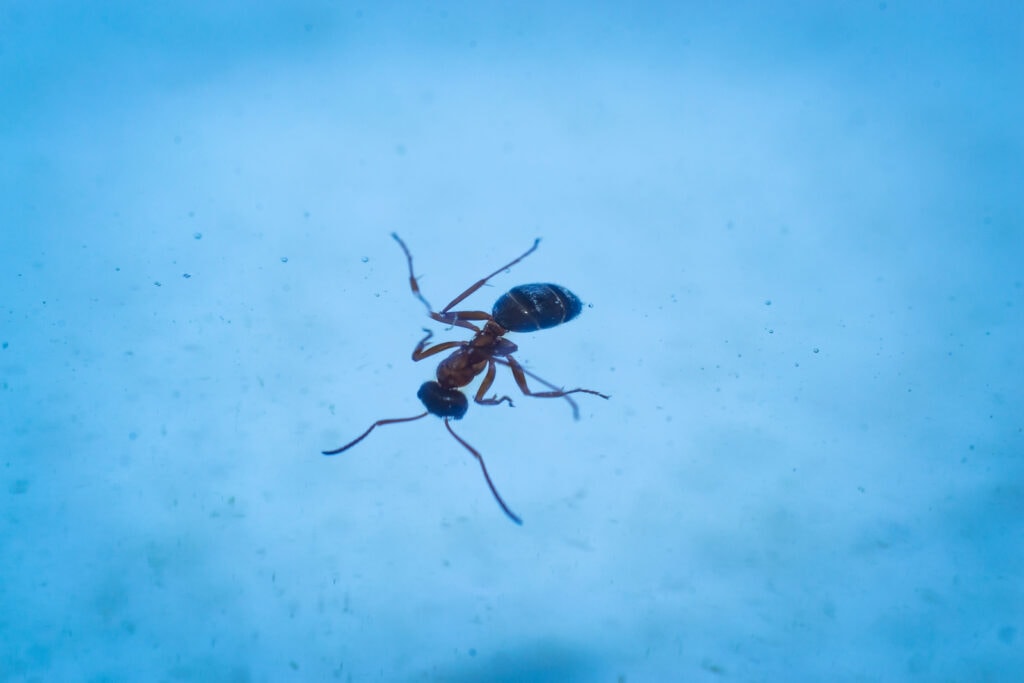
For instance, they hold their breath underwater for long periods helping them to survive floods.

Do ants emit carbon dioxide?
Like all living organisms, ants breathe in oxygen and emit carbon dioxide (CO2). In the same way, our lungs work, the ant’s respiratory system regulates the oxygen breathed in and exhaled carbon dioxide. However, the oxygen-CO2 regulation in ants is not a constant inhalation-exhalation activity as in humans and animals.
Ants can close the tracheal openings for long, even hours at any given time or phase. In this period, the oxygen in the body system is preserved and not converted to CO2 immediately.
Similarly, CO2 is not released because the spiracular openings are closed.
Instead, the CO2 is slowly dissolved in the tissues.

The preserved oxygen is slowly absorbed until a certain threshold is attained. When the lowest possible oxygen level is reached, the spiracle valves begin to reopen, allowing oxygen to enter the respiratory system again.
Ants do not have lungs, but can they suffocate?
Air diffuses in and out of the ant via the spiracular openings. Even though ants lack lungs, they suffocate if their spiracles get clogged or blocked. The potency to kill ants of pest control chemicals used to get rid of ants is their suffocation strength.
Humans and animals that depend on their lungs to breathe cannot survive underwater unless they have oxygen reservoirs.
On the other hand, ants can stay underwater for a long time by holding their breath for hours without suffocating, and humans can only dream of such an ability.
Even though ants are not suffocated by water, some substances easily clog and block the ants breathing openings.
Certain substances on the spiracles prevent air from entering or leaving the tube network, which assists air circulation, and this action chokes and kills the ants.
Baking soda powder and essential oils such as neem are two good examples of substances that block the air passages killing ants by suffocation. (Source)
Which ant body parts have spiracles?
The spiracular system is located on the abdomen and thorax. Spiracles are laterally arranged per segment of the abdomen and thorax of the ant, and the exact location varies widely across species. On the stomach, they mostly form on the soft membrane of the lower parts of the abdomen.
On the thorax, they develop intersegmental locations towards the front of their occupied segments. (Source)